Salmon vs. Rockfish — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Compared to rockfish, salmon is richer in vitamin D, vitamin B12, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, vitamin B1, vitamin B5, and vitamin A RAE. Salmon also has a 14 times higher vitamin A content and less saturated fat.
Rockfish, on the other hand, have more selenium and vitamin B2.
Introduction
The main nutritional differences between salmon and rockfish will be covered in this article. Salmons are lengthy fish with a silver-to-pink color range.
A rockfish is a silverfish with a white belly. The Atlantic striped bass is another name for it.
Taste and Use
Rockfish is a popular choice for cooking techniques, including steaming, broiling, or roasting, because of its buttery and non-fishy flavor.
On the other hand, salmon is a flexible fish that can be utilized in many different recipes. It is frequently substituted for other ingredients in the kitchen and is adored for its flavor. Island salmon is especially coveted and utilized in many cuisines in Charlotte. Salmon pasta, salmon tacos, and sesame-crusted salmon are popular recipes highlighting the fish's adaptability to many cultures and cooking techniques.
Varieties
Rockfish are frequently encountered in the North Pacific and Bering Sea regions. Examples of these fish include Canary Rockfish, Copper Rockfish, and Widow Rockfish.
In contrast, salmon is a member of the family Salmonidae and comprises some species, including the Atlantic, Chum, and Masu salmon. These salmon species belong to the larger class of fish known as salmonids, including char and whitefish.
Nutrition
Meat from salmon and rockfish is a good source of macronutrients and beneficial chemicals. However, we developed the nutritional infographic to help you distinguish between them. Locate it below.
Macronutrients and Glycemic Index
Salmon and rockfish flesh provide almost the same amounts of protein and cholesterol. Neither contains any sugar or fiber, and both have a glycemic index of 0.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+662.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+15.3%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+85%
Calories
Compared to rockfish, which has 109 calories per serving, salmon has 206 calories per serving.
Protein
With 22.1g and 22.23g of protein per meal, respectively, rockfish and salmon are great protein providers.
Fats
Salmon has a far greater fat and omega-3 concentration than rockfish.
Compared to rockfish, salmon has higher levels of omega-6 (eicosadienoic acid), polyunsaturated fats (such as DHA, EPA, and DPA), and monounsaturated fats.
On the other hand, rockfish contain no trans fats and more saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+797.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+838.8%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-82.5%
Vitamins
Compared to rockfish, salmon is much richer in the majority of vitamins. Compared to rockfish, it has a higher level of vitamin A, vitamin A RAE, vitamin E, vitamin D, vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, folate, and vitamin B12. However, compared to salmon, rockfish has a tiny bit more vitamin B2.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+1280%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+159.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+184.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+1159.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+177.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+265.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+168.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+76.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+240%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+67.4%
Minerals
Rockfish have somewhat higher quantities of calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, and selenium compared to salmon.
On the other hand, the amounts of Phosphorus, Sodium, and Copper in Salmon are more significant than in rockfish. Both fish offer the exact amounts of zinc and manganese content.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+19.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-31.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+23.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+13.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+21.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+84.1%
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to offer various cardiovascular benefits, including reducing triglycerides and blood pressure and lowering the risk of heart disease (1). Salmon is an excellent source of omega-3s, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and DHA. Salmon also contains bioactive PLs with cardioprotective effects (2). Studies suggest consuming 0.45–4.5 grams of omega-3 fatty acids daily can improve arterial function (3). Similarly, rockfish is associated with a lower risk of heart disease thanks to its omega-3 fatty acid content. These essential nutrients are crucial for overall health, as the human body cannot produce them and must obtain them through our diet. Incorporating fish like salmon and rockfish into our meals can contribute to a heart-healthy diet.
Downsides and Risks
Foods with modest mercury content include rockfish. While it's safe for healthy middle-aged people, it can harm young, pregnant, or teenagers (4). Reduce your seafood intake to prevent mercury poisoning.
Salmon, which is high in salt, is vital for health. But keep consumption to no more than 2.3mg each day. Swelling may be brought on by too much salt (5).
Infographic
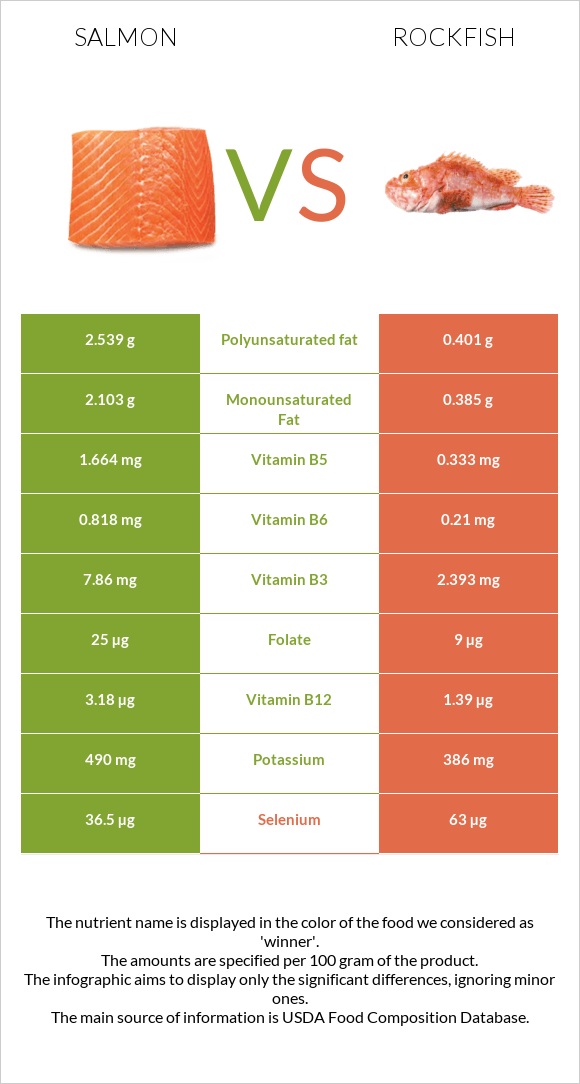
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 41.4µg | 76.2µg | 63% |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.8µg | 1.59µg | 50% |
| Vitamin D | 526 IU | 183 IU | 43% |
| Vitamin D | 13.1µg | 4.6µg | 43% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.045mg | 2.897mg | 32% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.647mg | 0.241mg | 31% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 4.553g | 0.485g | 27% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.34mg | 0.027mg | 26% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.475mg | 0.404mg | 21% |
| Fats | 12.35g | 1.62g | 17% |
| Saturated fat | 2.397g | 0.42g | 9% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.181g | 0.466g | 9% |
| Vitamin A | 69µg | 5µg | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.135mg | 0.226mg | 7% |
| Folate | 34µg | 10µg | 6% |
| Calories | 206kcal | 109kcal | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 1.14mg | 0.44mg | 5% |
| Vitamin C | 3.7mg | 0mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 384mg | 467mg | 2% |
| Choline | 90.5mg | 78.7mg | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 63mg | 61mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 30mg | 33mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.049mg | 0.041mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 252mg | 248mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 61mg | 89mg | 1% |
| Protein | 22.1g | 22.23g | 0% |
| Calcium | 15mg | 17mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 0.36mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0.43mg | 0.43mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.016mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.025g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.248mg | 0.296mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.969mg | 1.014mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.018mg | 1.06mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.796mg | 1.835mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.03mg | 2.188mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.654mg | 0.707mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.863mg | 0.935mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.139mg | 1.106mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.651mg | 0.502mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.69g | 0.107g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 1.457g | 0.238g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.17g | 0.027g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.005g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Salmon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175168/nutrients
- Rockfish - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175131/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






