Cumin vs. Garlic powder — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Garlic powder is made from dehydrated garlic, while cumin seeds are the dried seeds of the Cuminum herb. Given that the serving sizes for both are extremely small, any nutritional differences observed are not important when placed in the context of the daily need for macronutrients, minerals, or vitamins. Nevertheless, per the same serving, cumin seeds provide more fat, while garlic powder contains more carbs.
Moreover, cumin seeds contain more vitamins B1, B2, B3, A, and E, while garlic powder provides higher amounts of Vitamin B6 and folate. When it comes to minerals, cumin seeds generally provide more of them as well when compared to garlic powder. Particularly, they provide 12 times more calcium and iron and 5 times more magnesium.
Introduction
In this article, we will discuss the main differences between garlic powder and cumin seeds, focusing on their nutritional and health impact.
What's the Actual Difference?
Garlic powder is a spice made from dehydrated garlic used in cooking to add flavor, while cumin is dried seeds of the Cuminum herb.
Cumin seeds are usually brown in color, while garlic powder is white-yellow.
Cumin is earthy, spicy, and slightly bitter spice. On the other hand, garlic powder tastes sweeter and less assertive than fresh garlic but lacks the caramelly undertones of roasted or sautéed garlic.
Nutrition
The nutritional differences here are depicted for garlic powder and cumin seeds.
The serving sizes for both spices are usually about 0.5g, but depending on the dish, you might add more. One teaspoon of whole cumin seeds is about 2.1 grams, while one teaspoon of garlic powder is about 3.1 grams.
However, to keep the comparison between the two spices simple, we will sometimes refer to 100-gram servings of each.
Macronutrients and Calories
As can be seen from the macronutrient comparison chats below, cumin consists of 44% carbs, 22% fats, and 18% protein. On the other hand, carbs make up about 73% of the entire macronutrient composition of garlic powder. Protein amount also makes up a similar percentage in garlic powder as it did in cumin.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+2950.7%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+25%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+115.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+64.4%
Calories
Given that cumin seeds and garlic powder are served in small quantities, their calories are not significant.
One teaspoon of garlic powder (3.1 grams) provides around 10 calories, while one teaspoon of cumin seeds (2.1 grams) provides around 8 calories. Of course, if we consider 100-gram servings of both, the calorie count would be very high – 375 calories for cumin and 331 calories for garlic powder.
Fats
Cumin seeds contain around 30 times more fat than garlic powder; however, given their small serving sizes, none of these fats are significant fat contributors to your diet.
One teaspoon of garlic powder (3.1 grams) provides around 0.468 grams of total lipid fat, while one teaspoon of cumin seeds (2.1 grams) provides around 0.023 grams. Again, none of these spices are significant sources of fat, given their small serving sizes.
Carbohydrates
Garlic powder provides more carbs than cumin seeds.
Cumin seeds have 0.928g of carbs per teaspoon, while garlic powder contains 2.25g of carbs. Per 100-gram serving, cumin seeds have 44.24g of carbs, while garlic powder contains 72.73g.
Fiber
One teaspoon of garlic powder (3.1 grams) provides around 0.279 grams of fiber, while one teaspoon of cumin seeds (2.1 grams) provides around 0.22 grams.
Per 100-gram serving, cumin has 10.5g of fiber and 33.74g of net carbs, while garlic powder has 9g of fiber and 63.73g of net carbs.
Both garlic powder and cumin have no cholesterol.
Vitamins
A single serving of neither garlic powder nor cumin seeds provides significant amounts of vitamins to contribute to your daily needs; however, they still do contain various vitamins that we can discuss here.
Cumin seeds contain more Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin A, and Vitamin E. On the other hand, garlic powder provides higher amounts of Vitamin B6 and folate.
The amount of Vitamin B3 is around 6 times higher in cumin seeds, while the amount of Vitamin B6 is around 4 times higher in garlic powder.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+541.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+397%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+44.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+131.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+475.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1250%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+280.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+370%
Minerals
Just like the vitamin content, the amounts of minerals per single serving for both cumin seeds and garlic powder are not significant enough to contribute to the daily need; however, we can still compare the content.
Cumin seeds provide 12 times more calcium and iron and 5 times more magnesium than garlic powder. They are also high in phosphorus, zinc, copper, and potassium. On the other hand, garlic powder provides more selenium and slightly less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+375.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1078.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+49.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1074.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+62.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+60.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+20.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+240.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-64.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+359.6%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index is a rating system used for foods containing carbohydrates. As both cumin and garlic powder contain very few carbohydrates, their glycemic index is low, which means their consumption has minimal effect on blood sugar levels.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of cumin and garlic powder are -32 and -4.7, respectively, which means cumin has greater potential to alkalize the body.
Health Benefits
Diabetes
Research indicates that cumin can help reduce blood glucose levels. Cumin supplementation resulted in a significant decrease in blood glucose levels and increased total and glycosylated hemoglobin in alloxan-induced diabetic rats (1).
According to a 2006 study, raw garlic may help lower blood sugar levels and the risk of atherosclerosis (2). Diabetes increases a person's risk of atherosclerosis-related inflammation, so this is of particular interest to researchers.
Cancer
Garlic powder's bioactive compounds and antioxidants may reduce oxidative stress, relieve inflammation, and prevent cellular mutation, which are the main factors that lead to cancer (3).
According to research, cumin's chemopreventive effects are linked to its ability to modulate carcinogen metabolism. Several mouse studies show that cumin significantly inhibits the growth of stomach and cervical tumors (4).
Cardiovascular Health
Both cumin and garlic powder have antioxidant properties, but garlic powder's allicin is particularly well-studied for its cardiovascular benefits (5).
Studies have shown that both may help reduce arterial blood pressure, which is important in reducing cardiovascular risk (6, 7).
Studies have also shown that garlic and cumin powders may help reduce LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels in the blood and decrease the risk of atherosclerosis, the main cause of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction (8, 9, 10).
Moreover, studies have revealed that women's estrogen levels significantly decrease during menopause, increasing their susceptibility to heart disease. Cumin extract has shown hypolipidemic properties, indicating potential benefits for managing cardiovascular risk in this group (11).
To sum up, incorporating either into your diet can be beneficial for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Allicin is the most biologically active sulfur-containing compound found in garlic, which can cause allergic reactions. A skin rash and asthma are common symptoms of garlic allergies. Other symptoms include hives, itching, and skin redness (12).
Profilin, a compound found in cumin, can cause an allergic reaction. Individuals who are sensitive to profilin may also be sensitive to coriander. Cumin allergies can exacerbate pollen allergies. Itching, swelling, and tingling in the mouth are common symptoms (13).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12220968/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5642189/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22480662/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1207/s15327914nc4702_10
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9409331/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321394949
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34262716/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26764327/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25489404/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25456022/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2841243/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4954633/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30883393/
Infographic
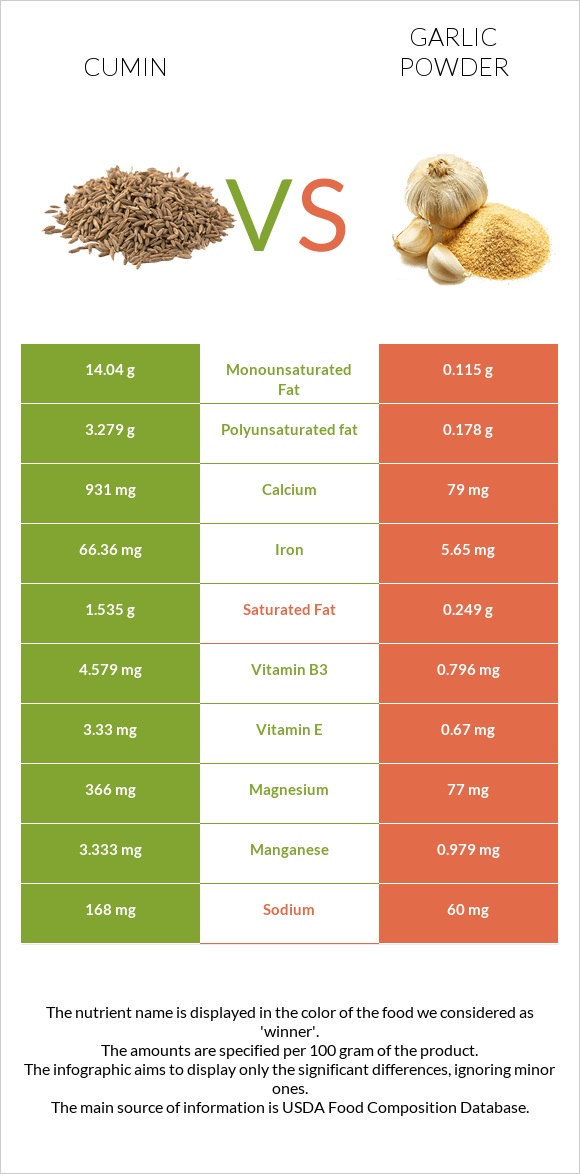
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 66.36mg | 5.65mg | 759% |
| Manganese | 3.333mg | 0.979mg | 102% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.435mg | 1.654mg | 94% |
| Calcium | 931mg | 79mg | 85% |
| Magnesium | 366mg | 77mg | 69% |
| Copper | 0.867mg | 0.533mg | 37% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 14.04g | 0.115g | 35% |
| Selenium | 5.2µg | 23.9µg | 34% |
| Fats | 22.27g | 0.73g | 33% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.579mg | 0.796mg | 24% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 3.279g | 0.178g | 21% |
| Potassium | 1788mg | 1193mg | 18% |
| Vitamin E | 3.33mg | 0.67mg | 18% |
| Zinc | 4.8mg | 2.99mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.628mg | 0.435mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.743mg | 15% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.327mg | 0.141mg | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 499mg | 414mg | 12% |
| Carbs | 44.24g | 72.73g | 9% |
| Folate | 10µg | 47µg | 9% |
| Choline | 24.7mg | 67.5mg | 8% |
| Vitamin C | 7.7mg | 1.2mg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 64µg | 0µg | 7% |
| Fiber | 10.5g | 9g | 6% |
| Saturated fat | 1.535g | 0.249g | 6% |
| Sodium | 168mg | 60mg | 5% |
| Vitamin K | 5.4µg | 0.4µg | 4% |
| Protein | 17.81g | 16.55g | 3% |
| Calories | 375kcal | 331kcal | 2% |
| Net carbs | 33.74g | 63.73g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.25g | 2.43g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.121mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.374mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.414mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.728mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.768mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.111mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.525mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.667mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.263mg | 0% | |
| Fructose | 0.31g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.012g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.022g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +12108.7% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1742.1% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -83.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cumin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170923/nutrients
- Garlic powder - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171325/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


