Turmeric vs. Ginger — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Turmeric contains 3.9 times more calories than ginger. Turmeric has 5.3 times the protein content of ginger. Both turmeric and ginger have tiny amounts of fat. Both turmeric and ginger have no cholesterol.
The amount of carbs in turmeric is 3.7 times higher than in ginger. Turmeric contains 11.35 times more fiber compared to ginger. The estimated glycemic index of turmeric is 0, whereas the GI of ginger is 10.
Turmeric contains a higher concentration of minerals and vitamins compared to ginger.
Introduction
Both turmeric and ginger belong to the Zingiberaceae family.
Turmeric has been used for approximately 4000 years, dating back to the Vedic civilization in India, where it was utilized as a culinary spice and had religious importance. Because of its bright yellow color, turmeric is sometimes known as "Indian saffron."
Ginger's modern name is derived from the Middle English word gingivere, although its origins stretch back over 3000 years to the Sanskrit term srngaveram, which means "horn root" based on its look. Ginger, however, does not grow in the wild, and its exact origins are unknown.
India grows and consumes most of the world's turmeric and ginger. Indian turmeric is regarded as the best in the world due to its natural properties and high amount of the essential bioactive component curcumin.
This article will discuss the main differences in the nutrition of turmeric and ginger, focusing on their health impacts.
Appearance and Use
Turmeric has a golden yellow color and a bitter taste with a peppery flavor, whereas ginger is warmly spicy and has a light brown and pale yellow color.
The rhizome, which is the horizontal stem from which the roots grow, is the most commonly consumed part of ginger. Ketones in ginger, particularly gingerols, that appear to be its principal component and have been studied in many health-related scientific studies, contribute to its pungent scent.
Unlike turmeric, there are fresh, dried, pickled, preserved, crystallized, candied, powdered, and pulverized forms of ginger.
Turmeric and ginger are used in cooking, cosmetics, and medicine.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are described for 100-gram servings of turmeric (ground) and raw ginger root.
You can find nutritional infographics at the bottom of this page that visually show the differences between turmeric and ginger.
Calories
Turmeric contains 3.9 times more calories than ginger. Turmeric has 312 calories per 100g, whereas ginger contains 80 calories per 100g. However, people usually consume them in tiny amounts, so calories don't matter much.
Protein
Turmeric has 5.3 times the protein (including essential amino acids) content of ginger (9.68g against 1.82g per 100g, respectively).
Fats
Both turmeric and ginger have tiny amounts of fat. Turmeric contains 3.25g of fat per 100g, whereas ginger provides only 0.75g of fat. Both turmeric and ginger have no cholesterol.
Carbs
The amount of carbs in turmeric is 3.7 times higher than in ginger. Turmeric has 67.14g of carbs per 100g, whereas ginger has 17.77g of carbs per 100g.
Turmeric contains 11.35 times more fiber compared to ginger (22.7g and 2g per 100g, respectively).
Glycemic Index
The estimated glycemic index of turmeric is 0, whereas the GI of ginger is 10. However, both are considered low GI foods.
Minerals
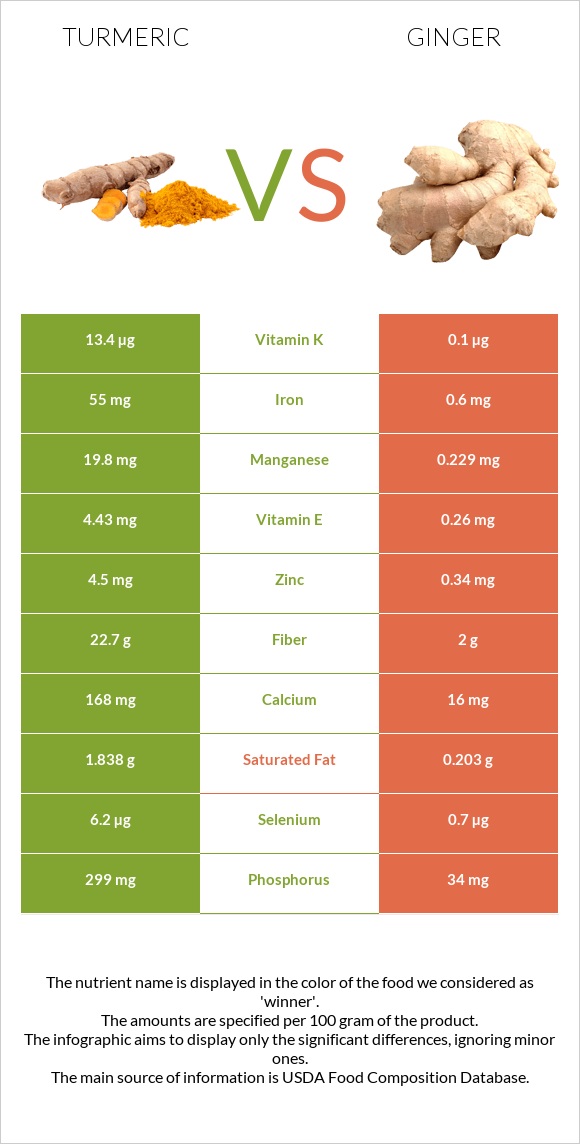
Turmeric contains a higher concentration of minerals. It has more calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc, copper, manganese, and selenium compared to ginger.
Iron is 90 times higher in turmeric than ginger. It also falls within the top 2% of foods as a source of iron and can fully meet your daily iron needs.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+383.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+950%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+401.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+9066.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+475.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+1223.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+779.4%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+8546.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+785.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-51.9%
Vitamins
Turmeric contains a significantly higher amount of vitamins compared to ginger. It provides more vitamin E, vitamin K (it’s 130 times higher in turmeric than in ginger), and B vitamins such as B1, B2, B3, B5, and B9. Ginger is high in vitamin C (it contains 7 times more vitamin C compared to turmeric) and vitamin B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1603.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+132%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+341.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+80%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+167%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+13300%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+81.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+614.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+49.5%
Health impacts
Cardiovascular Health
Studies suggest that taking turmeric and ginger over extended periods of time may lower systolic blood pressure. However, further studies are needed to identify the mechanisms of action and confirm these findings. It should be noted that, unlike turmeric, ginger has diuretic effects, which also contribute to the reduction of blood pressure (1.2).
As mentioned above, the essential bioactive component of turmeric is curcumin, and the essential bioactive component of ginger is gingerol. Research has found that curcumin and gingerol may lower LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in the blood. This effect is important for preventing atherosclerosis. It’s also important for people with coronary artery disease and for people who have had a myocardial infarction (3.4).
Salicylates, which are present in ginger and turmeric, allow them to mimic some of the antiplatelet actions of aspirin and other cardiovascular drugs (5).
They also have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which may prevent atherosclerotic plaque formation due to a variety of mechanisms such as inhibition of LDL oxidation, reduction of generated reactive oxygen species, improvement of endothelial dysfunction, vasodilation, and others (5.6.7).
Statin therapy is known to impair liver function. The benefits of using statins in combination with other lipid-altering medications include an increased lipid-lowering effect, a lowered statin dosage, and a lower risk of side effects. In this investigation, it was shown that, compared to treatment with AT alone, the combination of ginger extract and Atorvastatin (AT) significantly reduced AT-induced hepatic alterations and increased total AT efficacy in decreasing cholesterol (8). This kind of study has not been done with turmeric.
Diabetes mellitus
Both of these products have beneficial effects on people with diabetes mellitus.
Most of the major symptoms of diabetes, such as insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and pancreatic islet apoptosis and necrosis, may be positively impacted by curcumin, so turmeric extract may help stabilize blood glucose levels and make diabetes more manageable. Additionally, diabetic nephropathy, microangiopathy, and retinopathy are some of the harmful effects of diabetes, and curcumin may help with their treatment (9).
This study of 41 people with type 2 diabetes found that consuming 2 grams of ginger powder per day reduced fasting blood sugar by 12% (10).
Cancer
Ginger and turmeric derivatives have important antiproliferative, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory properties, whether they are isolated chemicals or extracts (11.12).
Curcumin in turmeric has been shown in vitro and in animal studies to inhibit cancer cell development. It can promote cancer cell death and reduce angiogenesis. In addition, curcumin is a desirable therapeutic development prospect since it can only kill tumor cells and not healthy cells (12).
Brain Function
According to animal studies, ginger's antioxidants and bioactive compounds can inhibit inflammatory responses in the brain (13).
There is also some evidence that ginger can directly improve brain function. Daily doses of the ginger extract improved reaction time and working memory in a 2012 study of healthy middle-aged women (14).
According to a UCLA study, curcumin may aid macrophages in removing the amyloid plaques linked to Alzheimer's disease, making turmeric a potentially effective treatment for the disease (15).
Digestive Health
Due to its ability to increase bile secretion, curcumin is not suggested for those with biliary tract obstruction. Additionally, those who have gallstones, obstructive jaundice, or acute biliary colic should avoid it. Gallbladder contractions in healthy individuals have been shown to increase with a 20–40 mg daily curcumin dose (15). This effect is unknown for ginger.
Allergy
Ginger can alleviate rhinitis symptoms because of its anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties (16). These effects are also characteristic of turmeric (17).
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1043661819301252
- https://journals.lww.com/cardiovascularpharm/Fulltext/2005/01000/Ginger_Lowers_Blood_Pressure_Through_Blockade_of.13.aspx
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29020971/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464622002444
- https://www.indianjournals.com/ijor.aspx?target=ijor:ijar2&volume=50&issue=2&article=001
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167527307016853
- https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/9/8/301
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0944711310001406
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3857752/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4277626/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S027869150600322X
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2758121/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3253463/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4211852/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781139/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0955286315002260
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mnfr.200700293
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 19.8mg | 0.229mg | 851% |
| Iron | 55mg | 0.6mg | 680% |
| Copper | 1.3mg | 0.226mg | 119% |
| Fiber | 22.7g | 2g | 83% |
| Potassium | 2080mg | 415mg | 49% |
| Magnesium | 208mg | 43mg | 39% |
| Zinc | 4.5mg | 0.34mg | 38% |
| Phosphorus | 299mg | 34mg | 38% |
| Vitamin E | 4.43mg | 0.26mg | 28% |
| Protein | 9.68g | 1.82g | 16% |
| Carbs | 67.14g | 17.77g | 16% |
| Calcium | 168mg | 16mg | 15% |
| Calories | 312kcal | 80kcal | 12% |
| Vitamin K | 13.4µg | 0.1µg | 11% |
| Selenium | 6.2µg | 0.7µg | 10% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.15mg | 0.034mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.542mg | 0.203mg | 7% |
| Saturated fat | 1.838g | 0.203g | 7% |
| Vitamin C | 0.7mg | 5mg | 5% |
| Fats | 3.25g | 0.75g | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.35mg | 0.75mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.107mg | 0.16mg | 4% |
| Choline | 49.2mg | 28.8mg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.756g | 0.154g | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.058mg | 0.025mg | 3% |
| Folate | 20µg | 11µg | 2% |
| Sodium | 27mg | 13mg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.449g | 0.154g | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.45g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 44.44g | 15.77g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.21g | 1.7g | N/A |
| Trans fat | 0.056g | 0g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.17mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.33mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.47mg | 0.051mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.81mg | 0.074mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.38mg | 0.057mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.14mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.53mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.66mg | 0.073mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.15mg | 0.03mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.081g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +431.9% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +333.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +277.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +819.5% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +513.9% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +191.6% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +390.9% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -89% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Turmeric - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172231/nutrients
- Ginger - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169231/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.