Paprika vs. Cumin — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Paprika is a dried form of pepper, specifically bell peppers, while cumin is the dried seeds of the Cuminum herb.
Although the serving sizes of spices are not large enough to contribute to the daily needs of vitamins and minerals, paprika is still relatively richer in vitamins, while cumin seeds are richer in minerals. Paprika provides 39 times more Vitamin A, 15 times more Vitamin K, and 9 times more Vitamin E. On the other hand, cumin seeds provide 4 times more calcium and 3 times more iron.
Introduction
This article will discuss the main differences in the nutrition of paprika and cumin while also exploring their health impact.
What's the Actual Difference?
Cumin and paprika have different colors and tastes. Firstly, paprika is a dried form of pepper, particularly bell peppers. The spice flavor can therefore range from mild and sweet to extremely hot, depending on the peppers. Paprika has a mild and sweet flavor.
On the other hand, cumin is the dried seeds of the Cuminum herb. It is sold in either ground form or as whole seeds. Cumin has an earthy, spicy, and slightly bitter flavor.
Nutrition
In this section, nutritional differences are explored for paprika and cumin seeds.
The serving sizes for both spices are usually about 0.5g-2g, but depending on the dish, you might add more. One teaspoon of whole cumin seeds and one teaspoon of paprika is around 2 grams.
However, to keep the comparison between the two spices simple, we will sometimes refer to 100-gram servings of each.
Macronutrients and Calories
As can be seen from the macronutrient comparison charts below, carbs are the predominant macronutrient in both spices. Paprika consists of 54% carbs, while cumin consists of 44% carbs.
Given that the serving sizes for both cumin seeds and paprika are very small as they are mostly used as seasonings, the differences in macronutrients are not relevant in the context of the daily recommended amount of nutrients and calories.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+22%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+39.5%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+26%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+72.8%
Calories
Cumin seeds and paprika contain similar amounts of calories.
One teaspoon serving of paprika (2.3 grams) provides around 6-7 calories, while one teaspoon of whole cumin seeds (2.1 grams) provides around 8 calories.
Fats
Cumin seeds contain around 2 times more fat than paprika.
One teaspoon of paprika provides around 0.297 grams of total lipid fat, while one teaspoon of whole cumin seeds provides around 0.468 grams of total lipid fat.
Per 100-gram serving, cumin seeds contain 22.27g of fats, whereas paprika contains 12.89g.
Both contain no cholesterol.
Carbohydrates
The total carbohydrate content in both of these spices is not very different. One teaspoon serving of paprika (2.3 grams) provides 1.24 grams of carbs, while one teaspoon of whole cumin seeds (2.1 grams) provides 0.928 grams.
Per 100-gram serving, cumin seeds contain 44.24g of carbs, of which 10.5g is fiber, and the rest are net carbs.
Paprika contains only 53.99g of net carbs, of which 34.9g is fiber and 19.09g are net carbs.
Vitamins
A single serving of neither of these spices provides significant amounts of vitamins to contribute to your daily needs; however, they still do contain various vitamins that we can discuss here.
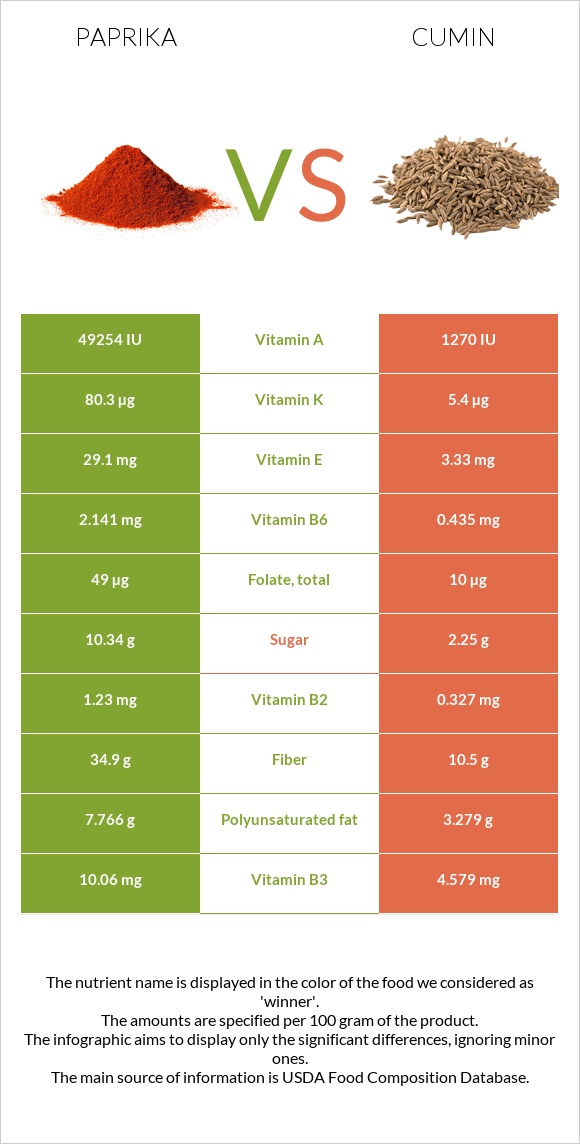
Paprika contains significantly higher amounts of Vitamin E, Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin K, and Vitamin B6 when compared to cumin seeds.
Specifically, paprika contains 39 times more Vitamin A, 15 times more Vitamin K, and 9 times more Vitamin E. On the other hand, cumin seeds contain slightly more amounts of Vitamin B1 and Vitamin C.
Both of these spices completely lack Vitamin D and Vitamin B12. While paprika contains some amounts of Vitamin B5, cumin seeds are completely absent in that vitamin as well.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+3748.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+773.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+276.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+119.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+392.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1387%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+390%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+755.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+90.3%
Minerals
As discussed above, single servings of these spices do not contribute any significant amounts of vitamins or minerals to your daily need; however, we can still discuss their differences.
Cumin seeds provide 4 times more calcium, 3 times more iron, as well as more magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper when compared to paprika.
However, paprika provides slightly less sodium and more potassium and selenium than cumin seeds.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+27.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-59.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+21.2%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+105.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+306.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+213.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+21.6%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+10.9%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+58.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+109.6%
Glycemic Index
The estimated glycemic indexes of cumin and paprika are 0. Both are considered low-GI foods.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of cumin seeds and paprika are -32 and -36.9, respectively, which means paprika has greater potential to alkalize the body.
Health Benefits
Diabetes
Several studies have found that cumin helps to reduce blood glucose levels. In alloxan-induced diabetic rats, cumin supplementation resulted in a significant decrease in blood glucose and an increase in total hemoglobin and glycosylated hemoglobin (1).
Paprika contains capsaicin, a chemical compound first isolated from chili peppers. Capsaicin is used to treat psoriasis and diabetic neuropathy as a topical treatment (2).
Cardiovascular Health
Paprika contains capsaicin, which is responsible for its spiciness. Research suggests that capsaicin may help lower blood pressure, improve blood circulation, and reduce LDL ("bad" cholesterol) levels, all of which are beneficial for cardiovascular health (3, 4).
It’s important to note that similar changes associated with improving lipid profiles were observed with Simvastatin (4).
Additionally, paprika is rich in antioxidants like carotenoids, which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially lowering the risk of atherosclerosis, a main cause of coronary heart disease (5, 6).
On the other hand, cumin contains phytosterols, which may help reduce cholesterol absorption in the gut, thus potentially lowering LDL levels. Cumin also contains antioxidants like flavonoids, which have been associated with cardiovascular benefits such as reducing inflammation and improving blood vessel function (7, 8).
In summary, both paprika and cumin can contribute to cardiovascular health through different mechanisms, including their antioxidant effects and cholesterol management. It's important to consider their overall impact as part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Curcumin is a bioactive compound found in cumin. Curcumin is a potent antioxidant that also has anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin has been shown in studies to inhibit free radical activity while increasing the activity of other antioxidants (9).
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
A compound known as profilin in cumin can cause an allergic reaction. Cumin allergy can also aggravate pollen allergies. Symptoms usually include itching and tingling in the mouth.
Paprika allergy symptoms are typically mild, but severe paprika allergies can result in anaphylaxis, so it is critical to be tested if you have a history of food allergies (10).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12220968/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29083760/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circ.131.suppl_1.p038
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009279717303745
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8156602/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0271531714001171
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25456022/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4039583/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5618098/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30883393/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 21.14mg | 66.36mg | 565% |
| Vitamin A | 2463µg | 64µg | 267% |
| Vitamin E | 29.1mg | 3.33mg | 172% |
| Vitamin B6 | 2.141mg | 0.435mg | 131% |
| Fiber | 34.9g | 10.5g | 98% |
| Manganese | 1.59mg | 3.333mg | 76% |
| Calcium | 229mg | 931mg | 70% |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.23mg | 0.327mg | 69% |
| Vitamin K | 80.3µg | 5.4µg | 62% |
| Vitamin B5 | 2.51mg | 50% | |
| Magnesium | 178mg | 366mg | 45% |
| Vitamin B3 | 10.06mg | 4.579mg | 34% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1.695g | 14.04g | 31% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 7.766g | 3.279g | 30% |
| Phosphorus | 314mg | 499mg | 26% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.33mg | 0.628mg | 25% |
| Copper | 0.713mg | 0.867mg | 17% |
| Fats | 12.89g | 22.27g | 14% |
| Potassium | 2280mg | 1788mg | 14% |
| Folate | 49µg | 10µg | 10% |
| Vitamin C | 0.9mg | 7.7mg | 8% |
| Fructose | 6.71g | 8% | |
| Protein | 14.14g | 17.81g | 7% |
| Calories | 282kcal | 375kcal | 5% |
| Choline | 51.5mg | 24.7mg | 5% |
| Zinc | 4.33mg | 4.8mg | 4% |
| Sodium | 68mg | 168mg | 4% |
| Carbs | 53.99g | 44.24g | 3% |
| Saturated fat | 2.14g | 1.535g | 3% |
| Selenium | 6.3µg | 5.2µg | 2% |
| Net carbs | 19.09g | 33.74g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.34g | 2.25g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.07mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.49mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.57mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.92mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.69mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.2mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.61mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.75mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.25mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.453g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +136.8% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -28.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +728.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Paprika - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171329/nutrients
- Cumin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170923/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






