Onion vs. Onion powder — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Onion powder loses several nutrients during dehydration, primarily heat labile such as vitamin C and B complex vitamins. Thus, onions are richer in vitamin C and B complex. In addition, onions are richer in phytochemicals which provide several positive health impacts, specifically antioxidative effects.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between onion and onion powder. Well, onion powder is a dried and ground form of onions. In this article, we will focus on some of their nutritional contents that get destroyed during the drying process and the flavor difference between them.
Actual differences
Onion powder is dehydrated and dried, and turned into powder. It loses flavor, especially the pungent taste of onions. Onion powder has a milder taste profile and is more concentrated. Fresh onions are pungent and more potent in flavor.
It is also essential to consider the shelf life of each. Even if adequately stored, onion has a shorter shelf life than onion powder.
Here you can read in-depth about onion nutrition.
Nutritional content comparison
Since we are comparing onions to onion powder in this article, it is the dehydrated version of onion. In addition, we need to remember that onion powder is eaten in minimal amounts, not exceeding half a teaspoon. Thus comparing them is not a practical matter.
However, you can visualize their macronutrient, vitamin, and mineral distributions in the section below. As the macronutrient chart shows, onions consist of 89% of water, while onion powder contains 79% of carbs and only 5% of water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+1553.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+846.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+940%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+747.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+1054.3%
It is essential to note this while undergoing the drying process. Vitamins C and B complex are destroyed since they are heat labile.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+216.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1250%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+893.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+196.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+176.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+495.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+498.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+925%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+236.8%
Contains
more
CholineCholine
+539.3%
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-94.5%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+1030%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1569.6%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+574.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1757.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+1412.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+2282.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+1010.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+907.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+2760%
The health impacts section discusses some nutrients in onion and onion powder.
Health impacts
Onion is a rich source of phytochemicals that are not destroyed during dehydration. From these nutrients, we have Quercetin, Anthocyanin, and Alliin.
These are potent antioxidants that have many benefits on overall health. They have anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, and immune-supporting properties (1).
However, they are primarily in lower amounts. In addition, we consume onion powder in small quantities and cooking, which denatures these phytochemicals even more.
Onions contain saponins that have antifungal properties. In comparison, the saponin in onion powder is insignificant (2).
Onions are richer in vitamin C and B complex vitamins since they are not destroyed. (Although the diagrams show that onion powder is richer, consider the comparison between onions which are 90% water vs. onion powder).
Vitamin C has antioxidative properties and immune system-supporting properties. In addition, B complex vitamins are necessary for several physiological and biochemical reactions regarding the immune, nervous, metabolism, and cardiovascular systems (3)(4).
Infographic
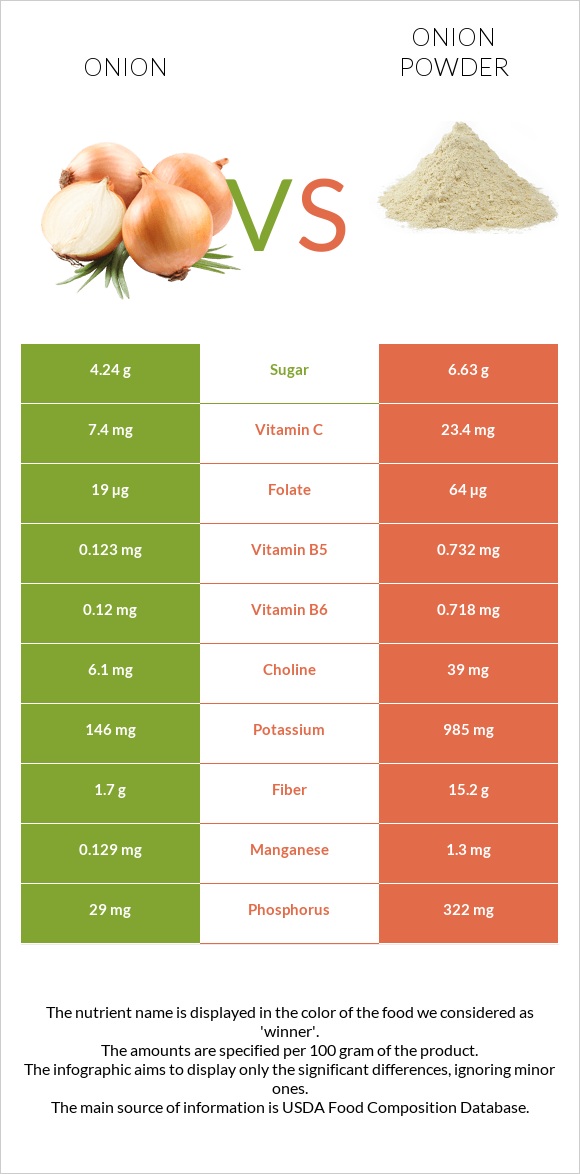
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 0.039mg | 0.59mg | 61% |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 15.2g | 54% |
| Manganese | 0.129mg | 1.3mg | 51% |
| Iron | 0.21mg | 3.9mg | 46% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12mg | 0.718mg | 46% |
| Phosphorus | 29mg | 322mg | 42% |
| Calcium | 23mg | 384mg | 36% |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 4.05mg | 35% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.046mg | 0.457mg | 34% |
| Selenium | 0.5µg | 14.3µg | 25% |
| Potassium | 146mg | 985mg | 25% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 113mg | 25% |
| Carbs | 9.34g | 79.12g | 23% |
| Protein | 1.1g | 10.41g | 19% |
| Vitamin C | 7.4mg | 23.4mg | 18% |
| Calories | 40kcal | 341kcal | 15% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.123mg | 0.732mg | 12% |
| Folate | 19µg | 64µg | 11% |
| Choline | 6.1mg | 39mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.08mg | 4% |
| Sodium | 4mg | 73mg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg | 4.1µg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.27mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.017g | 0.31g | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.116mg | 0.321mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.1g | 1.04g | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.042g | 0.219g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 7.64g | 63.92g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.24g | 6.63g | N/A |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.013g | 0.202g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.014mg | 0.06mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.021mg | 0.14mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.014mg | 0.14mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.025mg | 0.22mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.039mg | 0.49mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0.09mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.025mg | 0.28mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.021mg | 0.17mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0.16mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 1.29g | 1.67g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.015g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -80.8% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1453.8% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1723.5% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +169.9% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +290.9% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +29.5% |
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Onion - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170000/nutrients
- Onion powder - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171327/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






