Palm kernel oil vs. Palm oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Palm oil and palm kernel oil, both derived from the oil palm tree, have distinct properties and uses. Palm oil is extracted from the fruit's flesh, while palm kernel oil is obtained from the seed's kernel.
Palm oil is rich in phytochemicals like tocotrienols and carotenoids, offering potential health and skin benefits. In contrast, palm kernel oil is valued for its high lauric acid content, providing excellent moisturizing and antimicrobial properties but with a higher risk of clogging pores.
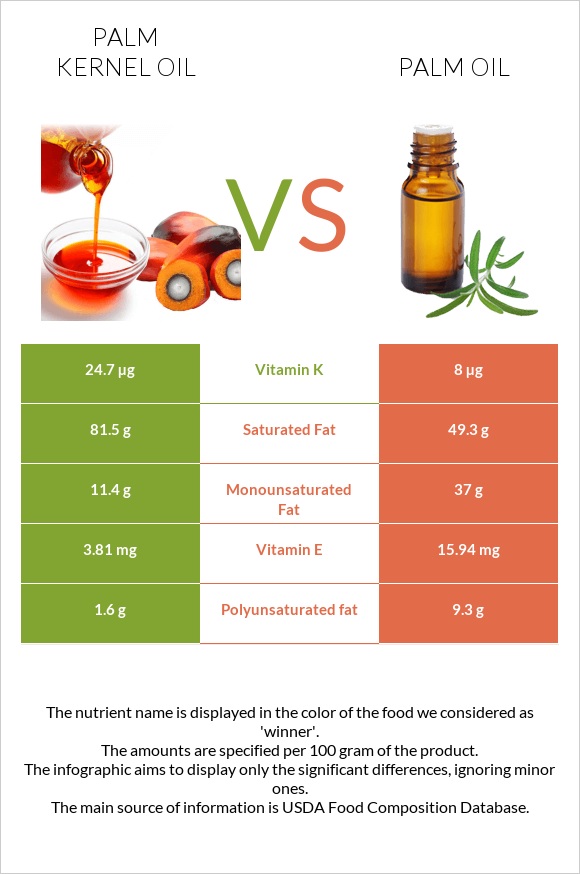
Palm oil is higher in vitamin E, polyunsaturated fat, and monounsaturated fat. On the other hand, palm kernel oil contains 3 times more vitamin K than palm oil. Palm kernel oil contains 24.7µg of vitamin K, while palm oil contains 8µg.
Introduction
Palm oil and palm kernel oil are two widely used vegetable oils derived from the oil palm tree but differ significantly in their composition, extraction process, and applications. In this article, we will compare their actual differences, nutritional profiles, and health impacts.
Actual Differences
Classification
Palm kernel oil and palm oil are two distinct types of oils derived from the oil palm tree (Elaeis guineensis) (1).
Palm oil is extracted from the fleshy pulp of the palm fruit, giving it a reddish hue due to its high beta-carotene content, while palm kernel oil is obtained from the seed or kernel of the fruit and is pale yellow.
Production Methods
The production methods for palm oil and palm kernel oil differ due to their sources within the oil palm fruit (2) (3).
Palm Oil: The extraction process begins with the sterilization of harvested fruit bunches to prevent enzymatic breakdown. The fruit is then stripped from the bunches, softened through steaming or boiling, and mechanically pressed to release the oil from the mesocarp. The crude palm oil (CPO) undergoes clarification to remove impurities and may be further refined for edible or industrial use.
Palm Kernel Oil: After separating the kernel from the fruit's flesh, the kernels are dried and cracked to remove the shell. The kernel is then subjected to mechanical pressing or solvent extraction to produce crude palm kernel oil (CPKO). This oil also undergoes refining, bleaching, and deodorizing depending on its intended application.
Taste and Appearance
Palm oil has a reddish-orange hue due to its high beta-carotene content. It has a mild, earthy flavor with a slightly nutty undertone, making it suitable for various culinary applications.
In contrast, palm kernel oil is pale yellow or white when solidified. Its taste is more neutral but slightly creamier, with a subtle hint of nuttiness resembling coconut oil.
Smoke Point and Usage
Palm oil and palm kernel oil differ in their smoke points and usage. Palm oil has a smoke point of about 223°C (443°F), making it suitable for frying, baking, and other high-heat cooking applications (4). It is commonly used in processed foods and as a base in margarines and shortenings. In contrast, palm kernel oil has a slightly lower smoke point of around 220°C (428°F) but is less commonly used in cooking due to its higher saturated fat content. Instead, it finds widespread use in the production of cosmetics, soap, and industrial products because of its creamy texture and stability.
Nutrition
Although the standard serving size for vegetable oils is considered one tablespoon weighing 14g, the infographics below are presented for 100g servings for palm oil and palm kernel oil.
Macronutrients and Calories
Just like most vegetable oils, palm oil and palm kernel oil contain approximately 100% of fats. There are some differences in fat type, vitamin, and phytochemical contents.
Calories
Palm oil is slightly higher in calories than palm kernel oil. Palm and kernel oil contain 884 and 862 calories per 100g of serving, respectively.
When considering the serving size of each, palm oil is also higher in calories. Compared to 117 calories in palm kernel oil, it provides 120 calories per 14g.
Fat Type Comparison
Saturated Fats
Palm oil contains 49.3g of saturated fats, primarily palmitic acid. On the other hand, palm kernel oil is much higher in saturated fats, comprising 81.5g, predominantly lauric acid, which gives it a firmer texture at room temperature and greater oxidative stability.
These differences in saturated fat content influence their functional properties: palm oil is widely used in food products, and palm kernel oil is preferred for non-food applications like cosmetics and detergents.
Monounsaturated Fats
Palm oil is more than three times higher in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA). Compared to 11.4g of MUFA in palm kernel oil, it provides 37g of them. Both mostly contain oleanolic acid.
Polyunsaturated Fats
Palm oil is also higher in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) than palm kernel oil. It contains nearly 6 times more PUFA, providing 9.3g of them per 100g, compared to 1.6g in 100g of palm kernel oil.
Both of these vegetable oils mostly contain omega-6 linoleic acids with negligible amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. The omega-6 / omega-3 ratio equals 17,5:1 in palm kernel oil and 33,6:1 in palm oil (5). The WHO recommends this ratio to be 20:1 in vegetable oils (6). Thus, in this case, palm kernel oil is preferable with a lower omega-6 / omega-3 ratio and is linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases and inflammation.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-39.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+224.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+481.3%
Vitamins
Palm oil and palm kernel oil are composed entirely of fats and contain only fat-soluble vitamins. They are notable sources of vitamin K and vitamin E.
Palm kernel oil is more than 3 times higher in vitamin K than palm oil. It provides 24,7µg of it, while palm oil contains only 8µg.
On the other hand, palm oil contains more than 4 times more vitamin E. It has 15.94mg of it per 100g, while palm kernel oil has 3.81mg.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+208.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+318.4%
Phytochemicals
Palm oil is rich in carotenoids that indicate the reddish-to-orange color of this vegetable oil. It contains noticeable amounts of beta-carotene, neurosporin, and lycopene (7). Also, it contains some amounts of terpenoids and aromatic acids (8). On the other hand, palm oil is a rich source of plant sterols, especially beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol, and campesterol (9).
Carbs and Proteins
Palm oil and palm kernel oil do not contain any amounts of carbohydrates and proteins.
Glycemic index
All vegetable oils, including palm oil and palm kernel oil, lack carbohydrates. Thus, they have a glycemic index of 0.
Health impact
Cardiovascular Health
Palm oil and palm kernel oil, widely used in food products, cooking, and industry, have a complex relationship with heart health. Their effects largely depend on the type and processing of the oil. Unrefined red palm oil contains antioxidants like vitamin E and carotenoids, which may have protective cardiovascular benefits (10). However, palm kernel oil is high in saturated fats, which can elevate low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol (11). This increase may contribute to a higher risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease if consumed in excess (12).
Brain Health
Palm oil, rich in tocotrienols, a type of vitamin E, has been studied for its potential neuroprotective properties (13). Tocotrienols may help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, potentially protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's (14).
However, palm kernel oil is high in saturated fats, which, when consumed excessively, may contribute to cardiovascular issues that indirectly affect brain health by impairing blood flow to the brain (15). Thus, its role in brain health is less favorable.
Skin Health
Palm kernel oil is beneficial for skin health due to its rich composition of fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins. Its high lauric acid content provides excellent moisturizing properties, helping to hydrate dry and rough skin by restoring the skin's natural barrier. The oil’s antimicrobial properties can also support the management of acne and minor skin infections (16). Additionally, antioxidants, such as vitamin E, help combat free radicals, promote skin elasticity, and reduce the appearance of fine lines (17). However, its comedogenic nature may clog pores in some individuals with oily or sensitive skin, so it’s best suited for dry or normal skin types and should be used in moderation.
References
- https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.1079/cabicompendium.20295
- https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/13/17/2814
- https://www.fediol.eu/data/Risk%20Assessment%20Palm%20Food%20FEDIOL%20Final%20160522.pdf
- https://www.benexia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Smoke-Point_Detailed-Fats-Values.pdf
- https://www.mpevans.co.uk/palm-oil/palm-oil-nutrition/composition-of-palm-oil
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8504498/
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/156482659401500212
- https://mjas.analis.com.my/mjas/v25_n4/pdf/Idayu_25_4_13.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/palm-kernel-oil
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4365303/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/by-the-way-doctor-is-palm-oil-good-for-you
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5837225/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32085610/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.754086/full
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22879097/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2772209/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4976416/
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 81.5g | 49.3g | 146% |
| Vitamin E | 3.81mg | 15.94mg | 81% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 11.4g | 37g | 64% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.6g | 9.3g | 51% |
| Vitamin K | 24.7µg | 8µg | 14% |
| Calories | 862kcal | 884kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Choline | 0.2mg | 0.3mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Palm kernel oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171422/nutrients
- Palm oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171015/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



