Feta vs. Blue cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Blue cheese is higher in calories, sodium, and fat (saturated fats). It is also richer in calcium, zinc, phosphorus, and vitamins B5 and A. Feta contains higher amounts of carbohydrates and cholesterol and is richer in B-complex vitamins.
Introduction
This article compares feta cheese and blue cheese. We will discuss different aspects of their differences, such as their nutrition content, health impacts, and general differences. One of the most important points is to showcase which cheese is healthier.
Nutrition
Calories
Blue cheese contains higher amounts of calories compared to feta.
Carbs
They are both low in carbs; however, feta contains higher carbs than blue cheese.
Proteins
Blue cheese is higher in proteins than feta.
Fat
Blue cheese contains higher amounts of fat compared to feta cheese.
Saturated fats
Blue cheese contains higher amounts of saturated fats.
Cholesterol
Feta is higher in cholesterol compared to blue cheese.
Minerals
Both these foods have nearly similar amounts of minerals and types of minerals. They are both rich in calcium, zinc, and phosphorus. However, blue cheese is richer in calcium, zinc, and phosphorus than feta.
Sodium
Sodium in both these foods is a critical mineral to mention.
Blue cheese contains higher amounts of sodium compared to feta. They are both very high in sodium.
In the diagram below, we can visualize the difference in their mineral difference.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+109.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-20%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+211.1%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+21.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+312.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+25%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+14.8%
Vitamins
Feta cheese is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B6, and B12. In comparison, blue cheese is richer in vitamins B5 and A.
Noting that blue cheese contains high amounts of B12 also.
The diagram below displays the difference between their vitamin profiles.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+431%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+120.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+155.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+38.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+58.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+38.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+78.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+33.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+12.5%
Health Impacts
Bone Health
Blue cheese and feta are high in calcium and positively impact bones, particularly osteoporosis. (1) (2)
Gastrointestinal Health
They are high in probiotics; they include lactobacilli, which enhance general gut health and digestion. (3)
Furthermore, when the gut microbiota is healthy, general inflammations in the gastrointestinal tract are kept at low levels. (4) (5)
Blue cheese contains less lactose, which could be a better option for lactose-intolerant individuals.
Cancer
Blue cheese, which is aged and ripened, has apoptotic activity on leukemic cells. Reducing risks of leukemias. (6)
Feta cheese reduces the risk of developing colorectal cancer. (7)
However, calcium-rich foods are linked with an increased risk of developing prostate cancer. (8)
Cardiovascular Health
They both contain a high amount of saturated fat and sodium. Saturated fats increase the risk of atherosclerosis, while high-sodium foods increase the risk of hypertension and hypertension-related kidney damage. As a result, it is critical to keep an eye on these parameters. (9)(10)
While taking MAO inhibitor medications these cheeses should be limited to prevent hypertension crisis. (11)
Blue cheese contains spermidine with multiple positive health impacts, most focusing on aging and cardiovascular health. It directly affects cardiac muscles and is linked with decreased cardiovascular diseases. In addition, it has neuroprotective and anti-carcinogenic properties. (12)
Ultimately, the key to minimizing cardiovascular risk is moderation, balance, and overall dietary patterns. Both feta and blue cheese can be enjoyed as part of a healthy diet, but it's essential to be mindful of portion sizes and to incorporate them into a diet that prioritizes whole, nutrient-dense foods.
Diabetes
Consumption of blue cheese and feta is linked with decreased risks of developing type 2 diabetes (13)(14).
Infectious agents
Penicillium roquforti, the fungus that makes blue cheese, has anti-infectious activity against chlamydia strains and improves immune functions (15).
General Differences
Feta cheese is a fresh cheese usually prepared from sheep or goat's milk. It is a white cheese that doesn't have a very long shelf life—approximately seven days refrigerated. Feta cheese can be used for salads, pasta, and everyday sandwiches.
On the other hand, we have blue cheese, an aged cheese with a particularly stingy taste. It is made with cow's milk, and Penicillium roqueforti fungus is added. Blue cheese is mainly used on charcuterie boards with wine. It is a more refined cheese. Blue cheese has a longer shelf life; it can stay up to four weeks refrigerated.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33237064/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3796667/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3279064/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20838859/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21477383/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20338416/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12869397/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16522915/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30402970/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-86324-w
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2738414/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29371440/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23945722/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002822304004316
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3655667/
Infographic
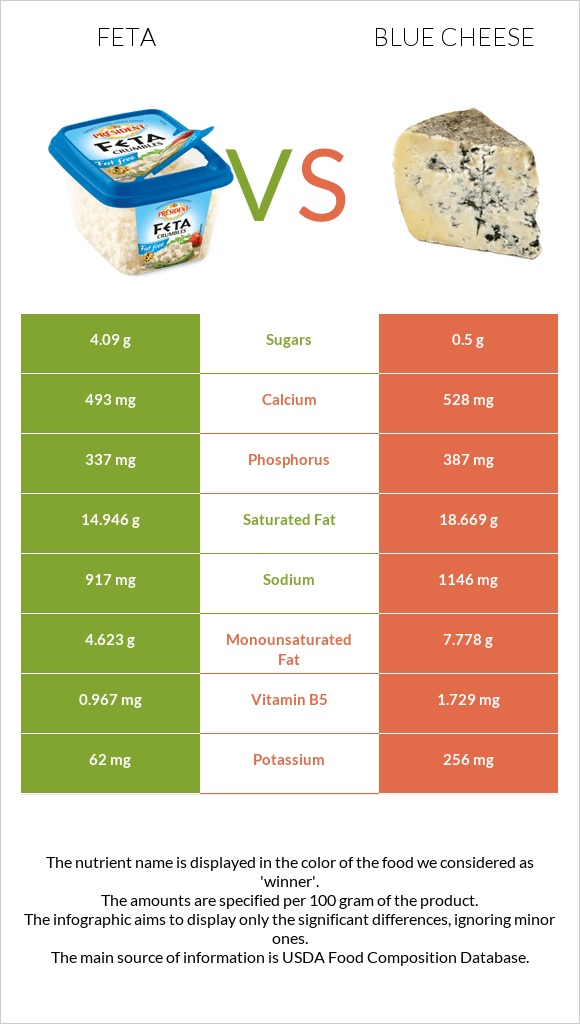
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.844mg | 0.382mg | 36% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.424mg | 0.166mg | 20% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.69µg | 1.22µg | 20% |
| Saturated fat | 14.946g | 18.669g | 17% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.967mg | 1.729mg | 15% |
| Protein | 14.21g | 21.4g | 14% |
| Fats | 21.28g | 28.74g | 11% |
| Sodium | 917mg | 1146mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.154mg | 0.029mg | 10% |
| Vitamin A | 125µg | 198µg | 8% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.623g | 7.778g | 8% |
| Phosphorus | 337mg | 387mg | 7% |
| Potassium | 62mg | 256mg | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 89mg | 75mg | 5% |
| Calories | 264kcal | 353kcal | 4% |
| Calcium | 493mg | 528mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.65mg | 0.31mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 2.88mg | 2.66mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 4.09g | 2.34g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 16 IU | 21 IU | 1% |
| Magnesium | 19mg | 23mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.032mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.5µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.028mg | 0.009mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 15µg | 14.5µg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 1.8µg | 2.4µg | 1% |
| Folate | 32µg | 36µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.591g | 0.8g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.09g | 2.34g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.09g | 0.5g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.18mg | 0.25mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.991mg | 1.016mg | 0% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 15.4mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.2mg | 0.312mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.637mg | 0.785mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.803mg | 1.124mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.395mg | 1.919mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.219mg | 1.852mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.368mg | 0.584mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.675mg | 1.087mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.065mg | 1.556mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.397mg | 0.758mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +74.8% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +30.2% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +50.6% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +35.1% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -19.9% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +68.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +35.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Feta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173420/nutrients
- Blue cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172175/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






