Powerade vs. Gatorade - Is There A Difference?


Summary
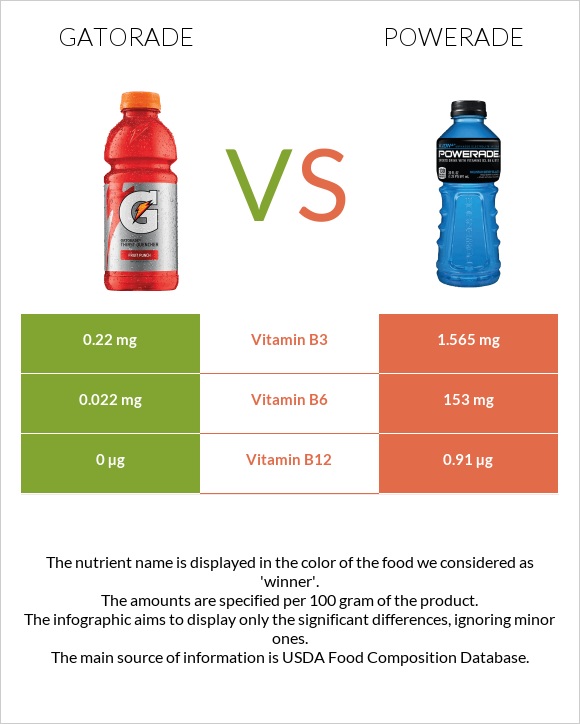
Powerade is richer in vitamins B3 (niacin), B6, and B12. Gatorade, in comparison, has a slightly lower carb content. However, Gatorade contains almost 5 times more sucrose, while Powerade is higher in other sugars, particularly fructose.
Powerade ION4 is more beneficial compared to regular Powerade and Gatorade. Powerade ION4 is richer in magnesium and calcium.
Introduction
Powerade and Gatorade are isotonic, non-carbonated, popular sports drinks specially made for athletes. During an athletic activity, a person loses body fluids and electrolytes from sweat; thus, it is essential to replenish water and electrolytes to stay active and not get tired quickly. Sports drinks are specially made to replenish electrolytes and fluids. Gatorade and Powerade are two of the most popular competitors for sports drinks.
Sports drinks do not stimulate you, so they are not energy drinks.
These are replenishing drinks to keep you on top of your performance during your performance. They do not contain stimulants such as caffeine, etc.
One of the fundamental differences is that Powerade is a Coca-Cola company drink, whereas Gatorade is a Pepsico drink.
In a way, it is similar to comparing Coca-Cola and Pepsi colas to one another; however, there are significant differences between Powerade and Gatorade.
Powerade is labeled as an ION4 electrolyte replenishing system. It mainly focuses on four electrolytes sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. That being said, not all Powerade have the ION4 composition.
There is a difference between Powerade and Gatorade concerning the available flavors and tastes. However, these are not major concerns regarding nutrition.
Ingredients
According to the Coca-Cola website Powerade contains water, glucose, citric acid, acidity regulators (Sodium Citrate, Potassium Citrate), fructose, stabilizers (Acacia Gum, Glycerol Esters of Wood Rosins), and sweeteners (Aspartame, Acesulfame-K) (1).
The official website for Gatorade states that this drink contains the following: sugar, dextrose, citric acid, salt, sodium citrate, monopotassium phosphate, calcium silicate, modified food starch, and natural and artificial flavors (2).
Nutritional Content
This section will compare the nutritional values of ready-to-drink lemon-lime flavored Powerade and ready-to-drink Gatorade G performance O2. These are low-carb versions of these sports drinks.
The comparison infographics below are based on 100ml of each. However, a person, on average, drinks at least 8fl oz bottle of Gatorade and Powderade, equal to 244ml., which equals to 244ml.
Calories
They are low in calories since they are not meant to refuel energy stores in the body. A 100ml of Powerade provides 32 calories, while the same serving of Gatorade has 26 calories.
Carbs
Powerade is higher in carbohydrates, containing 7.8g per 100ml, while the same serving of Gatorade has 6.4g of carbohydrates. These are the low-carb varieties of these drinks.
However, there are 0-carb versions of both, known as Powerade Zero and Gatorade G2 Zero. The regular carbohydrate versions are called Powerade and Gatorade Thirst Quencher.
Powerade contains almost 2 times more sucrose, while Gatorade is almost 5 times higher in sucrose.
Sweeteners
Regular Powerade is mainly sweetened by high-fructose corn syrup, while Gatorade mainly contains dextrose sugar. Powerade has a sweeter taste due to a higher content of fructose.
Protein and Fats
The protein and fat content are negligible.
Minerals
This is the most important part to consider when comparing these beverages. The main goal of Powerade and Gatorade are to refill your electrolyte and fluids during workouts.
Powerade has regular bottles and an edition with ION4 written on it. The main difference is that ION4 has additional magnesium and calcium ions. In comparison, the regular ones contain sodium and potassium. Considering the regular version of Powerade and not the ION4 composition, they are nearly similar in sodium and potassium contents.
However, if we consider the ION4 version of Powerade, it will be richer in magnesium and calcium.
It is important to understand that the mineral contents are not there to fill daily mineral values. They are just there to substitute for the lost electrolytes during a 1 to 2-hour workout.
The Gatorade G performance O2 is 10 times richer in phosphorus and contains copper and manganese, which Powerade lacks entirely.
On the other hand, lemon-lime-flavored Powerade is richer in iron and potassium.
We can visualize the mineral micronutrient comparison below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+900%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+20%
Contains
more
IronIron
+80%
Vitamins
Powerade contains higher amounts of vitamins B3 or niacin, B6, and B12. Gatorade is mostly absent in these vitamins.
In comparison, Gatorade provides low levels of vitamins C, B5, and K, which Powerade lacks.
You can find the comparison infographics below.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+611.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+695354.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Health impacts
This section will be based on research on this beverage in the athletic sphere. Showcasing if they are of any benefit or not.
Rehydration After Exercise
Gatorade and Powerade were shown to have higher hydration than water regarding the same volume consumed during the same time. However, there was no remarkable difference between the two regarding hydration (3).
However, the added sodium in these drinks did not replenish the amount lost to its previous amounts (4, 5).
Rehydration After Gastroenteritis
During gastroenteritis, there is decreased electrolyte and water absorption, leading to diarrhea. After several hours, the patient might become dehydrated.
A study has shown that consumption of Gatorade during mild viral gastroenteritis can lead to decreased risks of dehydration or at least slow down the rate of dehydration to settle in (6).
However, sports drinks are high in sugar, thus have a high osmolarity, contain little sodium and potassium, and may lead to worsened diarrhea and hyponatremia (7).
Impact on Dental Health
Powerade and Gatorade contain citric acid, which is linked to increased dental enamel erosion. However, it was shown that calcium-containing beverages decreased the risks of enamel erosion. According to research, the ION4 composition of Powerade has reduced the risks of enamel erosion since it contains calcium (8).
Video Summary
References
- https://www.coca-cola.co.uk/brands/powerade
- https://www.pepsicoproductfacts.com/Home/product
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10739268/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18461208/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18461208/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16931613/
- https://www.siumed.edu/sites/default/files/u1031/gastroenteritis_pir_2012.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28028987/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.022mg | 153mg | 11768% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.91µg | 38% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.22mg | 1.565mg | 8% |
| Fructose | 1.82g | 3.22g | 2% |
| Iron | 0.05mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.006mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 10mg | 1mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.013mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.055mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Calories | 26kcal | 32kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0g | 0.05g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 0.4mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 6.43g | 7.84g | N/A |
| Carbs | 6.43g | 7.84g | 0% |
| Calcium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 15mg | 18mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 5.24g | 6.11g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.01mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 39mg | 42mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.011mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.2µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0g | 0.008g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0g | 0.011g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0g | 0.028g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +∞% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +21.9% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +360% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +76.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Gatorade - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173660/nutrients
- Powerade - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175108/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






