Greek yogurt vs. Cream cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Regarding vitamin B12 content, Greek yogurt provides 0.75g compared to cream cheese's 0.22g; however, cream cheese contains more vitamin A, vitamin E, monounsaturated fat, and polyunsaturated fat. However, it's important to highlight that cream cheese covers 89% more daily saturated fat needs than Greek yogurt, indicating a potential concern for those mindful of saturated fat intake. Additionally, Greek yogurt contains less cholesterol compared to cream cheese.
Introduction
This article compares two types of dairy products: Greek yogurt and cream cheese. The differences will be discussed based on their general characteristics, nutritional content, and health effects.
Nutrition
This section will compare 100g of plain Greek yogurt made from whole milk and cream cheese.
Macronutrients and Calories
Cream cheese is denser in nutrients. About 80% of Greek yogurt is water, whereas the water content of cream cheese is 53%.
100g of Greek yogurt is higher in protein, whereas cream cheese is higher in fats and carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+46.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+54.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+588.8%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+38.7%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+76.4%
Calories
Cream cheese is over 3.6 times higher in calories than Greek yogurt. Cream cheese provides 350 calories, whereas Greek yogurt provides 97.
Protein
Greek yogurt is 1.5 times richer in proteins compared to cream cheese. The amount of protein in Greek yogurt is 9 g per 100g, and 6.15 g in cream cheese.
Fats
Greek yogurt is lower in fat compared to cream cheese. Cream cheese has its consistency due to its higher amounts of fat. The fat in Greek yogurt is 5 grams, while the fat in cream cheese is 34.44 grams.
Saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fat amounts are higher in cream cheese.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-88.2%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+317%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+216.2%
Cholesterol
In comparing Greek yogurt's and cream cheese's cholesterol content, Greek yogurt has a substantially lower cholesterol content. Greek yogurt contains 13mg of cholesterol, while cream cheese has a higher cholesterol content of 101mg.
Carbohydrates
Greek yogurt has lower amounts of carbs compared to cream cheese. Greek yogurt contains 3.98g of carbohydrates compared to cream cheese, which contains 5.52g. Both are not good sources of dietary fiber.
Vitamins
Cream cheese contains 74 times more vitamin A and 86 times more vitamin E. Greek yogurt, on the other hand, contains more vitamin B2 (riboflavin) and vitamin B3 (niacin) than cream cheese.
While cream cheese is richer in vitamin B5 (0.517mg) (Pantothenic Acid) and folate (9 mg), Greek yogurt provides more vitamin B12 (0.75 mg) and B6 (0.063 mg) compared to cream cheese. Cream cheese contains vitamin K (2.1 g), whereas Greek yogurt does not contain measurable amounts. Both contain an equal amount of vitamin B1 (thiamin).
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+20.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+128.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+12.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+240.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+15300%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+8500%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+56.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+80%
Minerals
There is a marginal difference of 3mg between Greek yogurt and cream cheese regarding calcium content. While cream cheese holds a slight advantage in iron (0.11mg) compared to Greek yogurt (0mg), the differences are minimal.
Greek yogurt showcases higher levels of magnesium (11mg) and phosphorus (135mg) in comparison to cream cheese (9mg and 107mg, respectively). Potassium content is slightly elevated in Greek yogurt (141mg) versus cream cheese (132mg). Notably, sodium is significantly higher in cream cheese (314mg) compared to Greek yogurt (35mg).
Zinc content is nearly identical, with Greek yogurt at 0.52mg and cream cheese at 0.5mg. Both the copper and manganese values are very close. Selenium content is marginally higher in Greek yogurt at 9.7 g, compared to 8.6 g in cream cheese.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+22.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+26.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-88.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+12.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+22.2%
Glycemic Index
Greek yogurt has a glycemic index 12, indicating a low impact on blood sugar levels. On the other hand, cream cheese has a glycemic index of 0, which is also categorized as low.
Acidity
Greek yogurt and cream cheese have acidic pH levels, but their potential renal acid load (PRAL) scores differ. Cream cheese has a PRAL score of 2.7 (acidic), indicating a lower acidity level than Greek yogurt, which has a PRAL score of 4.9 (acidic).
Weight Loss & Diets
Greek yogurt, being rich in protein, is considered a filling and satisfying food that can aid in weight management by promoting satiety between meals (1, 2). Studies have associated yogurt consumption with lower body fat, less weight gain, and a smaller waist circumference (3, 4). In contrast, cream cheese should be consumed in moderation during weight loss. It is calorie-dense and high in fat, which, when overconsumed, may hinder weight loss progress. Therefore, choosing Greek yogurt over cream cheese as a regular part of the diet may contribute to a more effective and satisfying weight-loss journey.
Health Impact
Potential Benefits
While cream cheese contains minimal protein, Greek yogurt is a robust source of this essential macronutrient. Various bodily functions depend on proteins, including muscle maintenance, immune support, and tissue repair (5). Beyond protein, Greek yogurt provides vital vitamins and minerals, including zinc, selenium, and B12. These nutrients support immune system performance, nervous system function, red blood cell creation, and energy generation (6, 7). In contrast, cream cheese's protein content is notably lower and lacks the nutrient richness of Greek yogurt. On the other hand, cream cheese is a notable source of vitamin A. Vitamin A is crucial for vision, immune system support, and the integrity of various tissues, including the skin, lungs, and intestines (8, 9). Additionally, cream cheese supplies antioxidants, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which defend the body against free radicals, preventing cellular damage. These antioxidants, essential for eye health, contribute to the overall nutritional profile of cream cheese (10, 11, 12).
Cardiovascular Health
In moderation, cream cheese can have neutral to positive impacts on cardiovascular health. However, excessive consumption may elevate the risk of cardiovascular diseases due to increased saturated fats (13). On the other hand, yogurt has demonstrated beneficial effects on heart disease risk factors, including high blood pressure and cholesterol (14). Yogurt's fermented dairy content improves cardiovascular health by reducing plaque buildup and artery stiffness (15). The probiotics in yogurt and cream cheese may contribute to lowering cholesterol levels, as evidenced by research showing a decrease in total and LDL (bad) cholesterol with daily probiotic-rich yogurt intake (16).
Digestive Health
Both cream cheese and Greek yogurt share the beneficial presence of probiotics, which are friendly bacteria known for their positive impact on health (17). These probiotics support the immune system, reduce inflammation, and foster a balanced gut microbiome (18, 19, 20, 21, 22). Additionally, both dairy products offer a low lactose content, making them suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance (23, 24, 25). However, while cream cheese is specifically recognized for its probiotic properties and antioxidant content, Greek yogurt stands out for its natural richness in protein.
Cancer
The risk of breast cancer may be raised by eating a lot of cream cheese. (26)
High-calcium diets are directly associated with prostate cancer development. (27)
Production and varieties
Greek yogurt, often labeled "strained" yogurt, undergoes a unique production process. It begins with the yogurt fermentation in tanks, followed by straining whey and other liquids in the final stages, resulting in a thicker consistency and higher protein content. Some manufacturers opt for Greek-style yogurt by incorporating milk proteins at the start or end of processing. This versatile yogurt comes in various forms, including total fat, reduced fat, fat-free options, and a spectrum of flavored and unflavored varieties. On the other hand, cream cheese is crafted from cream or a blend of cream and milk, gaining slight acidity from lactic acid bacteria. Cream cheese is available in different fat content variations and can be found plain or flavored, such as garlic, herb, or chive. The preparation methods for Greek yogurt involve straining and fermentation, while cream cheese is made through curdling, draining, and blending.
Appearance
Cream cheese is a smooth, dense, creamy product with a pale white color. On the other hand, Greek yogurt has a thick and creamy texture, often described as velvety, and a slightly off-white or pale yellowish color. As a result of the straining process, which removes excess whey, it may have a smoother appearance than regular yogurt.
Taste and Use
In terms of flavor profile, cream cheese has a rich and slightly sweet taste, while yogurt, especially Greek yogurt, has pronounced tangy and tart notes, offering a creamier and thicker mouthfeel. Cream cheese is a versatile ingredient commonly used in sweet and savory dishes. Its creamy and smooth consistency makes it ideal for spreading on bagels, toast, or crackers. Cream cheese is used in baked goods such as cheesecakes, frosting, and creamy fillings for pastries. It's also used in savory applications, like dips and sauces, and as a base for sure sandwiches.
Due to its thick and velvety texture, Greek yogurt is popular for savory and sweet dishes. It is also a standalone snack, especially when topped with fruits, granola, or honey. In recipes, Greek yogurt is often used as a healthier alternative to sour cream, providing a tangy and rich flavor. It's also a common ingredient in smoothies, parfaits, and various dishes.
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23022602/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26175486/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6554456/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5227968/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555990/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7415215/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3546623/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3471201/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3708350/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4892306/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5836018
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34649831/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5905602/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30370878/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29153184/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4053917/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5227968/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32232406/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23126664/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19756155/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20664519/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4586535/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24695892/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4586575/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5998914/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22081693/
Infographic
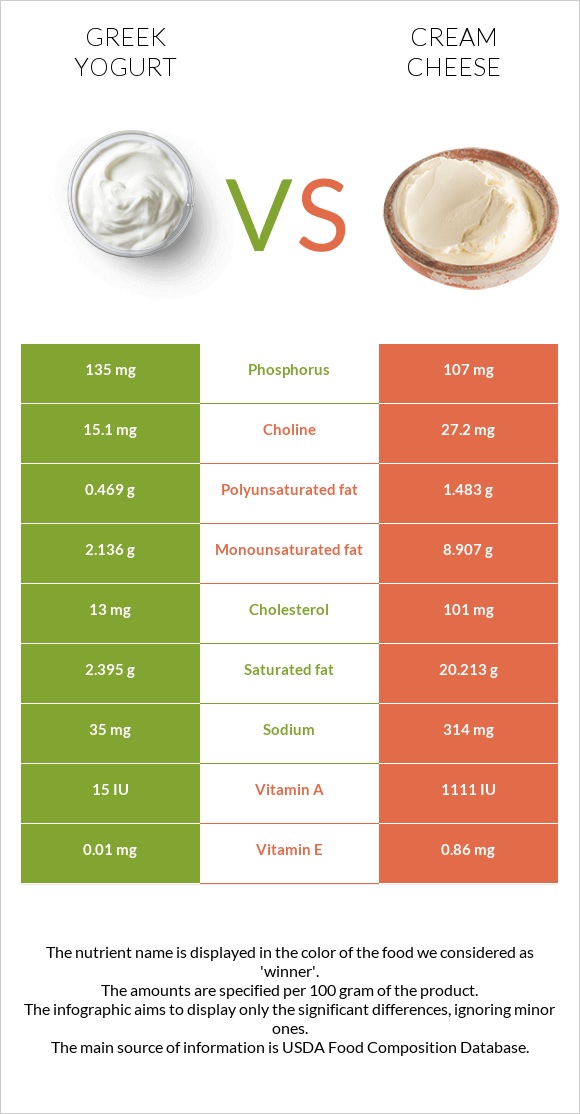
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 2.395g | 20.213g | 81% |
| Fats | 5g | 34.44g | 45% |
| Vitamin A | 2µg | 308µg | 34% |
| Cholesterol | 13mg | 101mg | 29% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.75µg | 0.22µg | 22% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.136g | 8.907g | 17% |
| Calories | 97kcal | 350kcal | 13% |
| Sodium | 35mg | 314mg | 12% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.469g | 1.483g | 7% |
| Protein | 9g | 6.15g | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.86mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 135mg | 107mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.278mg | 0.23mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.331mg | 0.517mg | 4% |
| Selenium | 9.7µg | 8.6µg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 2.1µg | 2% |
| Choline | 15.1mg | 27.2mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 3.98g | 5.52g | 1% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.11mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.208mg | 0.091mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.063mg | 0.056mg | 1% |
| Folate | 5µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 3.98g | 5.52g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 9mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 100mg | 97mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 141mg | 132mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 4g | 3.76g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.017mg | 0.018mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0.52mg | 0.5mg | 0% |
| Starch | 0.35g | 0% | |
| Manganese | 0.009mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.069mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.233mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.324mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.657mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.567mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.191mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.291mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.395mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.175mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.004g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.023g | 0.125g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.02g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0g | 0.002g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | 0.002g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | 0.036g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0g | 0.007g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.209g | 0.807g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Greek yogurt - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171304/nutrients
- Cream cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173418/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






