Pistachio vs. Almonds — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Almond has more Vitamin E, B2, magnesium, calcium, and fiber. It also has a lower glycemic index.
On the other hand, pistachios contain Vitamin B6, Vitamin B1, copper, and potassium.
Introduction
We’ll compare the two most famous nuts: pistachio and almond. Both are healthy snake options and have different nutritional benefits.
What’s The Actual Difference?
Pistachios are the edible seeds of a minor, long-lived Central Asian tree in the Anacardiaceae family. They are not true nuts but rather stone fruits known as drupes. The Prunus genus includes almonds, also known as Prunus dulcis.
Pistachios and almonds are different in color, size, and taste. Pistachio has a smooth texture and a sweet, sometimes earthy flavor, while almonds have an earthy flavor, while their skin might taste bitter.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for raw pistachio and raw almond. At the bottom of this page, you can find the nutrition infographics.
Minerals
Pistachio contains more potassium and copper. 100g of these pistachios can cover your daily need for potassium.
Almonds have more magnesium, calcium, and zinc than pistachio.
Both nuts have an equal level of iron, magnesium, and sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+39.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+26.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+70.7%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+123.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+156.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+41.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+81.6%
Vitamins
Pistachios have a higher amount of vitamins than almonds. They have 25 times more Vitamin A and 11 times more Vitamin B6.
Pistachios are also higher in Vitamin B6, B5, folate, and B1.
Despite that, almonds have more Vitamin E, B2, and B3 than pistachio.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+324.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+1140.9%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+15.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+796.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+611.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+178.3%
Protein and Fat
Both pistachio and almonds are rich in fats and protein. Almonds contain more monounsaturated fat, whereas pistachios contain more polyunsaturated fats.
Carbs
Both nuts have equal carbs; almonds have more fiber than pistachios.
Glycemic Index
Overall, nuts are low glycemic index food.
The glycemic index of pistachio is 28, whereas almonds have a glycemic index of 0.
Calories
Both nuts are rich in calories. Almonds have 579 calories per 100 g, whereas pistachio has 560 calories per 100 g.
Health Impact
Diabetes
Because of their unsaturated fats and fiber content, nuts are one of several foods that benefit people with type 2 diabetes.
According to the study, individuals with type 2 diabetes showed a 9% reduction in fasting blood sugar after eating 25 grams of pistachios twice a day [1].
Almonds in a diabetic patient's diet have been shown to improve insulin levels and glycemic control [2].
Cardiovascular Health.
According to this study, almond intake may reduce diastolic blood pressure; however, there was no effect of almond consumption on systolic blood pressure. Unlike almonds, pistachio consumption may significantly decrease systolic blood pressure [3,4].
Almond and pistachio have peptides that may inhibit ACE enzymes, like ACE-inhibitor medications (Captopril, Lisinopril, etc.) [5,6].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Pistachio and almond allergies are common in patients with tree pollen allergies. Itching, swelling, and burning in the mouth and throat are common symptoms.
If you are allergic to nuts, try to avoid eating tree nuts, even if you have only been diagnosed as allergic to one type [7].
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25396407/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20580779/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0965229920301849
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/effects-of-pistachios-on-anthropometric-indices-inflammatory-markers-endothelial-function-and-blood-pressure-in-adults-a-systematic-review-and-metaanalysis-of-randomised-controlled-trials/6451124FEA257E9A76295B6697FAFE6E
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/fo/c6fo00654j/unauth
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1359511314000816
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0091674976900865
Infographic
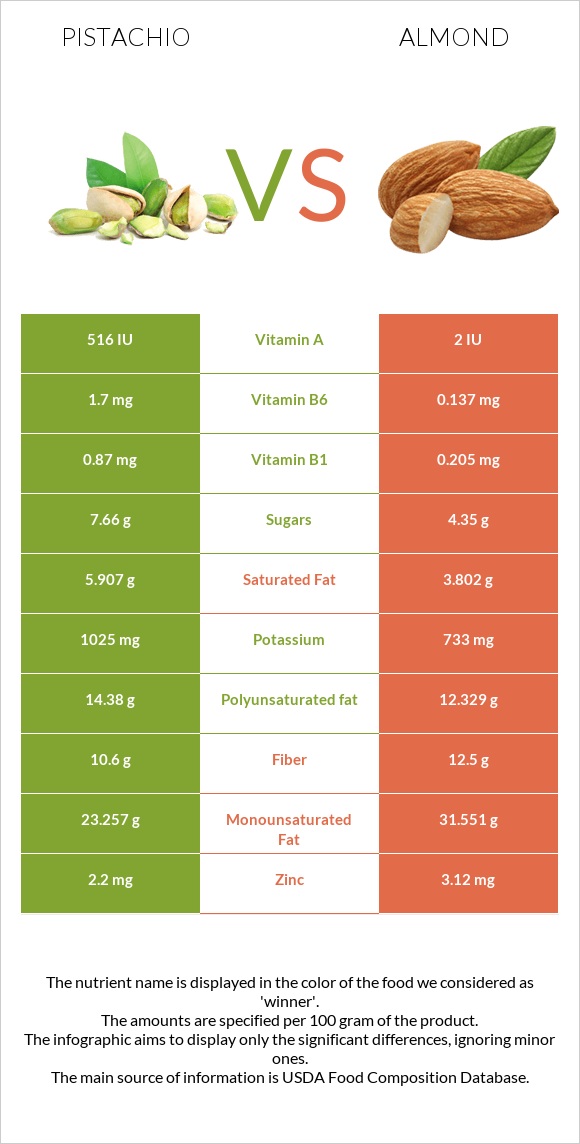
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 2.86mg | 25.63mg | 152% |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.7mg | 0.137mg | 120% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.16mg | 1.138mg | 75% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.87mg | 0.205mg | 55% |
| Manganese | 1.2mg | 2.179mg | 43% |
| Magnesium | 121mg | 270mg | 35% |
| Copper | 1.3mg | 1.031mg | 30% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 23.257g | 31.551g | 21% |
| Calcium | 105mg | 269mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.3mg | 3.618mg | 14% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 14.38g | 12.329g | 14% |
| Saturated fat | 5.907g | 3.802g | 10% |
| Potassium | 1025mg | 733mg | 9% |
| Choline | 52.1mg | 9% | |
| Fiber | 10.6g | 12.5g | 8% |
| Zinc | 2.2mg | 3.12mg | 8% |
| Fats | 45.32g | 49.93g | 7% |
| Vitamin C | 5.6mg | 0mg | 6% |
| Selenium | 7µg | 4.1µg | 5% |
| Iron | 3.92mg | 3.71mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 26µg | 0µg | 3% |
| Protein | 20.16g | 21.15g | 2% |
| Carbs | 27.17g | 21.55g | 2% |
| Folate | 51µg | 44µg | 2% |
| Calories | 560kcal | 579kcal | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 490mg | 481mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.52mg | 0.471mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 16.57g | 9.05g | N/A |
| Sugar | 7.66g | 4.35g | N/A |
| Starch | 1.67g | 0.72g | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0g | 0.015g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.251mg | 0.211mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.684mg | 0.601mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.917mg | 0.751mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.604mg | 1.473mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.138mg | 0.568mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.36mg | 0.157mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.092mg | 1.132mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.249mg | 0.855mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.512mg | 0.539mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.24g | 0.11g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0g | 0.002g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 14.091g | 12.32g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +26.1% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +10.2% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +16.6% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -35.6% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +35.7% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +131.9% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +73.9% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +88.2% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +118.2% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +325% |
| Contains more GalactoseGalactose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pistachio - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170184/nutrients
- Almonds - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170567/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





