Peas vs. Lentils – Nutrition and Health Impact Comparison


Summary
Lentils are significantly denser in nutrients, being richer in protein and carbohydrates due to high amounts of both net carbs and dietary fiber.
Unsurprisingly, lentils also provide more calories than peas.
Peas are richer in vitamins, while lentils are relatively higher in minerals.
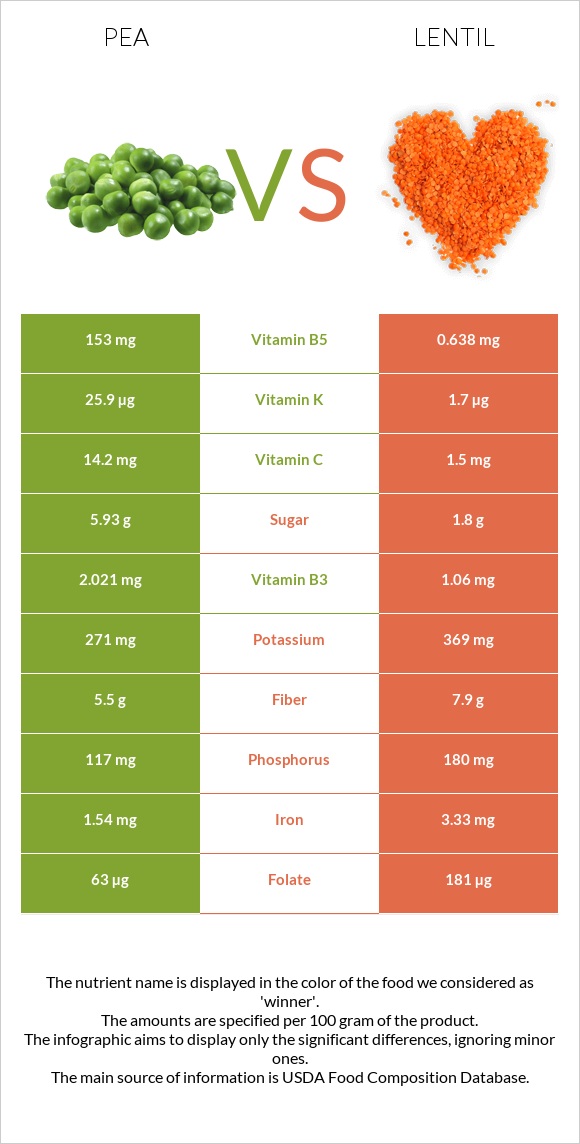
Peas contain 240 times more vitamin B5, 96 times more vitamin A, 27 times more vitamin C, and 15 times more vitamin K, whereas lentils are 3 times richer in vitamin B9 or folate.
Ultimately, the final choice is up to the consumer’s preferences.
Introduction
Since ancient times, legumes have been a staple food in many cultures worldwide. In this article, we will talk about two of the most popular legumes - peas and lentils. We will compare them and see their differences or similarities regarding nutrition and health impact.
Nutritional Content
The nutritional infographics below are presented for 100g servings of boiled and drained green peas and mature lentil seeds without added salt.
However, one average serving size of these legumes is considered one cup, which is equal to 160g for peas and 198g for lentils.
Calories
Lentils are 1.4 times higher in calories than peas. Peas and lentils have 84 and 116 calories per 100g, respectively.
Macronutrients
Lentils are somewhat denser in nutrients overall, consisting of 70% water and 30% nutrients, while peas are made up of 78% water and 22% nutrients.
The main macronutrients in both these legumes are carbohydrates, followed by protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+11.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+68.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+72.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+28.8%
Carbohydrates
Lentils contain 4.5g more carbohydrates compared to peas (20.13g and 15.63g, respectively), including both net carbs and dietary fiber. Lentils are 1.4 times higher in dietary fiber and only 1.2 times higher in net carbs.
Proteins
Legumes are excellent sources of protein. A 100g serving of lentils and peas covers 21% and 13% of the required daily value of this nutrient, respectively.
Lentils contain 1.7 times more protein than peas, providing 9g per 100g, whereas the same serving of peas contains 5.4g.
Both contain essential amino acids such as methionine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine, leucine, histidine, lysine, and valine, which cannot be synthesized in the body and must be consumed with food.
Fats
Both of these foods contain insignificant amounts of fat; however, lentils are slightly higher in fat. In their turn, peas have more saturated fat than lentils, which have more mono- and polyunsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-26.4%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+236.8%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+71.6%
Vitamins
Peas are undoubtedly the winner in this category, being richer in fat-soluble vitamins (vitamin A, vitamin E, and vitamin K), as well as water-soluble vitamins (B-group vitamins, vitamin C).
More exactly, peas contain 240 times more vitamin B5, 96 times more vitamin A, 27 times more vitamin C, and 15 times more vitamin K. Lentils, however, are 3 times richer in vitamin B9 or folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+846.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+27.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+53.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+104.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+90.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+23881.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+21.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1423.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+187.3%
Minerals
Contrastingly, lentils are a better source of minerals, being 2 times richer in iron and overall higher in phosphorus, potassium, and copper.
Instead, peas contain more calcium.
While both of these foods are low in salt, peas are lower in sodium. Peas have 3mg of sodium per 100g, whereas lentils have 2mg.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+42.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+36.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+116.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+45.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+53.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-33.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+47.4%
Glycemic Index
The average glycemic index of green peas based on two studies has been measured to be 36 (1).
Lentils have an even lower average glycemic index of 16, based on 8 studies (1). Canned brown lentils have a glycemic index value of 42.
Glycemic values below 55 are considered to be low.
Health Impact
Peas and lentils are perfect legumes to use as part of a healthy diet. They are not only tasty but also full of health-beneficial qualities.
Cardiovascular Health
The impact of consuming pulse crops (such as lentils and peas) on the prevention of cardiovascular disease by affecting serum lipids and plasma homocysteine levels is still being investigated (2).
On the other hand, according to some studies, consuming a lot of peas can increase the levels of high-density cholesterol, also known as "good cholesterol." Additionally, research has shown that diets that include pulses, such as peas, may help lower blood cholesterol levels (3, 4).
Lentils and lentil-based diets were shown to decrease high blood pressure and large-artery remodeling in experimental animals (4).
Cancer
The American Institute for Cancer Research recommends eating peas and lentils frequently to lower the risk of colorectal cancer due to their high dietary fiber content (5).
Diabetes
Including 190g or 1 cup of legumes, such as lentils and peas, a day was shown to significantly improve glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, and triglyceride levels, as well as reducing blood pressure, heart rate, body weight, and waist circumferences (6). Regular consumption of legumes can be an important behavioral dietary strategy to reduce risk and improve comorbidities of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Digestive Health
When red lentils were added to diets in various amounts, the intestinal microenvironment improved, which has been linked to improvements in intestinal health (7).
Along with the pea seed, pea fiber has also been associated with the modulation of gut microbiota, especially health-beneficial bifidobacteria. Some pea varieties have positive effects on the bioavailability of dietary iron and intestinal gut microbiome and improve brush border membrane functionality (8).
Classification and Varieties
Lentils and peas are both members of the legume or Fabaceae family; however, lentils belong to the Lens genus, while peas come from the Pisum sativum plant.
Some common types of lentils include brown, green, red, and black (Beluga) lentils. The most widely available type is brown with a mild and earthy flavor. Green lentils are larger and firmer with a slightly more peppery flavor. Red lentils also have a mild, nutty flavor.
Peas are usually classified into four groups: garden peas, snow peas, sugar peas, and split peas. Garden peas are also known as sweet or English peas and are the most widely used variety.
Appearance and Use
Lentils are small, lens-shaped legumes that come in various colors, including brown, green, red, and black, depending on the variety.
Lentils are known for their high protein content and are commonly consumed in many cuisines around the world. They are often used in soups, stews, salads, and side dishes. The most common use of lentils includes boiling them.
Green, brown, and black lentils hold their shape well after cooking and are often used in salads and side dishes, while red lentils become mushy when cooked and are good to use in stews, soups, and dals.
Peas are known for their sweet flavor and are consumed in various forms, including fresh, frozen, and canned.
Snow peas are often used in stir-fries and salads. Sugar snap peas can be eaten raw or lightly cooked, while split peas are added to soups, stews, and purees.
References
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://central.bac-lac.gc.caMR52214number720807374
- https://www.jstor.org/stable/25557982
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24063808
- https://www.aicr.org/cancer-prevention/food-facts/dry-beans-and-peas-legumes/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7915747/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6724071/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/leg3.82
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B5 | 153mg | 0.638mg | 3047% |
| Folate | 63µg | 181µg | 30% |
| Iron | 1.54mg | 3.33mg | 22% |
| Vitamin K | 25.9µg | 1.7µg | 20% |
| Vitamin C | 14.2mg | 1.5mg | 14% |
| Fiber | 5.5g | 7.9g | 10% |
| Copper | 0.173mg | 0.251mg | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 117mg | 180mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.259mg | 0.169mg | 8% |
| Protein | 5.36g | 9.02g | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.149mg | 0.073mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.021mg | 1.06mg | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 40µg | 0µg | 4% |
| Potassium | 271mg | 369mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.216mg | 0.178mg | 3% |
| Calories | 84kcal | 116kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 15.63g | 20.13g | 2% |
| Selenium | 1.9µg | 2.8µg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 39mg | 36mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 27mg | 19mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 1.19mg | 1.27mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.525mg | 0.494mg | 1% |
| Choline | 29.7mg | 32.7mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.41g | 1% | |
| Fats | 0.22g | 0.38g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 10.13g | 12.23g | N/A |
| Sugar | 5.93g | 1.8g | N/A |
| Sodium | 3mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.14mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.039g | 0.053g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.019g | 0.064g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.102g | 0.175g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.037mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.201mg | 0.323mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.193mg | 0.39mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.32mg | 0.654mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.314mg | 0.63mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.081mg | 0.077mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.198mg | 0.445mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.232mg | 0.448mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.105mg | 0.254mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Peas - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170420/nutrients
- Lentil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172421/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






