Kefir vs. Greek Yogurt — Nutrition & Health Impact Comparison


Summary
Greek yogurt is higher in fats, protein, and calories. It is also richer in phosphorus, selenium, and vitamins B2 and B12. In comparison, kefir is richer in probiotics, calcium, and vitamins A and D.
They provide several positive health impacts but may cause digestive symptoms in people with lactose intolerance.
Introduction
This article aims to understand the differences between Greek yogurt and kefir according to their nutritional content and health impact.
Kefir is made by using small white kefir grains in milk and letting it ferment. Kefir grains are symbiotic cultures of living bacteria and yeast.
Greek yogurt is made by fermenting regular yogurt and straining it afterward to remove the whey. It is also a product of dairy fermentation; however, kefir is fermented longer and contains more colony-forming units or CFUs.
Both kefir and Greek yogurt contain probiotics.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare 100g of plain Greek yogurt made from whole milk and low-fat plain kefir.
Calories
Greek yogurt is over 2 times higher in calories than kefir; however, both are considered to be low in calories. Kefir provides 41 calories, whereas Greek yogurt provides 97.
Macronutrients
Greek yogurt is denser in nutrients. About 80% of Greek yogurt is water, whereas the water content of kefir is 90%.
A 100g of Greek yogurt is higher in protein and fats, whereas kefir is higher in carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+12.6%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+137.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+437.6%
Carbs
Greek yogurt contains 4g of carbs per 100g, whereas kefir contains 4.5g.
Fats
Since we are considering low-fat kefir, the fat content will be negligible. Low-fat kefir contains less than 1g of fat. In comparison, Greek yogurt is from whole milk and contains about 5g of fats.
The predominant fats in kefir and Greek yogurt are saturated fats, followed by monounsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-72.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+589%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+784.9%
Proteins
Greek yogurt is over 2 times richer in proteins; it contains 9g, whereas kefir contains 3.8g.
Minerals
Kefir and Greek yogurt are not mineral-dense products, being high only in several minerals. Greek yogurt is 2.7 times richer in selenium; it is also slightly richer in phosphorus. In comparison, kefir is somewhat richer in calcium.
In the diagram below, we can see their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+30%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+16.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+∞%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+88.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+13%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+28.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-12.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+80%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+169.4%
Vitamins
Greek yogurt is 2.6 times richer in vitamin B12 and 2 times richer in vitamin B2. Kefir, on the other hand, is a good source of vitamins A and D, which are absent in Greek yogurt.
Kefir is also somewhat higher in most remaining vitamins than Greek yogurt; however, they are not particularly rich in them.
In the diagram below, we can see their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+8450%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+30.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+16.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+160%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+105.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+38.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+158.6%
Glycemic Index
Both Greek yogurt and kefir are low in carbs and, thus, have low glycemic index values.
The glycemic index of Greek yogurt is 12, whereas the glycemic index of low-fat kefir is 36.
Acidity
One of the ways to look at the food's acidity is by calculating its PRAL value. The PRAL value shows how much acid or base is produced in the organism by the given food.
The PRAL values of Greek yogurt and kefir are 4.9 and 0.3, respectively, making them acidic, with Greek yogurt being more acidic or acid-producing.
Diets
Kefir is better for low-calorie diets, whereas Greek yogurt is better for high-protein and low-carb diets.
Both kefir and Greek yogurt can be safely consumed during a gastroparesis liquid diet.
Health Impact: Benefits & Side Effects
Digestion
Kefir is richer in probiotics, linked to healthy gut microbiota and improved gut health. Probiotic strains also show antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activity (1).
People with lactose intolerance develop symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, bloating, or abdominal pain after dairy consumption and should substitute regular dairy with their alternatives. To read more, you can visit our "Dairy-Free Diet Plan: Benefits and Downsides" page.
Bone Health & More
Kefir is a good source of vitamin D and calcium, which are crucial for keeping the bones healthy. Greek yogurt, on the other hand, contains only calcium.
They can be added to one's diet to reduce the risk of developing osteoporosis, a disease characterized by bone mass loss and the risk of sudden fractures. At higher risk are people with malabsorption, malnutrition, and postmenopausal women (2).
Vitamin D may also benefit the nervous and immune systems and reduce muscle weakness. Calcium is also required for blood vessel contractions, nerve signaling, and normal heartbeat. For detailed information, you can visit here.
Anemia
Greek yogurt and kefir contain vitamin B12, with Greek yogurt containing 2.6 times more.
Regular dairy consumption decreases the risk of developing megaloblastic or vitamin B12-deficiency anemia, causing hematological and neurological symptoms, weakness, and sensation of pins and needles (3).
Cardiovascular Health and Diabetes
According to this study, kefir may decrease arterial blood pressure, thus, reducing the risk of cardiac hypertrophy; it may also improve baroreflex function, which is important for blood pressure regulation (4). These effects are unknown for Greek yogurt.
A reasonable intake of dairy products, including kefir and Greek yogurt, may reduce plasma cholesterol levels, which may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (5).
Dairy products contain peptides that may inhibit ACE enzymes (angiotensin-converting enzyme), which are important for blood pressure regulation (4). ACE-inhibitor medications (Captopril, Lisinopril, etc.) also work by this mechanism (6).
References
Infographic
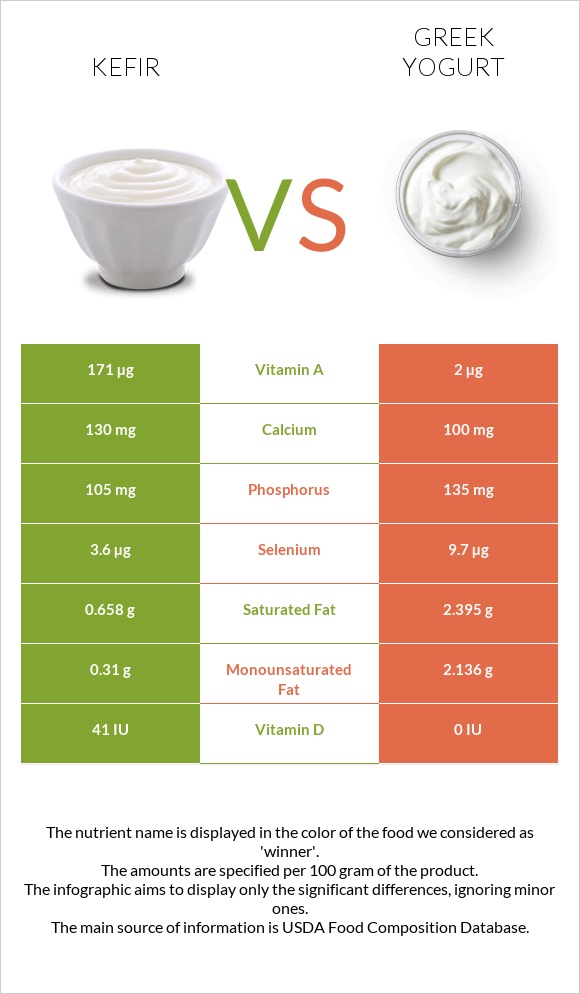
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 171µg | 2µg | 19% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.29µg | 0.75µg | 19% |
| Selenium | 3.6µg | 9.7µg | 11% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.135mg | 0.278mg | 11% |
| Protein | 3.79g | 9g | 10% |
| Saturated fat | 0.658g | 2.395g | 8% |
| Fats | 0.93g | 5g | 6% |
| Vitamin D | 41 IU | 0 IU | 5% |
| Vitamin D | 1µg | 0µg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.31g | 2.136g | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 105mg | 135mg | 4% |
| Calories | 41kcal | 97kcal | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 5mg | 13mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 130mg | 100mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.053g | 0.469g | 3% |
| Folate | 13µg | 5µg | 2% |
| Potassium | 164mg | 141mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.04mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.009mg | 0.017mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.46mg | 0.52mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.03mg | 0.023mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.385mg | 0.331mg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.2mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 4.48g | 3.98g | N/A |
| Carbs | 4.48g | 3.98g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 12mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.61g | 4g | N/A |
| Sodium | 40mg | 35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.005mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.15mg | 0.208mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.058mg | 0.063mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.037g | 0g | N/A |
| Choline | 15.2mg | 15.1mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.004g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.006g | 0.023g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.001g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.029g | 0.209g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Kefir - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170904/nutrients
- Greek yogurt - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171304/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




