Beans vs. Lentil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Compared to beans, lentils provide higher levels of folate, iron, phosphorus, and fiber. Regarding daily folate requirements, lentils provide a 39 percent increase, making them an excellent choice. The iron content in lentils is particularly noteworthy, with 3.33mg, a striking 11 times more than the 0.29mg found in beans. Lentils generally have a lower sugar content than beans.
Introduction
Lentils and canned beans are part of the legume family. In terms of nutrition and health, they can, however, differ.
Nutrition
We will compare the nutritional information of canned beans and lentils in this part of the article.
Macronutrients and Calories
Lentils are somewhat denser in nutrients compared to beans. Lentils comprise 70% water and 30% nutrients, while beans contain 73% water.
The average serving size of beans and lentils per person is one cup, weighing around 253g and 198g, respectively.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
OtherOther
+106%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+87.9%
Calories
Lentils contain 116 calories per hundred grams, whereas the same amount of beans provides 105 calories.
Protein
Lentils contain 9.02g of protein, whereas beans provide 4.8g. Lentils are higher in all essential amino acids, particularly leucine, lysine, and threonine. Lentils and beans are gluten-free.
Fats
Lentils and canned beans contain less than 1g of fat. Lentils are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas beans contain more polyunsaturated fats.
Both are cholesterol-free.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-48.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+82.9%
Carbohydrates
Both have almost equal amounts of carbs. 100g of beans contain 20.49g of carbohydrates, of which 5.5g are dietary fiber and 14.9g are net carbs. Lentils contain 20.13g of carbs, of which 7.9 g are dietary fiber and 12.23g are net carbs.
Vitamins
Lentils contain 7.5 times more folate and 2.5 times more vitamin B3, two times more vitamin K, and B5, whereas canned beans provide 13 times more vitamin A and two times more vitamin C.
Both contain almost equal amounts of vitamin E, B1, B2, and B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+106.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+36.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+12.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+21.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+146.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+36.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+112.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+654.2%
Minerals
Lentils provide more potassium, phosphorus, manganese, and iron. Canned beans, on the other hand, are higher in calcium and selenium.
Lentils contain 369mg of potassium and 180mg of phosphorus, whereas canned beans provide 50 mg of calcium. Both contain almost equal amounts of magnesium, zinc, and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+163.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+60.7%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+12.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+24.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1048.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+21.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+73.1%
Oxalates
The oxalate content of lentils is 13mg per 100 grams, and the oxalate content of beans is 27mg per 100 grams. Both are considered to be low in oxalates.
Glycemic Index
Lentils and canned beans are low-GI foods. Lentils have a glycemic index 29, whereas canned beans have a GI of 33.
Insulin Index
Lentil's insulin index is 58, whereas the insulin index of canned beans is 34.
Acidity
The PRAL value of lentils is 2.1, and the PRAL value of canned beans is -1.5. Lentils are acidic, whereas beans are alkaline.
Weight Loss & Diets
Canned beans, like lentils, are suitable for a vegan diet and can be included in the DASH diet. However, their high carbohydrate content may make them less suitable for the keto diet, which typically involves a low-carbohydrate intake. On the other hand, canned beans and lentils are generally considered compatible with the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes a balanced and varied intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Similar to lentils, canned beans are not considered paleo-friendly. Because the Paleo diet focuses on foods our ancestors would have access to during the Paleolithic era, legumes, including beans, are often excluded from the diet.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Lentils have been linked to lower risk factors for heart disease, such as improved cholesterol levels, reduced triglycerides, and potential blood pressure-lowering effects (1, 2, 3). Additionally, lentils are a good source of folate, which can help prevent the accumulation of excess homocysteine in the body, a risk factor for heart disease (3).
In contrast, the discussion about canned beans raises concerns about their salt content. Hypertension, kidney disease, and stroke are linked to a high salt intake (4,5). Nitrates and nitrites are contextualized in canned beans, acknowledging that they can disrupt blood flow and oxygen supply if consumed excessively (6, 7). However, these compounds may play an essential role in the body when consumed in small amounts. They contribute to nitric oxide production, positively affecting blood pressure, blood clotting, and heart disease risk (8, 9). For individuals looking to prioritize heart health, lentils, and canned beans have nutritional value, but sodium intake and canned bean sources should be considered.
Diabetes
Canned beans are a convenient source of plant-based protein that supports protein needs crucial for weight management (10). Diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and heart disease can be reduced with a plant-based diet, which includes lentils and canned beans (11, 12). On the other hand, lentils stand out for their richness in polyphenols and health-promoting phytochemicals that may contribute to enhanced blood sugar levels (13, 14). Animal studies suggest that lentil consumption can lower blood sugar independently of macronutrient content, and the retention of polyphenol benefits after cooking adds to their appeal (15). However, it's important to note that while these findings are promising, human studies are required for more conclusive evidence on the health benefits of both lentils and canned beans.
Digestive Health
Lentils and canned beans both provide essential nutrients but also contain some antinutrients. Phytic acid can reduce mineral absorption from lentils and interfere with protein digestion (16). Trypsin inhibitors in lentils may limit protein digestion (17, 18). Tannins may bind with proteins and inhibit nutrition absorption (19). However, these antinutrients can be reduced through soaking and cooking. On the other hand, both lentils and canned beans are:
- Rich sources of dietary fiber.
- Promoting feelings of fullness.
- Aiding in weight loss (20).
- Supporting lower blood cholesterol levels (21).
Canned beans, such as pinto beans, offer a convenient protein source and contribute to gut health as prebiotics, containing compounds with anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering properties (22, 23).
Cancer
The findings suggest that polyphenols in canned common beans, significantly darker varieties, may possess chemoprotective potential by influencing apoptosis and protein modulation (24). On the other hand, lentils have been associated with a decreased risk of breast, prostate, colon, and thyroid cancer, demonstrating their ability to induce cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy while inhibiting cell growth (25).
Appearance
Lentils are generally small, dried, lens-shaped, and split legumes. They can be found in various colors, such as brown, green, red, and black, and are characterized by their tiny, flat, and round shape. In contrast, canned beans, which include kidney, black, pinto, and white beans, typically have an oval or kidney-shaped appearance. These legumes are more significant than lentils and often have a plump and rounded structure.
Taste and Use
Vegetables and proteins are both essential food groups for keeping our bodies healthy. They are often used in soups, stews, salads, and side dishes. Lentils vary in texture and cooking behavior. Brown lentils are budget-friendly and blend well in soups. Various lentils can make lentil soup, including green, brown, and red. Green lentils, also known as French lentils, maintain firmness and are ideal for salads. When cooked, they become firm, similar to Beluga lentils. Red lentils cook quickly but may lose shape. In addition to being high in fiber, lentils offer a mild, earthy flavor, which contributes to various dishes.
Canned beans provide convenient and versatile options for cooking. They are recognized as pulses and dried seeds from legume plants and offer substantial protein, fiber, and vitamins. Combining beans and grains gives vegetarians more amino acids to complete a diet. Make them a standard diet that replaces meat products fully by adding them to curries, soups, and salads.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5713359/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11710352/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26634200/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7763082/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5098805/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6988620/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31244197/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31244197/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21968645/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25926512/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24871675/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26067245/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5713359/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31469378/
- https://ifst.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25599185/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5336446/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23885994/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31580563/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6921460/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31580563/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31353616/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5713359/
Infographic
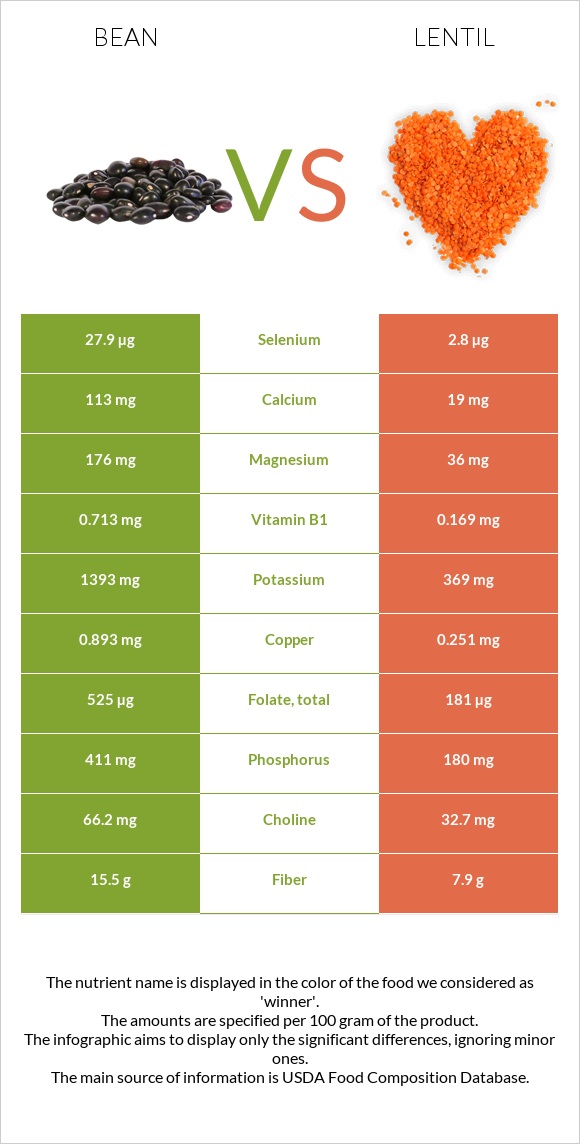
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Folate | 24µg | 181µg | 39% |
| Iron | 0.29mg | 3.33mg | 38% |
| Manganese | 0.494mg | 21% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.638mg | 13% | |
| Phosphorus | 104mg | 180mg | 11% |
| Fiber | 5.5g | 7.9g | 10% |
| Protein | 4.8g | 9.02g | 8% |
| Copper | 0.206mg | 0.251mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.43mg | 1.06mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.13mg | 0.178mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 50mg | 19mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 4.5µg | 2.8µg | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 3.1mg | 1.5mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 296mg | 369mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.15mg | 0.169mg | 2% |
| Calories | 105kcal | 116kcal | 1% |
| Magnesium | 32mg | 36mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 1.4mg | 1.27mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 5µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.06mg | 0.073mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.8µg | 1.7µg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.4g | 0.38g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 14.99g | 12.23g | N/A |
| Carbs | 20.49g | 20.13g | 0% |
| Sugar | 7.78g | 1.8g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.15mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Choline | 30.8mg | 32.7mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.103g | 0.053g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.035g | 0.064g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.172g | 0.175g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.081mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.323mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.39mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.654mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.63mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.077mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.445mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.448mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.254mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168128/nutrients
- Lentil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172421/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.