Summer Squash vs. Pumpkin - What Are Their Differences?


Summary
Summer squash contains twice as much fiber and is richer in manganese, magnesium, vitamins B2, B6, folate, and vitamin C. In comparison, pumpkin is twice as high in carbs and is richer in iron, potassium, copper, vitamin A, beta-carotene, and vitamin E. Pumpkin is richer in beta carotene. They both provide numerous positive health impacts.
Introduction
Summer squash and pumpkin, are they different than one another? Well, in short, yes, they are.
Their nutritional content is different, and thus, their health impacts. In addition, they are different for culinary usage, and they can't be used interchangeably since they can affect the flavor profile of the dish.
This article will discuss the differences between summer squash and pumpkin regarding their nutritional and health impacts.
General Differences
Pumpkins are more orange in color and bigger in size. In comparison, summer squash is a yellow zucchini. Their flavor profile is different and is peculiar for each. Pumpkins are more aromatic and flavorful.
Their culinary uses are versatile, and both should be part of our diets since they provide numerous positive health impacts.
You can read about summer squash vs. winter squash in this article.
Nutritional Content Comparison
This section will compare 100g of each in raw form.
Calories
They are both very low in calories, and the difference is insignificant.
Fats and Proteins
Their fat and protein contents are negligible.
Carbs and Fiber
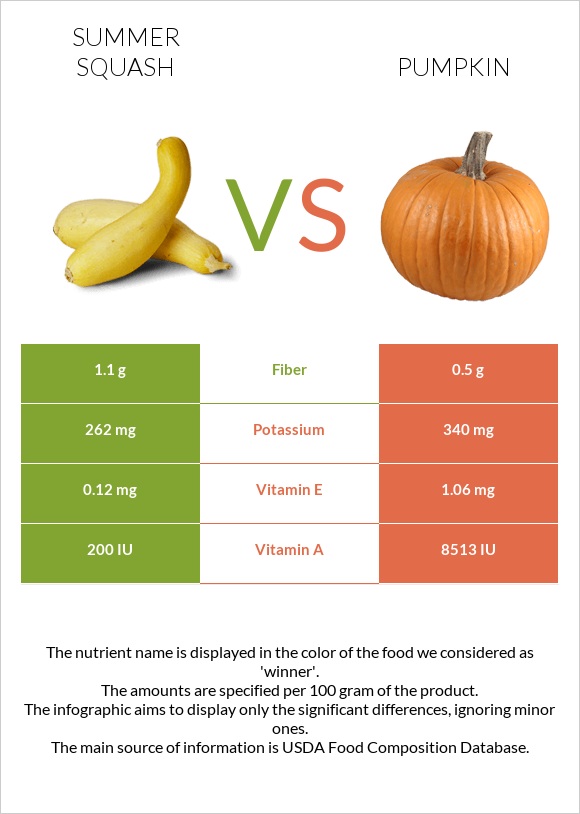
Pumpkins contain nearly 2 times more carbs compared to summer squash.
However, Summer squash contains 2 times more fiber than pumpkins.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+68.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+157.1%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+46.3%
Vitamins
Summer squash is richer in vitamins B2, B6, folate, and C. In comparison, pumpkin is richer in vitamins A, K, B1, beta-carotene, and vitamin E.
It is important to mention that beta-carotene is converted into vitamin A in our bodies.
One of the main points to consider is vitamin C in summer squash. During heating and cooking, vitamin C gets denatured since it is heat-labile, thus decreasing its bioavailability.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+261.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+54.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+82.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+17.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+395.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+275%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+222.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+2780%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+566.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+29.7%
Minerals
Summer squash is richer in manganese and magnesium. In comparison, pumpkin is richer in iron, potassium, and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+88.9%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+13.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+26.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+26.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+96.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+62.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+78.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Health Impacts
We often hear people say, "Eat the rainbow". This means eating different types of vegetables and fruits during the day and each season. Pumpkins and summer squash are mostly used during the fall season. Ever wondered why these orange/yellow fruits are one of the top foods consumed during these times?
Pumpkins and summer squash have a rich content of zeaxanthin, xanthophylls, lutein, beta-carotene, antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, and flavonoids such as catechin and kaempferol.
Pumpkins and summer squash contain these bioactive compounds. Some can be higher in pumpkins, and others higher in summer squash. In addition, the amounts depend on how they are grown, how they are stored, and how they are cooked. Overall, both can be said to have a similarly positive effect on our cardiovascular, immune, and eye health.
The antioxidants present in them reduce risks of carcinogenesis (1)(2)(3).
You can read about pumpkin vs. winter squash in this article.
Some of the data indicate that pumpkins are higher in these compounds. However, the combined cumulative effect of all of them present in both gives the most positive health benefits.
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 10µg | 288µg | 31% |
| Vitamin C | 17mg | 4.7mg | 14% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.218mg | 0.044mg | 13% |
| Vitamin E | 0.12mg | 0.8mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.142mg | 0.078mg | 5% |
| Folate | 29µg | 9µg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.051mg | 0.091mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.175mg | 0.089mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.35mg | 0.57mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 17mg | 9mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 3µg | 0.8µg | 2% |
| Protein | 1.21g | 0.72g | 1% |
| Carbs | 3.35g | 4.9g | 1% |
| Potassium | 262mg | 230mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.29mg | 0.23mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 38mg | 30mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.048mg | 0.031mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.155mg | 0.201mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.089g | 0.004g | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.95g | 1% | |
| Calories | 16kcal | 20kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.18g | 0.07g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2.25g | 3.8g | N/A |
| Calcium | 15mg | 15mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.2g | 2.08g | N/A |
| Fiber | 1.1g | 1.1g | 0% |
| Sodium | 2mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0.2µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.487mg | 0.413mg | 0% |
| Choline | 6.7mg | 6.2mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.044g | 0.037g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.016g | 0.009g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.011mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.028mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.042mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.069mg | 0.034mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.065mg | 0.039mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.017mg | 0.008mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.041mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.053mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.025mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +77.8% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +2125% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -15.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Summer squash - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170487/nutrients
- Pumpkin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168449/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



