Canola Oil vs. Palm Oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
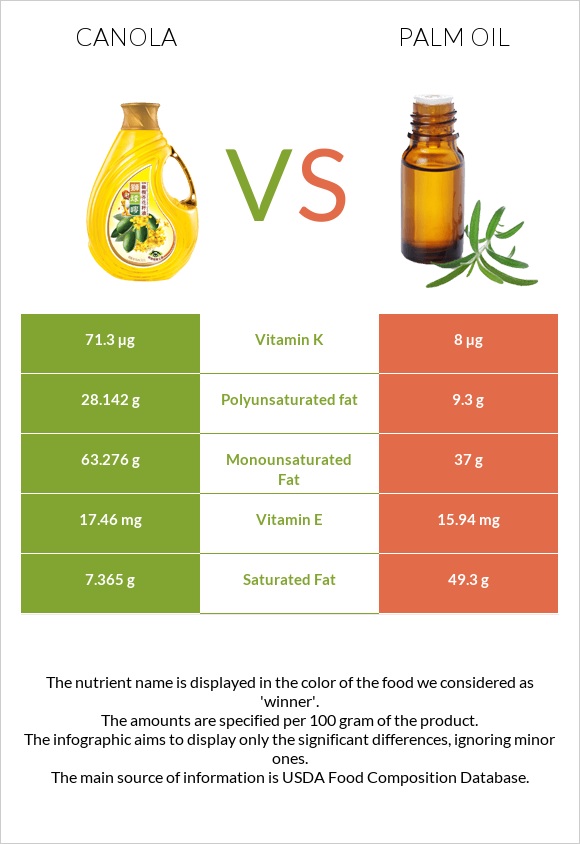
Canola oil is somewhat healthier than palm oil. Canola oil is higher in vitamin K, vitamin E, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Palm oil may be considered less healthy as it has a much higher saturated fat content.
Canola and palm oil may be beneficial for people with diabetes but can also cause cardiovascular issues. Nevertheless, you can definitely find much healthier oils to consume.
Introduction
Canola oil and palm oil are considered vegetable oils as they come from vegetable sources. Vegetable oils are highly processed. They are specially designed to tolerate high heat and resist going rancid.
Canola oil is extracted from the rapeseed plant. On the other hand, palm oil is extracted from palm fruits.
In terms of health benefits, canola oil is healthier than palm oil as it is higher in vitamin K, vitamin E, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Moreover, canola oil is lower in saturated fats (considered unhealthy fats).
In this article, we will examine the nutritional benefits and the downsides of these oils.
Uses in Cooking
Aside from the health benefits, the smoke point of oils is another important characteristic. The smoke point is the point at which the oil becomes harmful and produces free radicals.
The smoke point of the refined canola is nearly 206°C (400°F) (1). Meanwhile, the smoke point of palm oil is around 232°C (450°F) (1). While both these values are considered high smoke points, if you are looking for a better option for high-heat cooking, you can go with palm oil.
Nutrition
You can refer to the infographics below to understand the nutritional differences between these oils. They are presented for 100g servings of canola and palm oils. However, one average serving of these oils is considered one tablespoon, equal to about 14g.
The nutritional content for most oils, including palm and canola oils, is made up almost entirely of fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
The oils are equal in caloric value, which comes from their fat component.
A 100g of each of these oils provides 884 calories.
Fats
The oils are equal in the amounts of fats they provide. However, they differ in the proportion of the different fats they contain.
Canola oil is significantly lower in saturated fats, the difference being 42g for 100g of the oil. In addition, canola oil has almost double the amount of monounsaturated fat and more than double, almost triple, the amount of polyunsaturated fat compared to their corresponding amounts in palm oil.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-85.1%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+71%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+202.6%
Like most natural vegetable oils, canola and palm oils contain no cholesterol and only trace amounts of trans fats.
Proteins and Carbohydrates
Both oils do not contain proteins or carbohydrates.
Vitamins and Minerals
Canola oil and palm oil are absent in minerals. Palm oil only contains trace amounts of iron.
As for vitamins, canola oil is almost 9 times richer in vitamin K and slightly richer in vitamin E. Both oils do not have any other vitamins, so we can say that canola oil ranks higher in terms of vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+791.3%
Glycemic Index
Both oils have a glycemic index of 0 as they are composed entirely of fat and do not provide carbohydrates.
Weight Loss and Diets
A meta-analysis has shown that the consumption of canola oil causes a moderate decrease in body weight (2).
However, a study conducted on mice models revealed that a diet supplemented with canola oil caused the studied mice to weigh more than mice who did not receive the canola oil in their diet (3).
On the other hand, a systematic review showed that there is not enough evidence to conclude that palm oil causes any changes in weight (4).
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Some studies deny that palm oil and canola oil have any cardiovascular benefits or claim that they are harmful. Meanwhile, other studies claim that canola oil has positive cardiovascular benefits.
A study revealed that the consumption of canola oil, compared to the consumption of other oils rich in saturated fat, led to a decrease in total cholesterol and a reduction in the level of bad cholesterol (LDL cholesterol) (5). In addition, according to a research study, palm oil consumption is not related to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (6).
It should be noted that, unlike canola oil, by reducing oxidative stress and modulating endothelial function, palm oil reduces the course of salt-induced hypertension and mortality (7.8).
Diabetes
A study has shown that consuming a low glycemic index diet and canola oil leads to improved glycemic control (9). Another study has shown that palm oil has antioxidant potential that can benefit individuals with diabetes mellitus (10).
Cancer
Research has shown that carotene found in palm oil has immunomodulatory effects and may suppress the growth of human breast cancer cells (11).
Another study showed that canola oil has chemoprotective effects in rats (12). This study compared rats that consumed corn oil vs. rats that consumed canola oil. The canola oil group showed a reduction in colon tumor incidence and tumor multiplicity. This is due to the fact that canola oil is much richer in omega-3 fatty acids, while corn oil is much richer in omega-6 fatty acids.
Vitamin A Deficiency Prevention
A meta-analysis demonstrated that palm oil might play a role in alleviating vitamin A deficiency (13). This is because palm oil contains provitamin A, a precursor to vitamin A synthesis.
Neuroprotection
Palm oil contains a form of vitamin E that is not well known, α-tocotrienol. This compound is known to have neuroprotective functions (14). This study also mentions that supplementation with this compound derived from palm oil can protect the brain from stroke-mediated nerve dysfunction (14).
On the other hand, some studies show that canola oil worsens memory (15). There are very few if any, studies claiming that canola oil has any neuroprotective function.
Downsides and Risks
Cardiovascular Health
Canola oil has also been shown to reduce the lifespan of hypertensive stroke-prone rats (16). Moreover, canola oil is a highly processed oil that may contain some amount of trans fats. Trans fats cause arterial calcification and are harmful to heart health (17).
Palm oil is also not heart-healthy but through other mechanisms and activities. Palm oil is high in saturated fats. Palm oil is one of the vegetable oils with the highest saturated fat content. The consumption of a diet rich in saturated fats can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease (18).
Cancer
Canola oil increases inflammation by reducing antioxidant activity (11). Furthermore, cooking with canola oil releases a lot of free radicals. Free radicals damage cells and cause inflammation which, with time, may lead to the growth of cancerous cells (17).
According to the European Food Safety Authority, refined oils such as palm oil release harmful substances/contaminants when heated or processed at 200°C (392°F) or more (19). Glycidol is one of the contaminants released. Glycidol is genotoxic and carcinogenic (19).
Effects on The Brain
As mentioned above, a diet high in canola oil may affect working memory negatively (15). Moreover, canola oil causes the formation of plaques called beta amyloids. These plaques can signal the formation of neurodegenerative diseases (3).
References
- Do Cooking Oils Present a Health Risk?
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520036/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-17373-3
- https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation.aspx?paperid=86339
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3746113/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4365303/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16326639/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34900035/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24929428/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128157763000292
- https://aocs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1007/s11745-002-0932-0
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01635581.2011.523498
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5748732/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3065441/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5719422/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3215974/
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/diet/antioxidants-fact-sheet
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000510
- https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/press/news/process-contaminants-vegetable-oils-and-foods
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 7.365g | 49.3g | 191% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 28.142g | 9.3g | 126% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 63.276g | 37g | 66% |
| Vitamin K | 71.3µg | 8µg | 53% |
| Vitamin E | 17.46mg | 15.94mg | 10% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.395g | N/A | |
| Choline | 0.2mg | 0.3mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 9.137g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 18.64g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Canola oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172336/nutrients
- Palm oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171015/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






