Avocado oil vs Canola oil - Nutrition Comparison & Health Impact


Summary
When comparing its health benefits, avocado oil is a healthier and better alternative than canola oil. It is lower in vitamins. On the other hand, canola oil has a higher variety of usage, and it is cheaper and richer in vitamins K and E.
Introduction
Avocado oil is extracted from avocados which makes it a vegetable oil. It comes from the processing of avocados and extracting the oil from them. The pulp of the avocado is the primary source of the oil. Avocado oil can be eaten raw or can be used in cooking.
Canola oil comes from rapeseed; it is considered a type of rapeseed oil. The rapeseed is processed, and the oil is extracted from it. It is considered a vegetable oil. However, it differs from rapeseed oil because it is more refined, processed, and contains less erucic acid.
This article will discuss the difference between avocado oil and canola oil, comparing their general differences, nutritional content, weight loss and diet, and health impacts.
The food types used in this article are oil avocado and oil canola.
General differences
This section will compare avocado oil and canola oil according to smoke point, price, shelf life, and culinary usage.
Smoke point
It is essential to mention the most remarkable points of each oil in this case.
Avocado oil can be eaten raw or used in cooking or baking. One of the most important features of avocado oil is that it has a high smoke point. Avocado oil has a higher smoke point, and in this manner, it is a much better alternative, and it can be considered a healthy cooking oil.
The smoke point is an important indicator because when oil passes that degree of heat, it forms radicals. Thus it is always wanted to stay lower than that temperature.
Price
Canola oil is cheaper than avocado oil and widely available worldwide. The lower price of canola oil is because rapeseeds are mostly GMO and easy to grow, and it is easy to mass-produce canola oil. In the case of avocado oil, the avocado itself is more expensive, and it is harder to process the oil.
Shelf life
Canola oil has a much higher shelf life in years than avocado oil after exposure to air. Avocado oil becomes rancid after eight months of opening, even after refrigeration. However, canola oil has a longer shelf life.
Culinary usage
One of the most important characteristics of avocado oil is that it can be used in its raw state when eaten, whereas canola oil is not usually used. Avocado oil can be used in baking and cooking, like canola oil. Canola oil is also used in frying.
Canola oil usually doesn’t have much flavor and keeps the primary flavors of the prepared food exposed; however, avocado oil masks some flavors from a prepared dish.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare the nutritional composition of avocado oil and canola oil according to 100g of each.
Calories
They have the same calories, which are equal to 884 calories. They are high in calories.
Glycemic index
Their glycemic index is equal to 0.
Carbs and proteins
They contain 0g of carbs and proteins. They are pure oils.
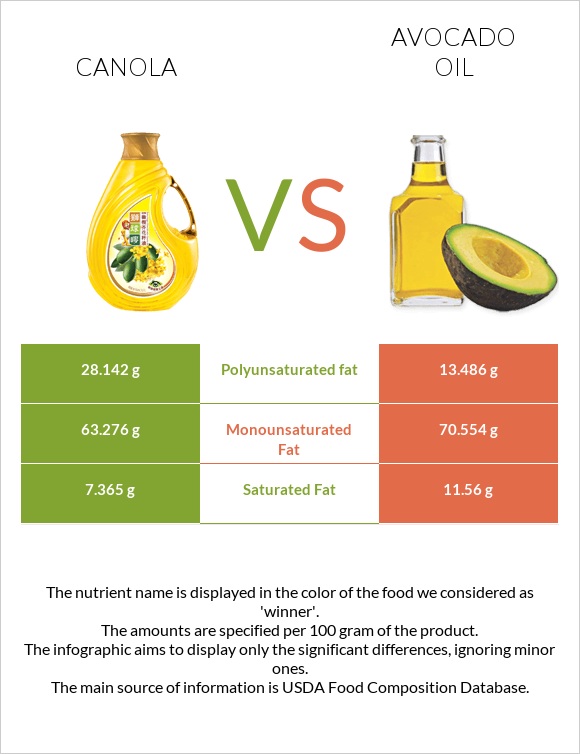
Fats
Their total weight is equal to their fat content. However, it is essential to dig into the fat profiles of both. They mostly contain unsaturated fats, which is an important indicator.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-36.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+108.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+11.5%
Saturated fats
Avocado oil contains more saturated fats than canola oil.
Unsaturated fats
Overall, canola oil has more unsaturated fats than avocado oil.
Vitamins and minerals
They are very low in vitamins and minerals. Avocado oil lacks many minerals and vitamins, whereas canola oil is richer in vitamin K and vitamin E.
Cholesterol
Both have no cholesterol.
Weight loss and diets
Avocado oil is a healthier alternative than canola oil when cooking. However, when it comes to comparing animal fats like butter and animal-derived oils, these oils are healthier.
In addition, comparing which oil is a better alternative for frying is pointless since frying food by itself is not a healthy thing to do.
Vegan diet
Vegans can consume both of these oils since they are plant-based oils. Avocado oil can also be used instead of butter in several situations since it has a stronger flavor than canola oil.
Keto
Both oils can be used in the keto diet since they contain 0g of carbs and a higher unsaturated to saturated fat ratio.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a significant concern worldwide, and dietary choices, including the types of oils consumed, can play a role in its prevention or exacerbation. Both avocado oil and canola oil are commonly used cooking oils, and they have different compositions that may affect cardiovascular health (1, 2).
Monounsaturated Fats (MUFA): Both oils are rich in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which can help improve cardiovascular health by reducing LDL (bad cholesterol) levels, thereby lowering the risk of heart disease.
Polyunsaturated Fats (PUFA): Canola oil contains a higher proportion of polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for reducing inflammation and promoting heart health.
Saturated Fats: Both oils are low in saturated fats, which are linked to increased cardiovascular risk. Choosing oils low in saturated fats, like avocado and canola oil, supports heart health.
Canola oil is rich in vitamin E, a potent antioxidant known for its ability to reduce oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development of various chronic diseases, including atherosclerosis, which is the hardening and narrowing of the arteries due to the buildup of plaque.
It's interesting to note that while both vitamin E and vitamin C are powerful antioxidants, studies have shown different effects regarding their impact on cardiovascular health. While vitamin E has shown potential benefits in reducing the risk of atherosclerosis, the evidence for vitamin C's similar effect is less consistent. This could be due to various factors, including differences in their mechanisms of action and how they interact with other compounds in the body.
The observation is intriguing as it suggests that avocado oil may have effects similar to those of losartan, an ARB medication. This could be due to a reduction in the actions of angiotensin II, a hormone involved in blood pressure regulation and myocardial remodeling. These findings point to a potential mechanism by which avocado oil could positively impact cardiovascular health, similar to the actions of ARB medications. Further research could help clarify these mechanisms and their implications for cardiovascular health (4).
Inflammation and antioxidation
Lutein which is high in avocado oil is an antioxidant that reduces oxidative damage. It is linked with decreased rates of cataract development and macular degeneration. (5)(6)(7)
Avocado oil is also linked with decreased inflammatory processes of arthritis. (8)
When it comes to canola oil, especially when it comes to frying, the system has increased inflammatory markers. In addition to that, there is increased damage caused by oxidative stress. Somehow the opposite effects of avocado oil. (9)
Cancer
Overall, avocado oil has decreased the risks of cancer development since it has antioxidative properties. (10)
Canola oil is linked with decreased risks of overall cancer. It suppresses breast cancer cells and colon cancer cells. (11)(12)(13)
However, this study indicated that the polycyclic aromatic compounds present in canola oil are linked with increased cancer development. (14)
Diabetes
Canola oil is linked with increased risks of metabolic syndrome and worsening the outcomes of obesity. (4)
Alpha-linoleic acid in avocado oil is linked with decreased risks of diabetes development. It is safe to consume for people who suffer from metabolic syndrome with no risks of worsening disease outcomes. (15) (16)
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6600360/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1756464618306583?via%3Dihub
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33127255/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29753173/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3664913/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17177553/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23571649/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518992/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29920087/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5551541/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24761850/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859037/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17571951/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34145544/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3224740/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24898228/
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +∞% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 17.46mg | 116% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 28.142g | 13.486g | 98% |
| Vitamin K | 71.3µg | 59% | |
| Saturated fat | 7.365g | 11.56g | 19% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 63.276g | 70.554g | 18% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.395g | N/A | |
| Choline | 0.2mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 9.137g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 18.64g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Canola oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients
- Avocado oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173573/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




