Coconut oil vs. Butter — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
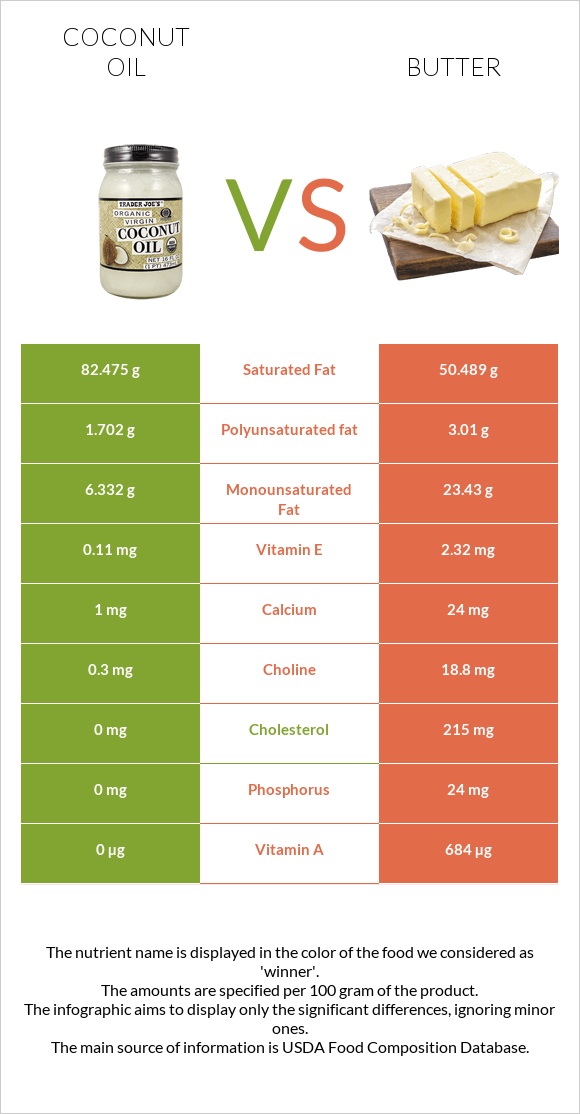
Butter and coconut oil are high-caloric foods and are high in saturated fats. While butter is high in cholesterol, coconut oil has negligible amounts of cholesterol. Butter is rich in vitamin A and calcium, while coconut oil has negligible amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Introduction
In this article, the nutritional content, health impact, downsides, usage accessibility, and myths about coconut oil and butter will be discussed in detail.
Actual differences
Butter is a dairy product processed from cow milk. When refrigerated, it’s in a solid form. However, at room temperature, it becomes a semi-solid emulsion. It has various forms of usage such as baking, frying, cooking, and used as a spread. Nearly all gastronomic cuisines use butter while preparing dishes.
On the other hand, coconut oil is a plant-based oil. It is the result of the processing of the coconut’s white part, known as the flesh. At room temperature, it is in a semi-liquid state, mostly liquid, with some solid parts suspended in it. Coconut oil is not as abundant in every region, given that it is produced from coconuts, a fruit that is found in tropical regions. It is commonly used in Indian and Filipino cuisines as an alternative to butter.
Nutrition
Butter is a dairy product that has low amounts of protein, 0.9g in 100 grams, to be specific. It has high amounts of fats, 81g per 100 grams, of which 50g are saturated fatty acids. The carbohydrate content in butter is negligible.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+22.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+2175%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+∞%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+∞%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+59700%
Cholesterol
Another aspect that should be considered when consuming butter is the amount of cholesterol in it. Butter contains 215 mg of cholesterol which is 71% of the daily recommended amount.
It is also good to note that butter has 19mg of choline per 100 grams, however, this amount is not remarkable relative to the daily recommended value.
When it comes to coconut oil, it is a plant-based oil that contains negligible amounts of cholesterol. However, coconut oil has high amounts of saturated fatty acids at 82g in 100g, which is 410% of the daily recommended value. In addition to this, coconut oil is considered to be one of the oils that have remarkable amounts of trans fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-38.8%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+270%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+76.9%
Vitamin content comparison
Butter is considered among foods that contain high amounts of vitamin A at 2500UI. It also contains considerable amounts of vitamins E and K and a small amount of vitamin B12.
Coconut oil, on the other hand, has negligible amounts of any vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2009.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1066.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Mineral content comparison
Given that butter is a dairy product, it contains calcium (24 mg per 100g). It also contains selenium and sodium, however, in small amounts.
Coconut oil has a negligible mineral profile.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+150%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+2300%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+∞%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+350%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+∞%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Health impact
Butter and coconut oil have linoleic acid as a component in their fat profile. Linoleic acid is known to reduce obesity (1).
Butter contains butyric acid, which has proven to be a very beneficial compound in food intake. Butyric acid consumed by individuals with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) has shown a decrease in symptoms (2).
Butyric acid is also a beneficial compound for patients who suffer from acute and chronic constipation (3).
Coconut oil is rich in lauric acid, which is a fatty acid, and reduces the risk of developing enlarged prostate and prostatic cancer (4).
For individuals who are diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease, it was observed that a diet with coconut oil showed improvement in the main cognitive functions (5).
Downsides
Butter and coconut oil are among foods that contain high amounts of saturated fatty acids. They lead to increased concentration of Low-density lipoproteins in the blood (LDL cholesterol). Individuals who have a family history or have already been diagnosed with blood lipid disorders should be careful while consuming butter and coconut oil (6)(7).
Butter and coconut oil are considered to be high-caloric foods. Butter has 717 calories per 100g, and coconut oil has 862 calories per 100g. So while consuming both butter and coconut oil, one must be careful of the daily caloric intake.
Usage and accessibility
Butter has different usages in cuisines. For instance, it can be used as a spread accompanied by bread and jam. However, the content of carbohydrates from the jam and bread and the content of saturated fats from the butter should be taken into consideration.
Butter can also be used for cooking purposes, sauce-making, and pan-frying.
Coconut oil can be used for cooking purposes as a vegan alternative to butter. It is also used for cooking and making vegan mayonnaise.
Coconut oil has an additional advantage over butter since it can be safely used for cooking at high temperatures.
Another aspect of coconut oil is that it can be used as a skin moisturizer and protection against UV. Even though using coconut oil as a moisturizer has no nutritional benefits, it has medical importance.
Myths
Coconut oil is a healthy and safe oil to consume
Coconut oil is famously used in the vegan community and individuals who follow the keto diet. It is claimed to be a healthy fat to consume. However, if coconut oil is not consumed in moderate amounts, 2-3 tablespoons a day at most, it increases the risk of high LDL concentrations in the blood.
Replace carbohydrates with fats
This is highlighted in the keto community mostly. When carbohydrates are eliminated from the diet and replaced with fats which are mostly saturated fats like butter or coconut oil, it increases the risks of cardiovascular disease (8).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4574006/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4027835/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5497138/#cit0020
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6201718
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30056419/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26135349/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29974400/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5492032/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 82.475g | 50.489g | 145% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 684µg | 76% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 215mg | 72% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 6.332g | 23.43g | 43% |
| Fats | 99.06g | 81.11g | 28% |
| Vitamin E | 0.11mg | 2.32mg | 15% |
| Calories | 892kcal | 717kcal | 9% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.702g | 3.01g | 9% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.17µg | 7% |
| Vitamin K | 0.6µg | 7µg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 0mg | 24mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0mg | 0.034mg | 3% |
| Choline | 0.3mg | 18.8mg | 3% |
| Protein | 0g | 0.85g | 2% |
| Calcium | 1mg | 24mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0mg | 0.016mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 1µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0mg | 0.11mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 0mg | 24mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.02mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Folate | 0µg | 3µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Carbs | 0g | 0.06g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 0mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.05mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Sodium | 0mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0mg | 0.004mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0mg | 0.005mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0mg | 0.003mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.028g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0mg | 0.038mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0mg | 0.051mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0mg | 0.067mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0mg | 0.041mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0mg | 0.057mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.019g | 0.315g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.676g | 2.166g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Coconut oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171412/nutrients
- Butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






