Bell pepper vs. Paprika — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Paprika is a dried form of peppers. It is richer in zinc, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, iron, and B complex vitamins, E, A, and K. Whereas, bell peppers are richer in vitamin C and richer in fibers. Capsaicin in paprika has health benefits.
Introduction
In this article, we will be comparing the difference between a bell pepper and Paprika.
However, it is essential to know that paprika comes from bell pepper. Bell peppers are dried and ground turning them into Paprika.
This article needs to understand both these foods' nutritional and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
Since Paprika is derived from bell pepper, we can assume that whatever is present in 100g of bell pepper would be more concentrated in paprika. However, during this drying and processing, some nutritional aspects are lost.
The serving size of bell pepper is 119g, whereas, Paprika is 0.5g.
It is only reasonable to consider bell peppers at 100g and Paprika at 1 g to make the comparison reasonable.
Water content
94% of bell pepper has a much higher water distribution than paprika.
Carbs
Bell peppers contain higher amounts of carbs. 100g of bell peppers contain 4.64g of carbs. In comparison, 1g of paprika contains 0.54g of carbs.
Calories
They are both very low in calories. 100g of bell peppers contain 20 calories, and 1g of paprika contains less than one calorie.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of paprika is 0. Bell pepper has a higher glycemic index.
Fiber
Bell pepper is richer in fibers; it contains 1.7g. In comparison, paprika contains 0.35g of fiber per 1g.
Protein and fat
The protein and fat content of both are negligible.
Minerals
In this section, we will consider equal amounts of each.
Paprika is richer in zinc, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and iron.
The diagram below displays the distribution of minerals.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -95.6% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +1680% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +2190% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +1202.9% |
| Contains more IronIron | +6117.6% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +980.3% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +3230.8% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +1470% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +1203.3% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +∞% |
Vitamins
Similarly to the minerals, we will consider them equal to each in this section.
Paprika is richer in vitamin B complex, E, A, and K. Whereas; bell peppers are richer in vitamin C.
The diagram below displays the distribution of vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +8833.3% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +13583.3% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +7764.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +478.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +4292.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +1995.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +2435.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +855.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +985.1% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +390% |
Health impacts
In the section on health impacts, we will focus on the different health impacts provided by each food and not their general health impacts.
Positive health impacts of bell pepper
Bell pepper is rich in vitamin C, which has numerous health benefits such as antioxidative action, improving immune response to fight off infections, and reducing the severity of allergic reactions. (1)
Positive health impacts of paprika
Paprika contains capsaicin which is the spicy flavor in Paprika. Capsaicin has analgesic properties that are used in musculoskeletal pain therapies. Capsaicin is also used as a topical treatment for psoriasis and diabetic neuropathy. (2) (3)
In addition, Paprika is packed with B complex vitamins, vitamins E, A, and K.
Conditionally a lot of Paprika has to be consumed to have the health effects of these vitamins. Since the serving size of Paprika is low, these vitamins will not impact overall health to a remarkable extent.
Infographic
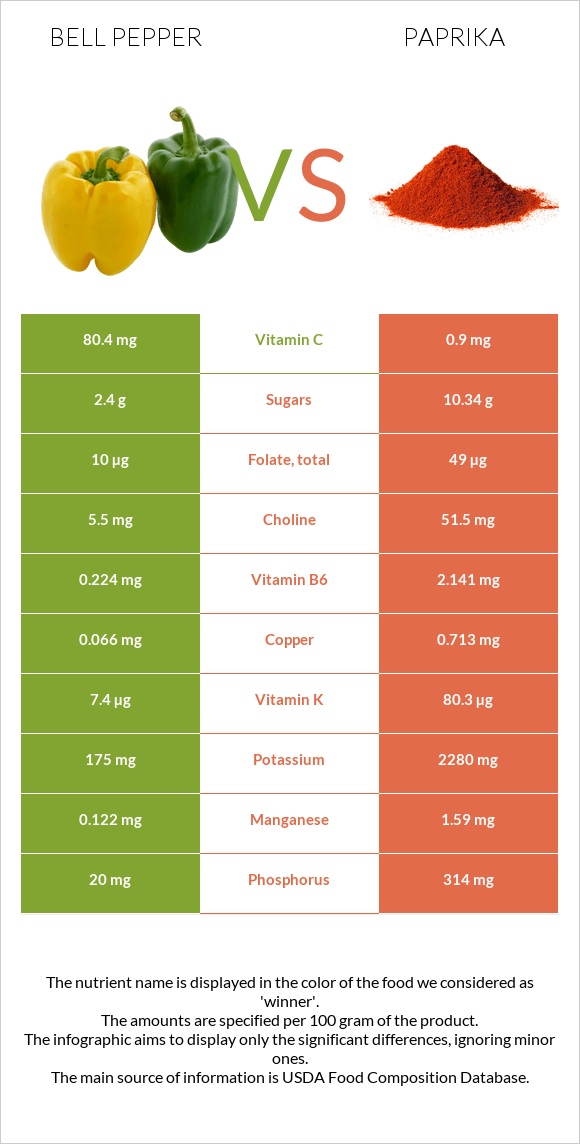
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 18µg | 2463µg | 272% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 21.14mg | 260% |
| Vitamin E | 0.37mg | 29.1mg | 192% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.224mg | 2.141mg | 147% |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 34.9g | 133% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.028mg | 1.23mg | 92% |
| Vitamin C | 80.4mg | 0.9mg | 88% |
| Copper | 0.066mg | 0.713mg | 72% |
| Manganese | 0.122mg | 1.59mg | 64% |
| Potassium | 175mg | 2280mg | 62% |
| Vitamin K | 7.4µg | 80.3µg | 61% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.48mg | 10.06mg | 60% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.062g | 7.766g | 51% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.099mg | 2.51mg | 48% |
| Phosphorus | 20mg | 314mg | 42% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 178mg | 40% |
| Zinc | 0.13mg | 4.33mg | 38% |
| Protein | 0.86g | 14.14g | 27% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.057mg | 0.33mg | 23% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 229mg | 22% |
| Fats | 0.17g | 12.89g | 20% |
| Carbs | 4.64g | 53.99g | 16% |
| Calories | 20kcal | 282kcal | 13% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 6.3µg | 11% |
| Folate | 10µg | 49µg | 10% |
| Saturated fat | 0.058g | 2.14g | 9% |
| Choline | 5.5mg | 51.5mg | 8% |
| Fructose | 1.12g | 6.71g | 7% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.008g | 1.695g | 4% |
| Sodium | 3mg | 68mg | 3% |
| Net carbs | 2.94g | 19.09g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.4g | 10.34g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.012mg | 0.07mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.036mg | 0.49mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.024mg | 0.57mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.036mg | 0.92mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.039mg | 0.69mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.007mg | 0.2mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.092mg | 0.61mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.036mg | 0.75mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.01mg | 0.25mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.453g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +735.3% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +1544.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +7482.4% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +1063.6% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +1659.1% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -97.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +21087.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +12425.8% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +636.4% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +126.7% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +499.1% |
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Bell pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170427/nutrients
- Paprika - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171329/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






