Cotija cheese vs. Feta — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cotija cheese is a Mexican cheese that is derived from cow’s milk. Cotija is higher in calories, total fats, saturated fats, and sodium but richer in proteins and monounsaturated fats, zinc, phosphorus, copper, and vitamin B12. In comparison, feta cheese is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B5, and B6.
Introduction
Cotija cheese is originally from Mexico. It is prepared from cow’s milk and has versatile usage in Mexican cuisine as a topping for different types of foods such as tacos and salads.
Cotija cheese is a white cheese that resembles feta. However, it is quite different.
Cotija cheese is a white crumbling cheese with a stronger flavor and a more solid and crumbly texture than feta cheese.
Feta cheese, on the other hand, is originally from Greece. The main difference is that it is made from sheep’s milk, something sheep’s milk and goat’s milk mixed.
Feta is put in brine, which makes it moister and less crumbly. Comparatively, it has a creamier texture; however, still considered a crumbly cheese.
Feta cheese has a variety of usages in the Greek and Mediterranean culinary world. It is used in salads and sandwiches. Recently, feta cheese pasta has been a trending dish on social media.
This article will compare cotija and feta cheese according to their nutritional content and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will compare 100g of each.
Calories
Cotija cheese is higher in calories compared to feta. Cotija contains 1.4 times more calories than feta cheese. 366 calories for cotija cheese and 264 calories.
Protein
Cotija cheese is a richer source of protein compared to feta cheese. It is a good protein source, containing 20g per 100g. In comparison, feta cheese contains 14g of protein per 100g. The difference is very remarkable.
Fats
Cotija is higher in fats. It contains 1.5 times more fats compared to feta. There are 30g of fats in cotija cheese compared to feta cheese which contains 21g.
Cotija cheese is higher in saturated fats and monounsaturated fats.
Below we can see their distributions.
@fattypecoverage
Carbs
They are low in carbs and have similar amounts of carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+40.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+41%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+54.4%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+45.3%
Minerals
Cotija cheese is richer in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, copper, and selenium. In addition, it contains more sodium than feta. Feta is richer in iron compared to cotija cheese.
Here is the diagram of their mineral distributions
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+100%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+62.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+101.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+643.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+34.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+116.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+18%
Contains
more
IronIron
+∞%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-34.5%
Vitamins
Both of these products are good sources of vitamins B2 and B12. In addition, Cotija cheese is richer in vitamin A. In comparison, feta cheese is richer in B1, B5, and B6.
Here is the diagram of their vitamin distributions
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+83.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+38.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+33.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+431%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+73.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+769.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+765.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+220%
Health impacts
Health benefits of vitamins
As mentioned above, cotija cheese is a good source of vitamins B2, B12, and vitamin A, while feta cheese is rich in vitamins B1, B2, B5, and B6, B12. It may be possible to prevent deficiency of these vitamins by moderately consuming cotija cheese and feta.
Symptoms of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) deficiency include megaloblastic anemia and progressive peripheral neuropathy (which frequently results in pain, numbness, and weakness, typically in the hands and feet; additionally, it may have an impact on many bodily processes like digestion, urine, and circulation).
Vitamin A is important for normal vision. However, it should be noted that if vitamin A is continuously ingested at a level greater than 15 mcg (The Recommended Dietary Allowance), toxicity develops; symptoms include excessive sweating, brittle nails, diarrhea, hypercalcemia, hepatotoxicity, vertigo, nausea, and vomiting.
Alcoholism is the most common cause of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. Beri-beri (peripheral neuropathy, which can cause prickling or tingling in your hands or feet), confabulation (a patient creates false memories without intending to deceive), and psychosis can all be brought on by vitamin B1 deficiency.
The symptoms of riboflavin (vitamin B2) deficiency include cheilosis, stomatitis, and a magenta-colored tongue. This condition may result in corneal neovascularization, which is harmful for vision. In the USA, riboflavin deficiency is incredibly uncommon. The majority of riboflavin-deficient cases occur in poor nations in Asia and Africa. The three groups most likely to experience riboflavin insufficiency are older people, drinkers, and women who use birth control pills (1).
Isoniazid medication, a medicine used to treat tuberculosis, is the most frequent cause of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) deficiency. Sideroblastic anemia, convulsions, cheilosis, and stomatitis are signs of vitamin B6 insufficiency.
Cardiovascular health
It is essential to mention that both cotija and feta cheese are high in sodium; however, cotija is significantly higher. Consumption of high amounts of sodium is associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension.
In addition, cotija cheese is higher in saturated fats, which poses a higher risk increase in atherosclerosis rates. Compared to feta cheese, cotija cheese has increased hypertension and atherosclerosis risks (2.3).
ACE protein raises blood pressure by various mechanisms. It should be noted, Cotija and Feta contain some peptides that inhibit ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme). The biopeptides found in cheese cause a decrease in both systolic and diastolic pressure by inhibiting the action of the ACE. ACE-inhibitor medications (Captopril, Lisinopril, etc.) also activate a similar mechanism (4.5).
People taking MAO inhibitors (particularly antidepressants) may experience a hypertensive crisis when eating cheeses (including these cheeses) that contain tyramine (6).
Bone health
Consuming these foods may help maintain normal levels of calcium in the body.
1–2% of the weight of an adult human is calcium. The teeth and bones contain more than 99% of the calcium in the body. So, in addition to its obvious structural function, the skeleton also acts as a calcium store. Dietary calcium consumption significantly affects bone metabolism and bone health. One of the main reasons for decreased bone mass and osteoporosis is chronic calcium insufficiency brought on by insufficient ingestion or poor intestinal absorption (7).
During menopause, estrogen levels are significantly reduced, which accelerates bone loss since estrogen slows the natural breakdown of bones. Based on this, during this period it is very important to control the concentrations of calcium, and phosphorus in the body to prevent osteomalacia and osteoporosis (8).
In addition, your body absorbs calcium through vitamin D. However, vitamin D overdose may activate osteoclasts (a type of bone cell that destroys bone tissue), so if you have vitamin D deficiency, you must give an analysis for the regulation of its concentration and for preventing vitamin D overdose.
Digestive Health
Milk and dairy products like cheese (including cotija and feta) contain the natural sugar lactose. Lactose cannot be adequately digested in the small intestine by people who are lactose intolerant. Instead, it enters the colon (large intestine) undigested, resulting in the following typical symptoms: stomach distension, cramps, or pain; noisy bowel movements; excessive gas; diarrhea with rapid or watery bowel movements; and an unexpected urge to urinate.
The optimal treatment for lactose intolerance combines dietary changes to avoid foods containing lactose and supplementation to help with lactose digestion when eating foods containing lactose (9).
Diabetes mellitus
According to this meta-analysis, there is a significant inverse relationship between dairy products, low-fat dairy products, cheese consumption, and the risk of type 2 diabetes (10).
Cancer
According to this study, among European Union countries, Greece has the lowest percentage of breast cancer mortality and the highest cheese consumption. This is the first evidence that cheese eating can help prevent breast cancer (11). This information is unknown for cotija cheese.
According to research, postmenopausal breast cancer risk might be reduced by consuming dairy products (12).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470460/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31438636/
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Micloth-Lopez-Del-Castillo/publication/319668728_ACEI_and_antioxidant_peptides_release_during_ripening_of_Mexican_Cotija_hard_cheese/links/59d119524585150177f3cd75/ACEI-and-antioxidant-peptides-release-during-ripening-of-Mexican-Cotija-hard-cheese.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996912001494
- https://europepmc.org/article/med/3283290
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12088515/
- https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/menopause-and-bone-loss
- https://gi.org/topics/lactose-intolerance-in-children/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/98/4/1066/4577090
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814602001590
- https://www.aicr.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/breast-cancer-report-2017.pdf
Infographic
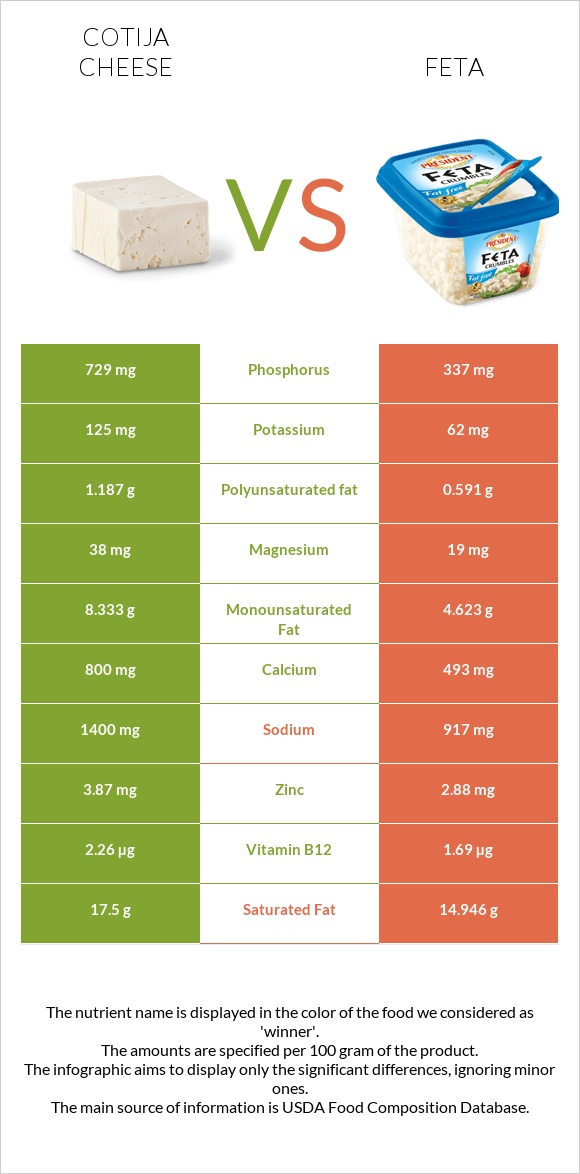
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Phosphorus | 729mg | 337mg | 56% |
| Calcium | 800mg | 493mg | 31% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.049mg | 0.424mg | 29% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.486mg | 0.844mg | 28% |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.26µg | 1.69µg | 24% |
| Copper | 0.238mg | 0.032mg | 23% |
| Sodium | 1400mg | 917mg | 21% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.967mg | 19% | |
| Fats | 30g | 21.28g | 13% |
| Protein | 20g | 14.21g | 12% |
| Vitamin A | 229µg | 125µg | 12% |
| Saturated fat | 17.5g | 14.946g | 12% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.029mg | 0.154mg | 10% |
| Zinc | 3.87mg | 2.88mg | 9% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.333g | 4.623g | 9% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.65mg | 8% |
| Folate | 10µg | 32µg | 6% |
| Calories | 366kcal | 264kcal | 5% |
| Magnesium | 38mg | 19mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 17.7µg | 15µg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.114mg | 0.991mg | 5% |
| Cholesterol | 100mg | 89mg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.187g | 0.591g | 4% |
| Potassium | 125mg | 62mg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 21 IU | 16 IU | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.5µg | 0.4µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.028mg | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 3.97g | 4.09g | N/A |
| Carbs | 3.97g | 4.09g | 0% |
| Sugar | 0g | 4.09g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.25mg | 0.18mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 1.9µg | 1.8µg | 0% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 15.4mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.2mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.637mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.803mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.395mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 1.219mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.368mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.675mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 1.065mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.397mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +80.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +100.8% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -14.6% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cotija cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170898/nutrients
- Feta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173420/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





