Banana vs Avocado Nutrition & Health Comparison — Potassium, Fats, & More


Summary
Avocados are significantly higher in calories, fats, predominantly monounsaturated fatty acids, and dietary fiber, whereas bananas are much higher in carbs. Avocados are richer in most vitamins and minerals, especially vitamins K, E, B5, B9 (folate), and copper. Conversely, bananas are richer in vitamin B6, manganese, and selenium and lower in sodium.
Introduction
Avocados are fruits, and bananas are classified both as fruits and vegetables. These two products are different in many ways; nutrition, appearance, and taste. Nevertheless, they still have certain similarities; they are incredibly healthy, cheap, and tasty.
Varieties
Bananas are known as fruits and vegetables as they belong to the Musa genus (Musa acuminate) (1). Avocados (Persea Americana) belong to the Persea genus and are a member of the flowering plant species (2). The most common banana species are Cavendish Bananas and Lady's Finger Bananas. All avocados are traced to either Guatemalan, Mexican, or West Indian origin.
Nutrition
Nutritionally, these two fruits are different. Avocados are significantly higher in calories, fats, and dietary fiber, whereas bananas are much higher in carbs.
One cup of bananas and avocados weigh around 150 grams; however, we will compare 100 grams of each fruit.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+167.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+83.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+4342.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+90.4%
Calories
Overall, avocados provide almost 2 times more calories: avocados provide 160 calories, whereas bananas provide 89.
Proteins
The fruits are not particularly rich in protein: avocados contain 2g of protein, whereas bananas contain 1g.
Fats
Unlike bananas, which contain negligible amounts of fats, avocados are high in fats, containing 14.66g, 70% of which are monounsaturated fatty acids.
The remaining fatty acids are polyunsaturated and saturated, with a slightly higher content of saturated fats. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are considered healthy fats; they are also linked to greater absorption of carotenoids, enhancing their health-promoting potential (3).
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-94.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+30521.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+2387.7%
Carbohydrates
Bananas are almost 2.7 times higher in total carbs than avocados. Bananas contain 22.84g of carbs, 11% of which are dietary fiber, while avocados contain 8.53g of carbs, 78.5% of which are dietary fiber.
Banana carbs are mostly starch (5.38g), glucose (4.98g), fructose (4.85g), and sucrose (2.39g).
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+4790.9%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+3883.3%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+1245.9%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+3941.7%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Contains
more
GalactoseGalactose
+∞%
Vitamins
Avocados are a better vitamin source than bananas; they are richer in B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
Avocados are 42 times richer in vitamin K, 21 times richer in vitamin E, and 4 times richer in vitamins B5 and B9 (folate).
Bananas contain some amounts of B-complex vitamins but are rich only in vitamin B6. Bananas are also very low in fat-soluble vitamins A, E, and K.
Both bananas and avocados are naturally absent in vitamin D and vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+42.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+14.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+133.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1970%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+116.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+78.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+161.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+315.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+4100%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+305%
Minerals
Avocados are 2.4 times richer in copper. Avocados are also higher in potassium, iron, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, and choline.
Bananas are richer in manganese and selenium and lower in sodium.
Both fruits are naturally very low in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-85.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+90.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+150%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+140%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+35.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+111.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+143.6%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+326.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+136.4%
Glycemic Index & Load
Bananas and avocados are considered low-glycemic index (GI) fruits.
Bananas have a low glycemic index of 48 and a medium glycemic load of 18. Comparably, avocados have a low glycemic index of 40 and a low glycemic load of 1.
Insulin Index
The insulin index of bananas is 81, whereas the insulin index of avocados is 6.
The insulin index shows how much a food increases blood insulin levels in the first 2 hours after consumption. You can visit our Glycemic Index vs. Insulin Index page to learn more.
Acidity
Bananas have a pH value ranging from 4.50 to 5.20, whereas avocados have a pH value ranging from 6.27 to 6.58 (4).
Another way of looking at their acidity is by calculating their PRAL (Potential Renal Acid Load) values. The PRAL values of avocados and bananas are -8.2 and -6.9, respectively, making avocados more alkaline or base-producing.
Diets & Weight Loss
Avocados are preferred during high-protein, high-fiber, and low-carb diets, while bananas are preferred during low-fat and low-glycemic-index diets.
Banana and avocado milks can be consumed as a milk alternative in vegan and vegetarian diets.
Avocados and bananas won’t directly lead to weight loss, but they may help you reduce your total food intake by making you feel full longer by delaying stomach emptying. Avocados may be more satiating than bananas, as they are much higher in dietary fiber and fats (5).
Health Impact: Benefits & Risks
These fruits are incredibly healthy. They are rich in nutrients with anti-cancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Cardiovascular Health
The blood pressure-lowering effect of avocados and bananas may have been attributed to their high content of potassium, which is also important for the regulation of the heartbeat, especially for people with arrhythmias and heart failure (6).
In addition, avocado oil mimics the effects of losartan as an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, which is important for people with high blood pressure as it lowers blood pressure. According to a study, banana consumption in pregnant women may decrease blood pressure. Still, it should be noted that norepinephrine and dopamine, which are present in the ripe peel and pulp of bananas, may elevate blood pressure (7, 8, 9). To fully understand this result, more research is necessary.
Gastrointestinal Health
Both avocados and bananas are generally safe for people with IBD (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis) and can be added to the flare-up diet (10).
In terms of IBS, the results are inconsistent. Bananas and avocados may cause symptoms for some individuals with IBS, while others may tolerate them without issue. However, small portions of avocados and unripe bananas are less likely to cause bloating and gas.
During diarrhea, the body loses water and minerals. Bananas and avocados may restore lost potassium caused by diarrhea of any cause (10).
Eye Health
Avocados and bananas contain vitamin A and the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin, which are crucial for healthy vision.
Avocados may be superior in maintaining eye health as you age, as they provide 2 times more vitamin A and 6.5 times more lutein and zeaxanthin.
Lutein and zeaxanthin have antioxidant properties, prevent oxidative damage, filter blue light, and may delay the progression of age-related macular degeneration and prevent cataracts (11, 12).
Vitamin A is required for the proper functioning of the retina and cornea. It is also important for proper immune function and T-mediated inflammation (13).
Cancer
Like most fruits and vegetables, avocados and bananas have anti-cancer properties due to their phytochemical and nutritional qualities.
For example, avocados are rich in carotenoids, plant pigments with an antioxidant activity that protect the cells from damage caused by free radicals. Carotenoids may activate apoptosis in some cancer cells as well (14, 15).
Bananas are also studied for their anti-cancer effects. Various bioactive banana components are shown to have antiproliferative, apoptotic, anti-invasive, and antiangiogenic effects (16).
Anti-aging Effects of Avocados
Did you know eating fruit helps to keep yourself looking youthful for as long as possible? And here we have an absolute favorite. Avocados are rich in many nutrients promoting skin health, such as monounsaturated fatty acids, the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin, polyphenols, vitamins A, E, B3 (niacin), and B9 (folate).
A study's findings suggest daily avocado consumption may protect the skin from harmful blue lights and enhance the skin's elasticity and firmness (12, 17).
Allergy
Allergic reactions to bananas are avocados may be present in people with pollen and latex allergies. The symptoms may vary from oral allergy syndrome to anaphylaxis (18).
Allergic reactions to avocados may also be caused due to their high histamine content (19). The symptoms may manifest as oral allergy syndrome, causing lip, mouth, and throat itching, and gastrointestinal symptoms, such as bloating, cramps, and diarrhea.
Sources
- https://www.scirp.org/html/13-2700276_16366.htm
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-011-1584-1_2
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34897461/
- https://www.clemson.edu/extension/food/food2market/documents/ph_of_common_foods.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31035472/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23425010/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29753173/
- https://publications.inschool.id/index.php/icash/article/view/918
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05212
- https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/sites/default/files/legacy/assets/pdfs/diet-nutrition-2013.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8874683/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19168000/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9339908/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1018364718315714
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0955286304001597
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8294041/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jocd.14717
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10651781/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8469513/
Infographic
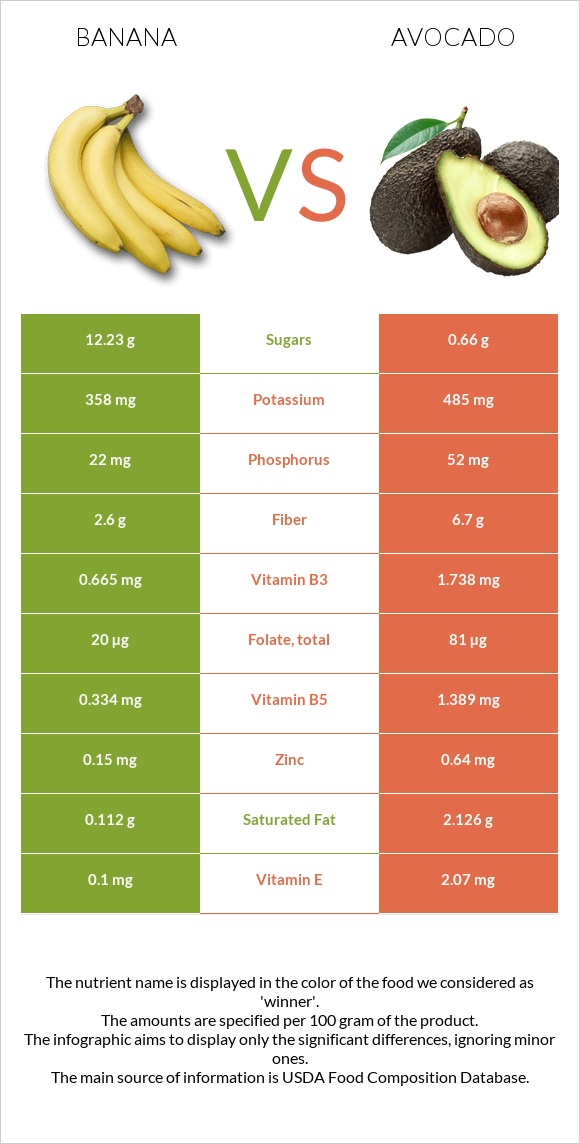
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.032g | 9.799g | 24% |
| Fats | 0.33g | 14.66g | 22% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.334mg | 1.389mg | 21% |
| Vitamin K | 0.5µg | 21µg | 17% |
| Fiber | 2.6g | 6.7g | 16% |
| Folate | 20µg | 81µg | 15% |
| Vitamin E | 0.1mg | 2.07mg | 13% |
| Copper | 0.078mg | 0.19mg | 12% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.073g | 1.816g | 12% |
| Saturated fat | 0.112g | 2.126g | 9% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.367mg | 0.257mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.665mg | 1.738mg | 7% |
| Manganese | 0.27mg | 0.142mg | 6% |
| Fructose | 4.85g | 0.12g | 6% |
| Carbs | 22.84g | 8.53g | 5% |
| Calories | 89kcal | 160kcal | 4% |
| Potassium | 358mg | 485mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.26mg | 0.55mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.15mg | 0.64mg | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 22mg | 52mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.073mg | 0.13mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.031mg | 0.067mg | 3% |
| Protein | 1.09g | 2g | 2% |
| Starch | 5.38g | 0.11g | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 8.7mg | 10mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 12mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 1µg | 0.4µg | 1% |
| Choline | 9.8mg | 14.2mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 20.24g | 1.83g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 27mg | 29mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 12.23g | 0.66g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 7mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 7µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.009mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.028mg | 0.073mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.028mg | 0.084mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.068mg | 0.143mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.05mg | 0.132mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.008mg | 0.038mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.049mg | 0.097mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.047mg | 0.107mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.077mg | 0.049mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.111g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.015g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Banana - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173944/nutrients
- Avocado - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171705/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.