Shallots vs. Onions — Nutrition and Health Impact Differences

Summary
Shallots are richer in fiber, copper, manganese, phosphorus, iron, potassium, vitamin C, B6, and folate. Overall, shallots are more nutritious than onions (yellow onions). Shallots are sweeter and have a milder taste. Shallots are richer in phytochemicals.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between shallots and onions. You might ask, "What's the difference between them?" They have several differences, primarily based on culinary usage, taste, and flavor. In addition to these, there are nutritional differences that we will be tackling in this article.
Nutrition
This article compares 100g of yellow onions to 100g of shallots.
Calories
Shallots are higher in calories compared to onions.
Shallots contain 72 calories, whereas onions contain 40 calories.
Carbs and fiber
Shallots are higher in overall carbs. However, they contain nearly twice the amount of fiber of onions.
Fat and protein
Their fat and protein content is negligible.
Oxalates
Onions contain 5mg of oxalates, whereas shallots do not contain oxalates. They have negligible amounts of oxalates.
Minerals
Shallots have a richer mineral profile. It is richer in all minerals compared to onions. Shallots are significantly richer in copper, manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, and potassium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-66.7%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+110%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+60.9%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+128.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+471.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+125.6%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+135.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+106.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+126.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+140%
Vitamins
Shallots are richer in vitamins B1, C, B6, and folate.
Overall, shallots contain more nutrients regarding their macros, vitamins, and minerals.
Health Impacts
Onions are associated with anticarcinogenic, antibacterial, antithrombotic, and antiallergic properties.
Overall, you can expect to treat cancer with onions. However, lifelong proper nutrition reduces the risk of developing cancer (1).
In comparison, shallots have been shown to have antioxidative and antiallergic activities. In addition, the consumption of shallots has been shown to have positive effects on the cardiovascular system and in the control of blood glucose levels in diabetes (2)(3)(4).
Raw shallots and raw onions are excellent vegetables to eat.
The health benefits of both onions and shallots are derived from phytochemicals such as quercetin, flavonoids, phenolic compounds, and organosulfur.
Shallots have a richer phytochemical profile than onions (5). From these are flavonoids, quercetin, phenolic compounds, and organosulfur.
General Differences
Usage
Onions are often used in stir-fry dishes and stews and overall in cooking. Shallots have a different flavor profile that can be used in garnishing, salad dressing, and sauces (vinaigrette).
In a recipe where you must caramelize onions, it's best to use shallots. This is mainly because shallots contain more carbs and sugars. Yellow onions are mainly used for French onion soups.
You can read about onion vs. garlic in this article.
Taste and flavor
Shallots are smaller and have a sweeter, milder taste with a hint of garlicky (alliums) flavor. Onions are more pungent.
They are both members of the allium family.
Substitutions
Well, you can substitute onions and shallots. However, the flavor profile of the dish might change.
For example, swapping onions with shallots will add sweetness to salads.
You can read about chives vs. scallions in this article.
To prepare vegetable broths, you can use onions, shallots, white onions, red onions, leeks, and onion peel.
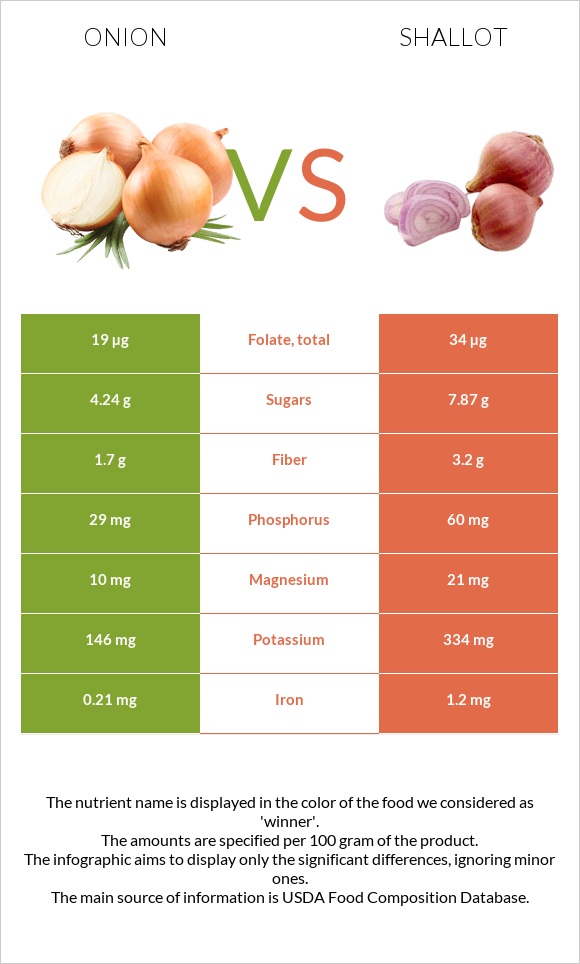
Infographic
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +35% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +100% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +30.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +72.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +135.8% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +187.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +100% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +78.9% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12mg | 0.345mg | 17% |
| Iron | 0.21mg | 1.2mg | 12% |
| Manganese | 0.129mg | 0.292mg | 7% |
| Potassium | 146mg | 334mg | 6% |
| Fiber | 1.7g | 3.2g | 6% |
| Copper | 0.039mg | 0.088mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 29mg | 60mg | 4% |
| Folate | 19µg | 34µg | 4% |
| Protein | 1.1g | 2.5g | 3% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 21mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.123mg | 0.29mg | 3% |
| Calories | 40kcal | 72kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 9.34g | 16.8g | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 0.4mg | 2% |
| Fructose | 1.29g | 2% | |
| Vitamin C | 7.4mg | 8mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 23mg | 37mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.5µg | 1.2µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.046mg | 0.06mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.02mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.116mg | 0.2mg | 1% |
| Choline | 6.1mg | 11.3mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.1g | 0.1g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 7.64g | 13.6g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.24g | 7.87g | N/A |
| Sodium | 4mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg | 0.8µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.042g | 0.017g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.013g | 0.014g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.017g | 0.039g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.014mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.021mg | 0.098mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.014mg | 0.106mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.025mg | 0.149mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.039mg | 0.125mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.025mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.021mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0.043mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +11.7% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +127.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +79.9% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +128.6% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -59.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +129.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Onion - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170000/nutrients
- Shallot - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170499/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



