Chorizo vs Italian sausage - In-Depth Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Italian sausage is higher in selenium and has low sugar, sodium, and saturated fat content. On the other hand, chorizo is higher in Vitamin B12, Vitamin B6, zinc, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B1 and has a lower glycemic index.
Introduction
Today, we will compare Italian sausages and chorizo and highlight the main differences focusing on nutritional values.
What's The Actual Difference?
Chorizo and Italian sausage have a lot in common, but they also have many differences.
Italian sausages can be cured or uncured and consist of at least 85% of pork meat. Chorizo is cured meat; it is a Spanish cured and smoked pork or beef sausage.
Italian sausages and chorizo also have different seasonings. Chorizo usually is seasoned with chili pepper, paprika, oregano, and salt, while Italia sausages are seasoned with fennel, onions, garlic, and corn syrup.
Production
One of the essential steps in making good sausages is weighing the meat and spice ingredients. Salt is essential for making the meat easier to handle and taste good.
Chorizo meat is typically crushed, salted, spice-seasoned, and pressed into the intestines in the shape of a shell before being hung in a meat cellar to keep it cool.
Nutrition
You can find nutritional infographics that visually show the differences between Italian sausages and chorizo. The food varieties used in this article are Italian sausages made from pork and chorizo made from pork and beef.
Macronutrients
Italian sausage is higher in water, so chorizo may seem to have a more solid texture. Chorizo is higher in fats and protein. Please, check the infographic below and read the more detailed information in the corresponding sections.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+69.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+22.2%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+186.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+45.7%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+60.4%
Fats
Chorizo contains more fats than Italian sausages. It has 38.27g of fat per 100g, while Italian sausage contains 31g of fat per 100g. In particular, Italian sausages have less saturated fats, but chorizo has more mono- and polyunsaturated fats. Chorizo, in addition, falls in the range of the top 4% of foods as a source of fat.
Cholesterol
Chorizo and Italian sausages are high in cholesterol. Chorizo provides 89mg per 100g, while Italian sausages have 76mg of cholesterol. Chorizo falls in the range of the top 16% of foods as a source of cholesterol. So if you have any cardiovascular issues, consume it in moderation.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+28.3%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-21.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+16.5%
Protein
Chorizo contains more protein than Italian sausages. Chorizo provides 24.1g, whereas Italian sausages have 14.25 protein per 100g.
Calories
Both Italian sausages and chorizo are considered high-calorie food. The number of calories in chorizo is higher than in Italian sausages. It provides 455 calories per 100g, whereas Italian sausage contains 346 calories per 100g.
Minerals
Chorizo contains more potassium, zinc, magnesium, and iron than Italian sausages.
On the other hand, Italian sausages have more calcium and less sodium.
Both have equal amounts of phosphorus and copper.
Slightly note: chorizos are high in sodium, so to avoid sodium's harmful effects on your health, consume them in moderation.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+28.6%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+57.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+34.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+90.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+125%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-40.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+45%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+17.5%
Vitamins
Chorizo contains significantly higher Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6, and Vitamin B12 concentrations.
Besides, chorizo falls in the range of the top 14% of foods as a source of Vitamin B1.
On the other hand, chorizo contains more Vitamin C and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+78.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+57.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+119.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+76.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+119.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+300%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of Italian sausages and chorizo is equal; it is 28. Both foods are considered low glycemic index food.
Health Benefits of Eating Red Meat
Iron is a mineral that our bodies require to produce hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. Iron is abundant in all types of red meat, including Italian sausages and chorizo. Red meat is also high in Vitamin B12, which helps keep nerves and red blood cells healthy, and zinc, which aids immune system function [1].
Side Effects
Red meat contains high amounts of vitamins and minerals; however, it is also rich in sodium and saturated fats.
Cardiovascular Health
Chorizo tends to have a higher fat content due to its pork base and the addition of spices and flavorings. Higher consumption of saturated fats is associated with an increased risk of heart disease [2].
Italian sausage may have a lower fat content depending on the specific recipe and preparation method, which could potentially make it a slightly better choice for cardiovascular health.
Both chorizo and Italian sausage can contain significant amounts of sodium, which is a concern for cardiovascular health. High sodium intake is associated with high blood pressure and an increased risk of heart disease [3].
Choosing low-sodium versions or moderating portion sizes can help mitigate the impact of sodium content. It should be noted that the recommended daily sodium intake for adults is 2.3 g.
Both chorizo and Italian sausage can be prepared in various ways, including grilling, frying, or baking. Cooking methods that minimize added fats, such as grilling or baking, can help reduce the overall calorie and fat content of the dish, potentially making it more heart-healthy.
In summary, while both chorizo and Italian sausage can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet, it's essential to be mindful of portion sizes and preparation methods to minimize their impact on cardiovascular health. Choosing leaner cuts, moderating portion sizes, and incorporating plenty of fruits and vegetables can help mitigate the potential negative effects of these delicious sausages on heart health.
Diabetes
According to research, there is a link between eating red meat and developing type 2 diabetes. Red meat, mainly processed meats, is high in heme iron, raising blood sugar levels. According to one study, women who consume red meat frequently have a nearly one-third higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes than women who consume less red meat [4].
Red Meat Allergy
Red meat allergy is a typical food allergy that affects people of all ages. Those allergic to cat serum albumin may develop an allergy to red meat, which cross-reacts with albumin found in pork.
A red meat allergy causes hives, vomiting, stomach cramps, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis. These symptoms usually last three to six hours after eating red meat [5].
Herb Allergy
Fennel seed, used to flavor Italian sausages, can cause an allergic reaction. Allergies to spices and herbs are typically characterized by local reactions in the mouth, resulting in itchy mucous membranes and swelling of the lips and tongue. Dizziness, hives, and throat swelling are common symptoms [6].
Infographic
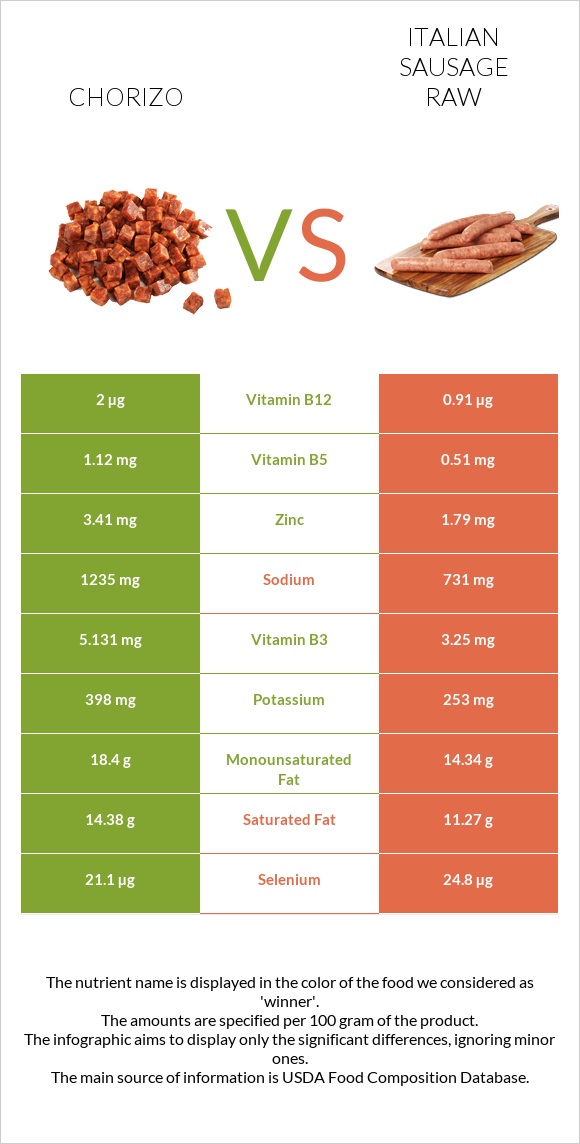
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2µg | 0.91µg | 45% |
| Sodium | 1235mg | 731mg | 22% |
| Protein | 24.1g | 14.25g | 20% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.53mg | 0.3mg | 18% |
| Choline | 96.7mg | 18% | |
| Zinc | 3.41mg | 1.79mg | 15% |
| Saturated fat | 14.38g | 11.27g | 14% |
| Vitamin B3 | 5.131mg | 3.25mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.12mg | 0.51mg | 12% |
| Fats | 38.27g | 31.33g | 11% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.3mg | 0.168mg | 10% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 18.4g | 14.34g | 10% |
| Vitamin D | 61 IU | 8% | |
| Vitamin D | 1.5µg | 8% | |
| Selenium | 21.1µg | 24.8µg | 7% |
| Calories | 455kcal | 346kcal | 5% |
| Iron | 1.59mg | 1.18mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.63mg | 0.568mg | 5% |
| Cholesterol | 88mg | 76mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 398mg | 253mg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.46g | 4.03g | 4% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 2mg | 2% |
| Folate | 2µg | 8µg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 18mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 8mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 150mg | 142mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.22mg | 1% | |
| Manganese | 0.04mg | 0.058mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 1.6µg | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 1.86g | 0.65g | N/A |
| Carbs | 1.86g | 0.65g | 0% |
| Copper | 0.08mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.278mg | 0.114mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.473mg | 0.563mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 2.206mg | 0.52mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.708mg | 0.956mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.414mg | 1.083mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.47mg | 0.346mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.149mg | 0.477mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.914mg | 0.572mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.721mg | 0.411mg | 0% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Chorizo - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173859/nutrients
- Italian sausage raw - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171631/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
