Coconut oil vs. Babassu oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Babassu oil and coconut oil can be used interchangeably. They increase the risk of overall cardiovascular mortality since they are high in saturated fats. Coconut oil contains higher amounts of saturated fats, whereas babassu oil is richer in monosaturated oils and vitamin E.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between babassu and coconut oil. Both are vegetable oils processed and used for several purposes. This article will compare these two oils' nutritional content and health impacts. In addition, it is essential to know about their smoke points since they are used in cooking.
Babassu oil is extracted from the babassu palm and is used in the culinary, industrial, and pharmaceutical spheres. In comparison, coconut oil is extracted from coconuts, and similarly to babassu oil, it has culinary, industrial, and pharmaceutical usage.
Babassu and coconut oils are often used interchangeably since they share several similar properties.
Both oils melt on contact with the skin at room temperature.
What's The Actual Difference?
Coconut oil has a sweet, nutty aroma and a thicker viscosity, whereas babassu oil is nearly scentless and has a lighter consistency.
Aside from texture, content, and function, the look of babassu oil is similar to that of coconut oil, as it is light in color.
Smoke point
Babassu oil and coconut oil have similar properties, and their smoke points are nearly identical. They are mainly used for skincare products and can be used in cooking, but not high-temperature frying. They are not used for deep frying.
Usage
Babassu oil can be used as a moisturizer since it is a lightweight oil; it absorbs into your skin faster than coconut oil. This also makes it less messy and may protect your skin better than coconut oil because babassu oil keeps moisture and dries with an invisible layer that acts as a barrier against skin pore pollution. Babassu oil is safe for all skin types, while coconut oilit is best for dry skin.
Both can be used as hair masks, but coconut oil must be washed out to avoid greasiness, whereas babassu oil can be kept in the hair due to its texture.
Nutritional content comparison
Calories
Both have nearly the same amount of calories, approximately 884 calories for babassu oil and 892 calories for coconut oil.
Carbs and proteins
The carb and protein profiles of both oils are negligible.
Fats
Per 100g of each oil, we have 100g of fats; however, their distribution of types of fats is different.
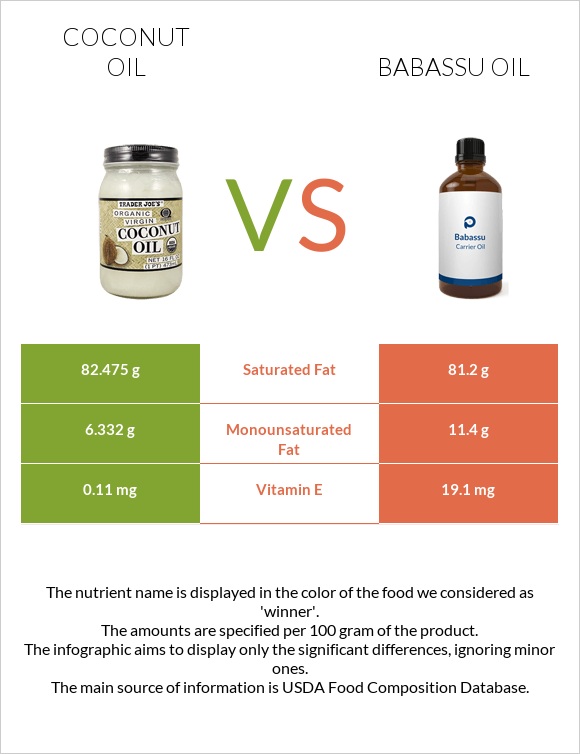
They are mainly composed of saturated fats. 81g of saturated fats for babassu oil and 82.5g of saturated fats for coconut oil. The amount of saturated fat is very high.
However, babassu oil's monounsaturated fats are higher than coconut oil. Their polyunsaturated fats are negligible.
Vitamins
Babassu oil is richer in vitamin E.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Coconut oil and babassu oil are considered “healthy fats” since they come from vegetables. However, that is wrong. Both these oils are packed with saturated fats, which increase the risk of atherosclerosis and dyslipidemia. Overall, these oils should not be considered healthy for cardiovascular health.
Vitamin E benefits
Babassu oil is richer in vitamin E. Babassu oil has anticarcinogenic, antioxidative, and immune-boosting properties due to its rich vitamin E profile. (3)
Miscellaneous
These oils have several benefits for skincare and other cosmetological points. However, this article focuses on how these oils affect the body regarding their consumption. (4)(5)
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +∞% |
| Contains more IronIron | +∞% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +∞% |
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +17263.6% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 0.11mg | 19.1mg | 127% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 6.332g | 11.4g | 13% |
| Saturated fat | 82.475g | 81.2g | 6% |
| Fats | 99.06g | 100g | 1% |
| Iron | 0.05mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.6µg | 1% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.702g | 1.6g | 1% |
| Calories | 892kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Calcium | 1mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0.02mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.028g | N/A | |
| Choline | 0.3mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.019g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.676g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +∞% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +∞% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +80% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Coconut oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171412/nutrients
- Babassu oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171428/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






