Fennel seeds vs. Fenugreek — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Fennel seeds contain more vitamins, minerals, fats, and sugars than fenugreek seeds. They also contain more calories and fiber. On the other hand, fenugreek seeds have lower sodium.
Fennel seeds are usually greenish, while fenugreek seeds are usually amber-colored. The first ones are sweeter, unlike more bitter fenugreek seeds. Both are used in small quantities.
Introduction
The main goal of this article is to compare two types of seeds: fenugreek and fennel seeds. We will discuss their nutritional profiles and their impact on human health.
Nutrition
You can find various charts and infographics at the bottom of our page that visually show the nutritional profile of fennel and fenugreek.
Consider that fennel and fenugreek seeds are usually consumed in smaller serving sizes (5.8g (1 tbsp) for fennel seeds and 11.1g (1 tbsp) for fenugreek seeds).
Macronutrients
Generally, fenugreek seeds are richer in macronutrients than fennel seeds. It contains more carbs and protein. Moreover, fenugreek contains less sugar than fennel. Both contain no cholesterol (1). Fennel seeds are more than two times higher in fats. Fenugreek's fat content is 100% saturated fats. Check the macronutrient chart to visualize the distribution of different nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+132%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+142.1%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+45.6%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+11.6%
Fiber
Fennel seeds and fenugreek seeds are excellent sources of fiber. 100g serving of fennel seeds contains 39.8g of fiber and the same amount of fennel seeds - 24.6g. Thus, fennel seeds are richer in fiber content too.
However, the fiber amount is negligible considering their largest actual serving sizes (5.8g for fennel seeds and 11.1g for fenugreek seeds).
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-67.1%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+∞%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+∞%
Calories
Fennel seeds have more calories than fenugreek seeds. Fenugreek seeds have 323 calories per 100 g, whereas fennel seeds have 345 calories per 100 g.
Minerals
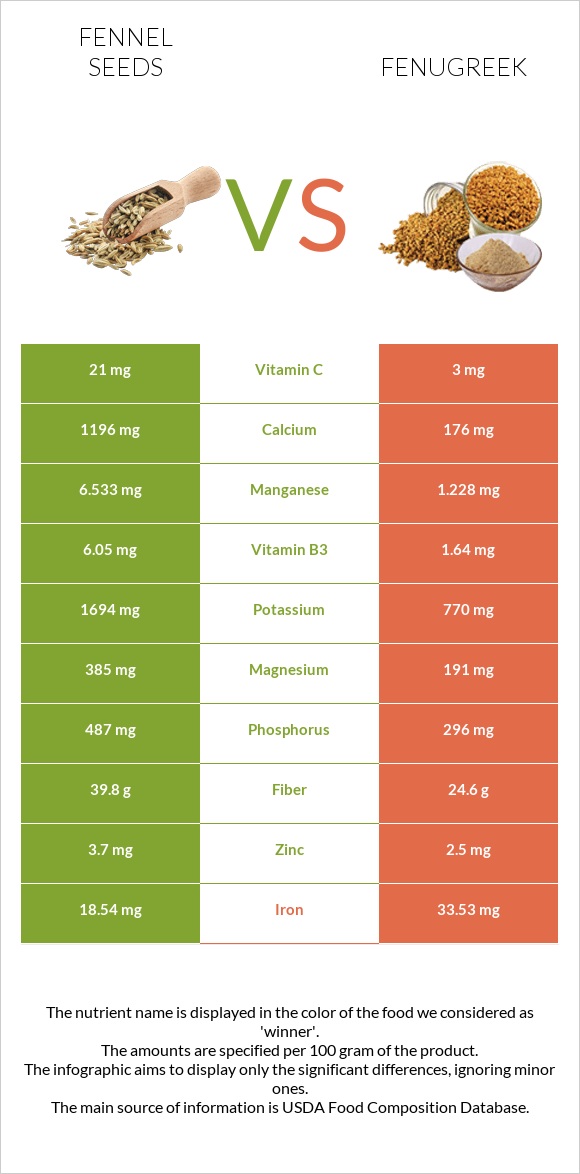
Fennel seeds contain more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and manganese.
The levels of iron are considerably higher in fenugreek. Moreover, the fenugreek contains less sodium (1) (2).
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+101.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+579.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+120%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+48%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+64.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+432%
Contains
more
IronIron
+80.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-23.9%
Potassium
Potassium is an essential mineral that helps muscles work and lowers the risk of kidney stones. Our body cannot produce potassium; it comes from our food.
Fennel seeds have a higher potassium amount. It contains 1694 mg per 100 g, whereas fenugreek seeds have 770 mg per 100 g (1)(2).
Vitamins
The vitamin content of fennel seeds is higher than that of fenugreek seeds. They contain more vitamins A, C, B1, and B3. On the other hand, fenugreek seeds contain more amounts of vitamin B6 (1)(2).
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+600%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+133.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+26.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+268.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+27.7%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index is a value assigned to foods based on how those foods cause increases in blood glucose levels. The difference between the glycemic indexes of these seeds is significant. The estimated glycemic index of fenugreek seeds is 0, whereas the glycemic index of fennel seeds is nearly 16.
Health Benefits
Breastfeeding
Fennel seeds and fenugreek seeds have significant galactogenic properties. This means they promote milk production in breastfeeding women's organisms.
Studies (18) (19) show that fenugreek seeds increase milk production and help babies gain weight. Thus, they may be a natural supplement for increasing milk amounts. Fennel seeds have similar properties (20). However, you must consult your doctor before using these seeds as a supplement during breastfeeding.
Diabetes
Fenugreek has properties that may affect both types 1 and 2 diabetes; moreover, it may increase general carb tolerance (3). According to one study, people who took 100 grams of fenugreek within ten days experienced better blood sugar levels (4). These benefits are connected to the high fiber level of fenugreek, which is a powerful effect seen when fenugreek is used in whole powder or seeds. Nevertheless, studies show that this herb has a role in improving insulin function (5).
Cancer
Fennel has potent antioxidants, such as Vitamin C and Vitamin A, that may help protect cells against damage from free radicals. Besides, fennel seeds contain folate that can play a role in DNA synthesis and repair, which helps prevent cancer cells from forming (6). According to studies, fennel contains limonene, which may help reduce the risk of oxidative stress and has been shown to protect rat cells from damage caused by certain chronic diseases (7).
Weight Loss
Dietary fiber is essential in weight management, as it helps people feel full longer. Besides, fenugreek contains vitamin B6, which is essential in energy metabolism by breaking down carbohydrates and proteins into glucose and amino acids. However, people usually use these seeds in minimal quantities, so calories will not matter (8).
Cardiovascular Health
Both fenugreek and fennel seeds have been studied for their potential cardiovascular health benefits, although they have different compositions and mechanisms of action.
Fenugreek seeds contain soluble fiber, which has been shown to help reduce total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL or “bad” cholesterol) levels. High levels of LDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases (9).
While research specifically on fennel seeds' effects on cholesterol is limited, some animal studies suggest that fennel may help reduce total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels, similar to fenugreek (10).
Fenugreek seeds have been researched for their potential to enhance blood sugar control in people with diabetes, which can help prevent complications like cardiovascular disease (9).
Fennel seeds and fenugreek have been studied for their potential to lower blood pressure, which could help maintain cardiovascular health. Additionally, they are rich in antioxidants like flavonoids and phenolic compounds, which may reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially lowering cardiovascular risk (9).
In conclusion, both fenugreek and fennel seeds offer potential cardiovascular health benefits, but fenugreek seeds, with their more extensive research backing, may have a slightly stronger impact on cholesterol and blood sugar regulation. However, incorporating both into a balanced diet may offer synergistic benefits for overall cardiovascular health.
Hormones Levels
One of the main reasons men use fenugreek is that this herb may boost testosterone. It has beneficial effects, such as increasing libido. According to one study, 30 men took 600 mg of fenugreek extract. Results show that most participants reported increased strength and improved sexual function (11). On the other hand, fennel seeds are a good source of phytoestrogens, which may help with hormonal balance in women. Fennel tea daily can reduce hormonal issues and risks, such as polycystic ovaries and hyperthyroidism (12).
Inflammation
According to the mice study, fenugreek extract has anti-inflammation effects. These effects are connected to the high level of antioxidants in fenugreek, such as flavonoids. However, more research is needed in humans (13). Fennel has an essential nutrient, which is called choline. This nutrient is similar to Vitamin B and can help sleep, muscle movement and reduce chronic inflammation (14).
Bone Health
The vitamin and mineral content in fenugreek is essential in building and maintaining bone structure. According to studies, food containing high levels of magnesium may help strengthen bones. Besides, iron and zinc are crucial for the production and maturation of collagen. Fenugreek is a good source of these minerals, preventing bone‐related disorders such as osteoporosis (15).
Downsides and Risks
Both herbs are safe for health if consumed in fewer doses. However, side effects of fenugreek include diarrhea and indigestion. The side effects of fennel may include sun sensitivity and a mild increase in menstrual flow (16) (17).
Allergy
Fenugreek allergy occurs mainly due to a primary allergy to peanuts. The symptoms usually include swelling in the throat and mouth, difficulty breathing, and severe asthma. People who have an allergy to peach, celery, or carrot may have an allergy to fennel. The symptoms include vomiting, hives, and rash (16) (17).
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319562X15002107
- https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/18313545.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3286242/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2194788/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19857068/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6160559/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28260017/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19353539/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0965229920300091
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21312304/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5909942/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19051589/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31368565/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25010626/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23210484/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9087156/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21261516/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4585338/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4165197/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 6.533mg | 1.228mg | 231% |
| Iron | 18.54mg | 33.53mg | 187% |
| Calcium | 1196mg | 176mg | 102% |
| Fiber | 39.8g | 24.6g | 61% |
| Magnesium | 385mg | 191mg | 46% |
| Vitamin B3 | 6.05mg | 1.64mg | 28% |
| Potassium | 1694mg | 770mg | 27% |
| Phosphorus | 487mg | 296mg | 27% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 9.91g | 25% | |
| Vitamin C | 21mg | 3mg | 20% |
| Protein | 15.8g | 23g | 14% |
| Folate | 57µg | 14% | |
| Fats | 14.87g | 6.41g | 13% |
| Zinc | 3.7mg | 2.5mg | 11% |
| Selenium | 6.3µg | 11% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.69g | 11% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.47mg | 0.6mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.408mg | 0.322mg | 7% |
| Copper | 1.067mg | 1.11mg | 5% |
| Saturated fat | 0.48g | 1.46g | 4% |
| Carbs | 52.29g | 58.35g | 2% |
| Calories | 345kcal | 323kcal | 1% |
| Sodium | 88mg | 67mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.353mg | 0.366mg | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 4.579710144927536g | 7.120743034055727g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 218.35443037974682kcal | 140.43478260869566kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 12.49g | 33.75g | N/A |
| Vitamin A | 7µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.253mg | 0.391mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.602mg | 0.898mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.695mg | 1.241mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.996mg | 1.757mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.758mg | 1.684mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.301mg | 0.338mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.647mg | 1.089mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.915mg | 1.102mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.331mg | 0.668mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Fennel seeds - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171323/nutrients
- Fenugreek - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171324/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





