Currants vs Cranberries - Nutrition Comparison and Health Impact

Summary
Currants are higher in fiber, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, folate, vitamin K, and vitamin C. Currants provide three times more vitamin C than cranberries. They also have a lower glycemic index than cranberries.
On the other hand, cranberries are lower in net carbs and calories and have more vitamin A.
Introduction
This article will compare currants and cranberries, focusing on their health impact and nutritional content. We will review the differences between raw currants (1) and raw cranberries (2).
Macronutrients
Both currants and cranberries have more than 80% of water, but they differ in the distribution of different macronutrients. The amounts of nutrients these berries provide are described below.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+204.3%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+53.8%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+15.3%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+441.7%
Calories
Currants and cranberries are plant food products. Hence, they both are low-calorie foods. However, currants are higher in calories, providing 56 calories, while cranberries have 45 calories per 100g.
Carbs
Currants are higher in carbs compared to cranberries.
Currants provide 4.3g of dietary fiber per 100g, while the same amount of Cranberry contains only 3.6g of it.
Currants are rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Cranberries are a bit lower in net carbs: 100g has 8․4g of net carbs, while the same quantity of currants contain 9.5g.
Protein
Currant and cranberries are not supposed to contain much protein. Still, currants are higher in proteins than cranberries.
Fats
Both berries have less than one gram of fat per 100g so we can neglect the fat content. Cranberries and currants do not contain any amount of cholesterol.
Vitamins
Currants are an excellent source of vitamin C: they are almost three times higher in vitamin C (41mg per 100g) than cranberries (14mg per 100g).
Currants are richer in vitamin E and vitamin K, while cranberries provide more vitamin B5 and vitamin A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+192.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+233.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+22.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+120%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+700%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1220%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+360.9%
Minerals
Currants are higher in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, zinc, iron, and copper. Currants are two times richer in copper than cranberries.
You can check the mineral composition of these two fruits in the chart below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+116.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+312.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+243.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+334.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+91.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+155.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+300%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+500%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+43.5%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of currants is equal to 25, while cranberries have a GI equal to 45.
However, both berries are classified as low-GI food.
Acidity
Both Currant and Cranberry are alkaline based on PRAL values. However, Currant is more alkaline than Cranberry: its PRAL value is -4.2, compared to -1.3 for Cranberry.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular health
The research found that currants have ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibiting activity, similar to antihypertensive medications (e.g., Captopril, Lisinopril, Perindopril, etc.). Regarding cranberry supplements, they had no effect on the blood pressure of individuals with cardiometabolic disorders. To get more up-to-date information, though, further research is required (3.4).
According to studies, cranberries may reduce LDL (bad cholesterol) and increase HDL (good cholesterol) levels in the blood, which are important for people with coronary artery disease. This effect for currants is unknown (5.6).
Furthermore, having a high flavonoid content, currants, and cranberries may be part of a balanced diet.
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173964/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171722/nutrients
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227950405_Evaluation_of_red_currants_Ribes_rubrum_l_black_currants_Ribes_nigrum_l_red_and_green_gooseberries_Ribes_uva-crispa_for_potential_management_of_type_2_diabetes_and_hypertension_using_in_vitro_models
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37963472/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17761017/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16923231/
Infographic
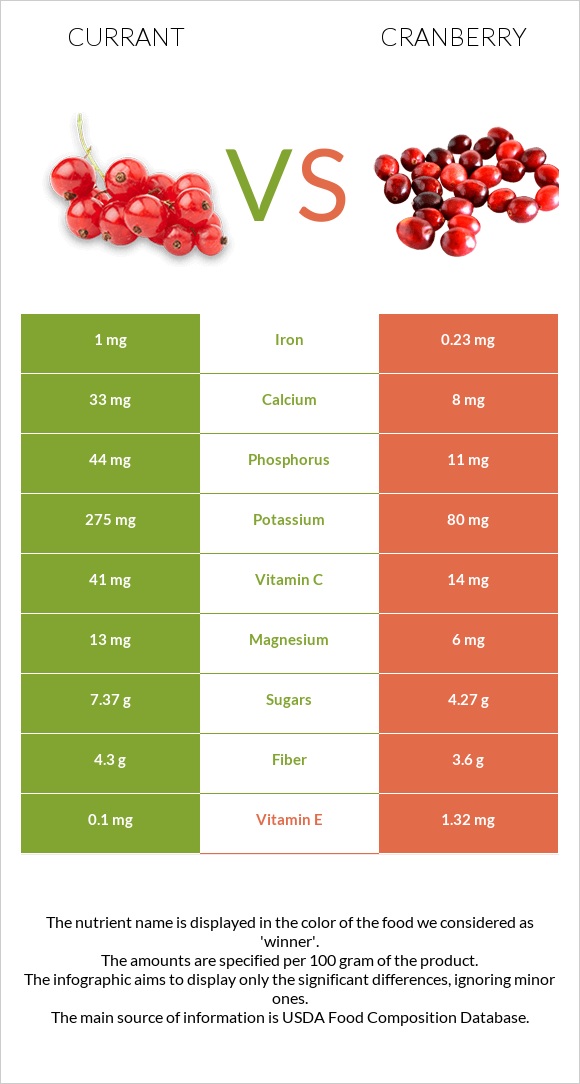
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 41mg | 14mg | 30% |
| Iron | 1mg | 0.23mg | 10% |
| Vitamin E | 0.1mg | 1.32mg | 8% |
| Potassium | 275mg | 80mg | 6% |
| Copper | 0.107mg | 0.056mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 44mg | 11mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.064mg | 0.295mg | 5% |
| Vitamin K | 11µg | 5µg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.186mg | 0.267mg | 4% |
| Fructose | 3.53g | 0.67g | 4% |
| Calcium | 33mg | 8mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 4.3g | 3.6g | 3% |
| Protein | 1.4g | 0.46g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 6mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 0.012mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.05mg | 0.02mg | 2% |
| Folate | 8µg | 1µg | 2% |
| Calories | 56kcal | 46kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 13.8g | 11.97g | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.23mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.07mg | 0.057mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.2g | 0.13g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 9.5g | 8.37g | N/A |
| Sugar | 7.37g | 4.27g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 2µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.1mg | 0.101mg | 0% |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 5.5mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.017g | 0.008g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.028g | 0.018g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.088g | 0.055g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.003mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.028mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.033mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.053mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.039mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.003mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.036mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.045mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.018mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +55.6% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +60% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -52.9% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +281.3% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +426.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Currant - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173964/nutrients
- Cranberries - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171722/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



