Banana vs. Potato — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Introduction
The main goal of this article is to compare bananas and potatoes in terms of nutrition. These products are different in many ways; nutrition, taste, and appearance. However, they both are very healthy.
Varieties
Bananas belong to the Musa genus and are categorized as fruits. They have many different varieties. The most common species are Cavendish Bananas and Lady's Finger Bananas.
On the other hand, potatoes are considered to be vegetables. They are part of the Solanaceae family, the Solanum genus. The Solanaceae family of flowering plants also includes tomatoes, chili, and bell peppers.
The most known species are Classic Russet and Bannock Russet potatoes (1, 2).
Uses
Bananas and potatoes are some of the most popularly consumed foods in the world.
Potatoes are grown around the world and have become a staple crop in many countries. They are mainly used boiled, baked, roasted, and fried in a massive range of different dishes.
Bananas can be eaten both raw and cooked. They are used in various dishes, salads, muffins, smoothies, etc.
Nutrition
Bananas and potatoes have very different nutritional profiles; the cooking methods may also alter the composition. We will be comparing the nutritional profiles of raw bananas and baked, unsalted potatoes.
In this section, we will explore their macronutrient composition, as well as compare their mineral and vitamin contents.
Macronutrients and Calories
The NLEA serving of cooked potato is 148 grams, while for bananas, it is a bit lower and equals 126 grams.
In order to make the comparison easier, we will be comparing a 100-gram serving of each.
As can be seen from the macronutrient composition charts below, their percentage distributions of the macronutrients are surprisingly similar. Both potatoes and bananas consist of 75% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+153.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+129.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+60.2%
Calories
Potatoes and bananas contain similar amounts of calories.
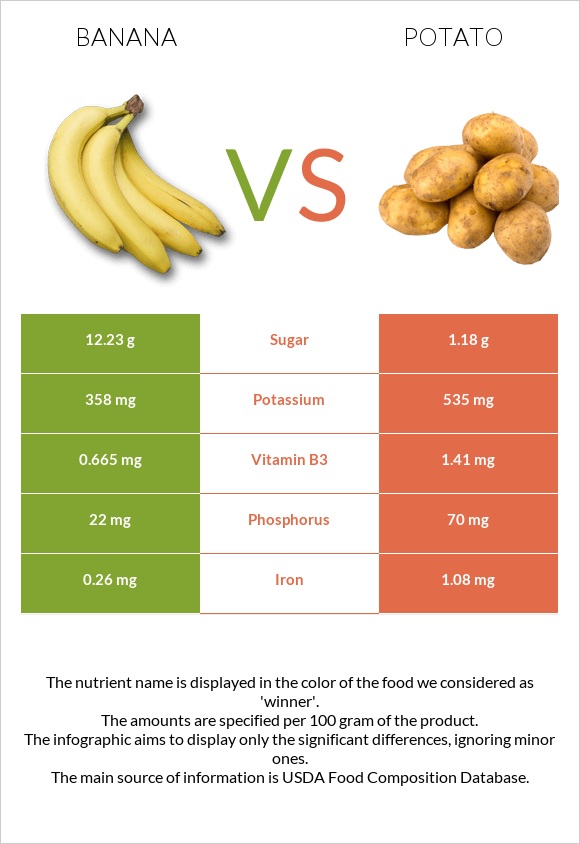
Bananas contain about 89 calories per 100g serving, while the same serving of potatoes contains 93 calories.
Proteins
Neither bananas nor potatoes are protein-rich food options, although potatoes contain 2 times more protein than bananas.
Per 100-gram serving, there are only 1.09 grams of protein in bananas and 2.5 grams of protein in potatoes.
Carbohydrates
Potatoes and bananas also contain similar amounts of carbohydrates, as well as fiber. Per 100-gram serving, there are 22.84 grams of carbs in bananas and 21.15 grams of carbs in potatoes.
Fats
Overall, both baked potatoes and raw bananas are low-fat foods. Per 100-gram serving, bananas contain 0.33 grams of fats, while the same serving of potatoes contains 0.13 grams of fats.
Both bananas and potatoes contain no cholesterol.
The fat-type breakdown charts of potatoes and bananas, as shown below, reveal that most of the fat in bananas is saturated fat, while in potatoes, it is polyunsaturated fat.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+966.7%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+28.1%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-69.6%
Vitamins
The vitamin content of bananas and potatoes is also surprisingly similar.
The predominant vitamin found in both is Vitamin B6, which is present in similar amounts in both foods. A 100-gram serving of bananas contains 0.367 grams of Vitamin B6, while the same serving of potatoes contains 0.311 grams.
Both potatoes and bananas do contain varying amounts of other vitamins; however, their content is not significant when put in the context of recommended daily vitamin intake. Nonetheless, potatoes contain slightly more Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B5, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+52.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+18%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+10.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+106.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+112%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+12.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+300%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+40%
Minerals
The predominant minerals found in bananas are manganese, copper, and potassium, whereas, in potatoes, these same minerals are present, along with the additional inclusion of iron.
In general, potatoes are relatively richer in minerals than bananas. They contain more iron, phosphorus, potassium, and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-90%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+23.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+150%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+200%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+49.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+315.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+51.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+140%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+218.2%
Glycemic Index
The difference between the glycemic indexes of these two is big.
The estimated glycemic index of bananas is 48, while the glycemic index of potatoes equals 86. Hence, bananas are considered a low glycemic index food.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of bananas and potatoes are -6.9 and -8.3, respectively, which means both are alkaline.
Weight Loss
Bananas and potatoes are moderate-calorie foods that contain minimal amounts of proteins and fats. Eating bananas can't directly lead to weight loss; nevertheless, some components can help reduce bloating and replace processed sugars.
By employing appropriate cooking techniques, vegetables can be incorporated into any diet. For example, the Potato Diet claims to help you lose one pound a day by eating nothing but plain potatoes. Nonetheless, the specific caloric intake and dietary details are contingent upon the cooking techniques employed for these vegetables (3, 4).
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Bananas' ability to lower blood pressure may be due to their high potassium content. Potatoes are also high in potassium; hence, they, too, have the potential to lower systolic blood pressure when consumed in boiled or baked form (5, 6).
According to one study, bioactive compounds with antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory characteristics can be found in the isolates of potatoes (7). ACE inhibition is typical for some antihypertensive medications like Lisinopril, Captopril, etc. This effect has not been studied in bananas․
According to another study, a high intake of baked, boiled, mashed, or fried potatoes may increase the risk of hypertension. This effect may be explained by a high glycemic load of potatoes (8, 9).
Cancer
According to a Swedish study, women who ate 4-6 bananas a week cut in half their risk of developing kidney cancer. Moreover, bananas contain lectins which have a distinctive role in the reduction of cancer metastasis.
Acrylamide is a chemical compound that can form in some foods during high-temperature cooking processes, such as French fries, potato chips, and foods made from grains. High doses of acrylamide can cause nerve damage. Lab animal studies show that acrylamide causes cancer (10, 11).
Diabetes
Based on various studies, potato consumption leads to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which is explained by their high glycemic index and glycemic load values. However, more research on humans is needed (12).
On the other hand, bananas are a good source of fiber; besides, they are considered a low glycemic index food. Unripe bananas can be included in diabetic diets in moderation (11).
Digestive Health
Both bananas and potatoes (mashed, without skin) are allowed for people with symptomatic IBD: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Bananas are also a good prebiotic and potassium source for patients with IBD (13).
Good Eye Health
Bananas offer notable benefits for maintaining good eye health. According to studies, Vitamin A present in bananas plays an essential role in keeping the mucus membranes in the eyes healthy. Besides, they are also high in carotenoids, which may help protect your eyes from the damaging effects of blue light and reduce your risk of macular degeneration, especially when you are older (14).
Side Effects
Toxicity
Some potato species may produce a toxic compound called solanine, a glycoalkaloid. Under specific adverse conditions, such as pest infestation, potatoes have the potential to produce increased levels of solanine, particularly when exposed to sunlight. Solanine gives potatoes a bitter taste and a green color, which may include symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal pains (15).
Allergies
Both bananas and potatoes are generally considered safe when consumed in typical servings. However, it's worth noting that individuals with latex sensitivity may also exhibit allergic reactions to bananas." The symptoms include irritation and itching of the mouth, diarrhea, and gas (16).
A potato allergy can impact individuals of any age and is typically attributed to specific compounds found in potatoes, such as patatin or solanine. The symptoms mainly include sneezing, runny nose, hives, and itchy skin (17).
Summary
While bananas are classified as fruits, potatoes are classified as vegetables. Both have similar macronutrient compositions and calories.
The predominant vitamin found in potatoes and bananas is Vitamin B6, which is present in similar amounts in both foods. However, in general, potatoes are relatively richer in most vitamins and minerals than bananas, containing more iron, phosphorus, potassium, and copper.
The difference between the glycemic indexes of these two is also quite big. The estimated glycemic index of bananas is 48, while the glycemic index of potatoes equals 86. Hence, bananas are considered a low glycemic index food, whereas potatoes are not.
References
- https://www.potatogoodness.com/potato-types/
- https://www.scirp.org/html/13-2700276_16366.htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11396693/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2014/01/24/the-problem-with-potatoes/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23425010/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34064968/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814607012800
- https://academic.oup.com/fqs/article/2/4/183/5164297?login=true
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/6/1222
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6272006/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15455348/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4965517/
- https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/sites/default/files/legacy/assets/pdfs/diet-nutrition-2013.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/fsn3.1308
- https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/solanine_poisoning_how_does_it_happen
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03889.x
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31606016/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 0.26mg | 1.08mg | 10% |
| Phosphorus | 22mg | 70mg | 7% |
| Fructose | 4.85g | 0.34g | 6% |
| Potassium | 358mg | 535mg | 5% |
| Starch | 5.38g | 17.27g | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.665mg | 1.41mg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.078mg | 0.118mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.367mg | 0.311mg | 4% |
| Protein | 1.09g | 2.5g | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.031mg | 0.064mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 2.6g | 2.2g | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.15mg | 0.36mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.27mg | 0.219mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.073mg | 0.048mg | 2% |
| Folate | 20µg | 28µg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 8.7mg | 9.6mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 22.84g | 21.15g | 1% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 15mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 1µg | 0.4µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.334mg | 0.376mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.5µg | 2µg | 1% |
| Choline | 9.8mg | 14.8mg | 1% |
| Calories | 89kcal | 93kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.33g | 0.13g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 20.24g | 18.95g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 27mg | 28mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 12.23g | 1.18g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.1mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.112g | 0.034g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.032g | 0.003g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.073g | 0.057g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.009mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.028mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.028mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.068mg | 0.119mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.05mg | 0.13mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.008mg | 0.038mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.049mg | 0.099mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.047mg | 0.125mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.077mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +497.5% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +1031.8% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +1326.5% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
| Contains more StarchStarch | +221% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Banana - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173944/nutrients
- Potato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170093/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.