Milk vs. Powdered Milk — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
After serving size correction, fresh milk is richer in vitamins B2, B12, D, and A. In addition, it is richer in calcium and phosphorus. In comparison, powdered milk is higher in calories, fats, and sodium but richer in magnesium. Powdered milk has a longer shelf life.
Introduction
In this article, we will be comparing regular milk with powdered milk. Milk in this article is fresh liquid milk, and powdered milk is powdered milk without adding water.
Please note that the nutritional comparison and infographics in this article will falsely tend more towards powdered milk since it contains more nutrients in dehydrated form, while most of the weight of fresh milk comes from water.
However, we will compare them based on the logic of consumption regarding their nutritional content and health impacts to understand if they are different.
General Differences
Shelf life is one of the most relevant differences in these milks.
Fresh milk has a shorter shelf life than powdered milk.
Another difference is taste; powdered milk has a creamier and stronger taste than fresh milk.
Nutritonal Content Comparison
Approximately 32g of powdered milk is equivalent to 1 cup of fresh milk, which is around 240 ml. This is a generalized estimate.
In this article, we are comparing whole-fat powdered milk without added vitamin D to 1% fresh milk with added vitamins A and D. This also means that the macronutrient composition and the vitamin content will differ given that we are comparing fortified milk to a non-fortified one.
Macronutrients and Calories
Calories
Powdered milk contains more calories than fresh milk.
If we compare 32g of powdered milk to 240 ml of fresh milk, we still come to the point where powdered milk is higher in calories. This is due mainly to it being whole milk, which contains a higher amount of fat.
Protein
When comparing 32g of powdered milk to 240 ml of fresh milk, we can conclude that they have similar amounts of proteins.
Fats
Whole powdered milk contains more fats than 1% fresh milk when we correct for equivalency.
Carbohydrates
When corrected for equivalency, we conclude that both powdered milk and regular milk have similar amounts of carbs.
Vitamins
This article considers fortified milk with vitamins A and D for fresh milk, while it considers unfortified milk for powdered milk. This is why the fresh milk discussed in this article is richer in vitamins B2, B12, D, and A.
Below this article, you can find the visualization of the vitamin content. However, the content is given according to an equal amount of serving in grams without correcting for serving size; hence the infographics are misleading.
Minerals
More often, we find powdered milk that has added iron in them. It is essential to check those labels.
One of the main differences in minerals is sodium. Powdered milk contains more sodium than fresh milk, even after serving size adjustment.
For the rest of the minerals, after adjustment for serving size, fresh milk is richer in phosphorus and calcium. In contrast, powdered milk is richer in magnesium.
Below this article, you can find the visualization of the mineral content. However, again, the content is given according to an equal amount of serving in grams without correcting for serving size; hence the infographics are misleading.
Health Impact
Check this article to learn about powdered milk and its health impacts.
During milk processing, heat dehydrates the milk for it to become powder. Considering this, we lose some nutrients during the dehydration process. An example of that is vitamin B12.
Based on this, fresh milk can have a higher nutrient content than powdered milk. However, most powdered milk is fortified with vitamins and minerals to compensate for that loss and add extra nutrients.
Cardiovascular Health
Powdered milk fortified with potassium and phytosterols is a cost-effective source of nutrients that positively affects cardiovascular health. Reassuring that people are getting an adequate amount of these nutrients in their diet.
Similarly, this study was made on another sample who had hypertension (1, 2).
Powdered milk fortified with potassium and phytosterols has an advantage over fresh milk regarding this. However, simply choosing fortified fresh milk will have the same effect.
Bone Health
Both powdered milk and fresh milk positively affect bone health in children; however, we also need to consider vitamin D and magnesium in association with calcium intake for proper bone mineralization.
The difference comes from the accessibility of milk, as in some countries, powdered milk is cheaper and more accessible with added vitamins and minerals (3, 4).
Infographic
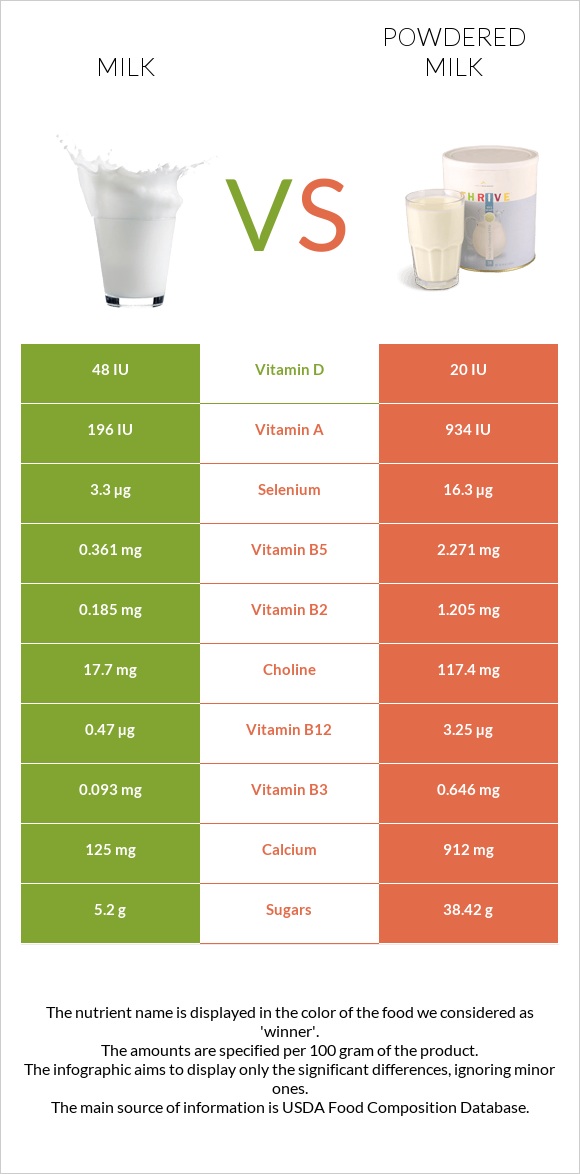
Mineral Comparison
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -88.1% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +672.7% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +629.6% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +786.7% |
| Contains more IronIron | +1466.7% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +700% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +695.2% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +716.8% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +1233.3% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +393.9% |
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin DVitamin D | +140% |
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +344.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +5700% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +1315% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +551.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +594.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +529.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +716.2% |
| Contains more Vitamin B12Vitamin B12 | +591.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +2100% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +640% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.47µg | 3.25µg | 116% |
| Phosphorus | 95mg | 776mg | 97% |
| Calcium | 125mg | 912mg | 79% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.185mg | 1.205mg | 78% |
| Saturated fat | 0.633g | 16.742g | 73% |
| Protein | 3.37g | 26.32g | 46% |
| Fats | 0.97g | 26.71g | 40% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.361mg | 2.271mg | 38% |
| Potassium | 150mg | 1330mg | 35% |
| Cholesterol | 5mg | 97mg | 31% |
| Zinc | 0.42mg | 3.34mg | 27% |
| Selenium | 3.3µg | 16.3µg | 24% |
| Calories | 42kcal | 496kcal | 23% |
| Vitamin A | 58µg | 258µg | 22% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.02mg | 0.283mg | 22% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.037mg | 0.302mg | 20% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.277g | 7.924g | 19% |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 85mg | 18% |
| Choline | 17.7mg | 117.4mg | 18% |
| Sodium | 44mg | 371mg | 14% |
| Carbs | 4.99g | 38.42g | 11% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 8.6mg | 10% |
| Copper | 0.01mg | 0.08mg | 8% |
| Folate | 5µg | 37µg | 8% |
| Iron | 0.03mg | 0.47mg | 6% |
| Vitamin D | 48 IU | 20 IU | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0.58mg | 4% |
| Vitamin D | 1.2µg | 0.5µg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.035g | 0.665g | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.093mg | 0.646mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.003mg | 0.04mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 2.2µg | 2% |
| Net carbs | 4.99g | 38.42g | N/A |
| Sugar | 5.2g | 38.42g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.043mg | 0.371mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.143mg | 1.188mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.174mg | 1.592mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.319mg | 2.578mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.282mg | 2.087mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.088mg | 0.66mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.174mg | 1.271mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.22mg | 1.762mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.101mg | 0.714mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.027g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +3540.5% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +681% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +2653.6% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +669.9% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +710.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -96.2% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +2760.6% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1800% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Milk - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170872/nutrients
- Powdered milk - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173454/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



