Chicken vs Lamb - Nutrition and Health Impact Comparison


Summary
Chicken is a healthier option compared to lamb meat. The health impacts of chicken are more beneficial than those of lamb. Chicken is lower in fats and richer in proteins, vitamins B3, B5, and B6. Lamb is richer in selenium, zinc, copper, potassium, phosphorus, iron, and vitamins B2 and B12.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between two types of highly consumed protein foods, chicken and lamb.
These two types of meats differ regarding their nutritional content and health impacts. We will dig deep into the comparison of these two types of meats to better understand what they are composed of regarding their nutritional content and health impacts.
In this article, we will consider chicken and lamb in cooked forms. We are considering the broiled chicken, mainly raised for its meat. In comparison, we are considering a domestic form trimmed from fat for lamb.
Nutritional Content Comparison
This section is a deep dive into the nutrients of chicken meat and lamb. We will take into consideration 100g of each.
Calories
Lamb is slightly higher in calories compared to chicken meat. Their fat content difference mainly creates this difference.
Lamb contains 294 calories, whereas chicken meat has 239 calories.
Fats
Chicken meat is much lower in fats compared to lamb meat. Chicken meat contains 13.6 grams of fat, whereas lamb meat contains 21 grams.
This difference is quite significant between them.
Since the total fat is significantly different between them, their saturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and monounsaturated fatty acids will showcase a difference aswell.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+65.2%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-57.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+96.7%
Chicken meat is lower in saturated fat than lamb by 2.3 times, and it is lower in polyunsaturated fat aswell. However, lamb meat is richer in monounsaturated fats.
In the fat section, it is important to understand that different cuts in both chicken and lamb can have different fat content.
Trimming the lamb or removing the skin from the chicken can create a difference aswell.
Cholesterol
Lamb meat is higher in dietary cholesterol compared to chicken.
Protein
Chicken meat is richer in protein compared to lamb meat. Chicken meat contains 27g of protein, whereas lamb contains 24.5g.
They are considered high-quality proteins since their amino acid profile is diverse and rich in essential amino acids.
Chicken breast is the cut that is the richest in proteins.
Overall, chicken is a good source of protein.
Carbs
Their carb content is negligible.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+54%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+11.3%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+10.7%
Minerals
Lamb is richer in minerals compared to chicken. Lamb is richer in selenium, zinc, copper, potassium, phosphorus, and iron.
It is important to note that chicken has a rich content of selenium, iron, zinc, and phosphorous. However, considering the comparison, it is less than the amounts present in lamb.
Both have the same amounts of magnesium. Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+13.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+39%
Contains
more
IronIron
+49.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+80.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+129.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-12.2%
Vitamins
Chicken is richer in vitamin B3, vitamin B5, and vitamin B6. In comparison, lamb is richer in vitamin B2 and vitamin B12.
Lamb is richer in vitamin B1 and vitamin K; in turn, chicken is richer in vitamin A. However, their amounts are not very significant.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+58.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+48.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+750%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+91.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+260%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+92.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+27.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+56.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+207.7%
Health Impacts
One of the essential differences to remember is that chicken meat is white meat, and lamb meat is red meat. Because of this difference, we have numerous health impacts, which will be discussed in the section below.
Cancer
In this article, there is a controversy around lamb meat, which is red meat. However, it is important to understand the difference between processed red meat and unprocessed red meat.
Unprocessed lamb meat, or red meat, is generally considered safe to eat because there is no concrete link between cancer and the consumption of red meat.
IARC classified red meat as group 2A; the keyword in this classification is “probably” carcinogenic.
In moderation, the consumption of lamb meat is considered safe.
If you are wondering what the amount is, the WHO hasn’t determined the proper amount considered safe (1)(2).
In comparison, according to the IARC, it is considered safe to consume chicken. However, a question mark arises from the skin and high-temperature exposure, which would create heterocyclic amines that are associated with increased risks of cancer (3).
Chicken meat was negatively associated with risks of colorectal cancer (4).
In conclusion, eating chicken meat and lamb meat in moderation is safe.
You can read about lamb meat vs beef in this article.
Cardiovascular Health
When it comes to cardiovascular health, chicken meat is considered a better option compared to lamb meat. Lamb meat is higher in saturated fats and is positively associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases and ischemic heart diseases (5).
In comparison, chicken meat is a better option than lamb meat in terms of its effects on the cardiovascular system; overall, it is low in fat and saturated fats.
Substituting chicken meat with red meat, such as lamb meat, has decreased the risk of heart disease (6).
Consuming chicken is linked to lower levels of "bad" LDL cholesterol and may have a role in decreasing cardiovascular risk. Additionally, recent studies suggest that proteins in chicken breast may inhibit ACE, a key enzyme responsible for raising blood pressure. These proteins work similarly to antihypertensive medications like Captopril, Lisinopril, and Perindopril (7,8).
You can also read about the difference between chicken meat and salmon in terms of the cardiovascular system.
Weight Loss
Chicken meat is often recommended for athletes in sports nutrition. One of the main protein sources for bodybuilders is chicken. It’s mainly due to chicken meat being higher in protein and lower in calories and fats.
You can eat more chicken breast and feel fuller while getting fewer calories and more protein.
In addition, chicken meat is more practical than lamb meat. Chicken meat is cheaper, more accessible, and easier to cook with.
Pork vs chicken goes deep into the differences between these two types of meats.
Antibiotics Use
Antibiotic use in poultry is one of the main concerns in the food industry nowadays since there is no monitoring of what antibiotics are used and how much. Residual antibiotics are often found in cooked broiled chicken, which concerns the environment and nutrition (9).
The main issue regarding this is the microbes that are becoming resistant to certain antibiotics.
Questions
Which is better, chicken or lamb meat?
Considering all their health impacts, chicken meat is a better option to consume regarding its effects on our health.
Is chicken or lamb easier to digest?
Chicken meat is easier to digest than lamb.
What gives lamb its peculiar taste?
Lamb meat has a peculiar taste, and the older the sheep, the more prominent the taste, such as in the case of mutton meat. This is mostly due to compounds such as branched chained fatty acids. Lanolin is one of the most prominent fatty acids in sheep, which gives that taste profile to it aswell.
How do you remove the gamey taste from lamb?
Young lambs have a less gamey taste; this flavor is reduced when prepared with garlic and herbs.
References
- https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/cancer-carcinogenicity-of-the-consumption-of-red-meat-and-processed-meat
- https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/opinions_layman/en/electromagnetic-fields/glossary/ghi/iarc-classification.htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12067585/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15342453/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37363999/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34542332/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8203993/
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf020604h
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29537307/
Infographic
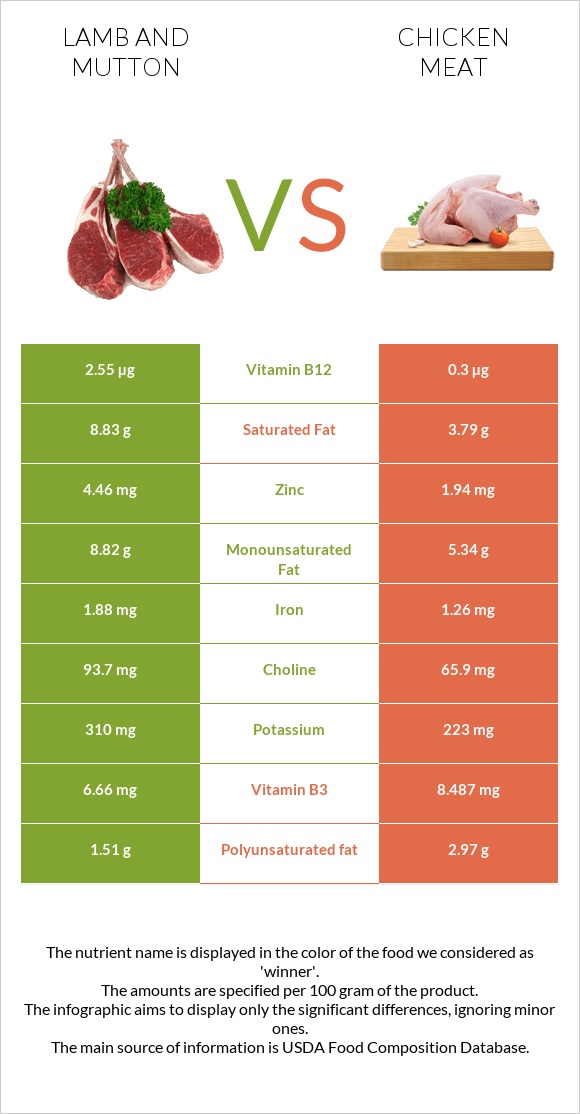
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.55µg | 0.3µg | 94% |
| Zinc | 4.46mg | 1.94mg | 23% |
| Saturated fat | 8.83g | 3.79g | 23% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.13mg | 0.4mg | 21% |
| Fats | 20.94g | 13.6g | 11% |
| Vitamin B3 | 6.66mg | 8.487mg | 11% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.51g | 2.97g | 10% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.82g | 5.34g | 9% |
| Iron | 1.88mg | 1.26mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.66mg | 1.03mg | 7% |
| Protein | 24.52g | 27.3g | 6% |
| Copper | 0.119mg | 0.066mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.25mg | 0.168mg | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 48µg | 5% |
| Selenium | 26.4µg | 23.9µg | 5% |
| Choline | 93.7mg | 65.9mg | 5% |
| Calories | 294kcal | 239kcal | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 97mg | 88mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 310mg | 223mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.1mg | 0.063mg | 3% |
| Folate | 18µg | 5µg | 3% |
| Vitamin K | 4.6µg | 2.4µg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 188mg | 182mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.14mg | 0.27mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 2 IU | 2 IU | 0% |
| Magnesium | 23mg | 23mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 17mg | 15mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 72mg | 82mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.022mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.287mg | 0.305mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.05mg | 1.128mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.183mg | 1.362mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.908mg | 1.986mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.166mg | 2.223mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.629mg | 0.726mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.998mg | 1.061mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.323mg | 1.325mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.777mg | 0.802mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.04g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.02g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lamb - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172480/nutrients
- Chicken meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171450/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




