Palm oil vs. Sunflower oil — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Palm oil and sunflower oil don’t contain water, carbs, proteins, and minerals. They are made of fats. Palm oil has higher saturated fats and vitamin K. In contrast, sunflower oil is higher in unsaturated fats and vitamin E. Sunflower oil is safer for overall health but more expensive.
Introduction
Palm oil is the most versatile and widely used oil in the world. It is processed to be used in the food industry, beauty products, and industrial applications like soap and car lubricants. Among its positive aspects, palm oil is cheap and readily available, and it is stable after usage and exposure to heat compared to other frying oils like sunflower.
Sunflower oil is extracted from sunflower seeds. It is a common and highly versatile cooking oil. However, it is more expensive than palm oil and burns faster, decreasing its frying and heating capacity. Despite this, it is considered one of the cheapest oils available on the market. Sunflower oil is versatile in the culinary world and is also used in biofuels and cosmetics.
In this article, we will compare the differences between palm oil and sunflower oil, focusing on their nutritional data, usage in diets, and health impacts.
Appearance
Comparing their fat profiles reveals that both have similar textures. Palm oil is semi-solid at room temperature because it contains more saturated fats, while sunflower oil is liquid at room temperature because it contains more unsaturated fats.
Nutritional data
Palm oil and sunflower oil do not contain any:
- Water
- Protein
- Carbs (so the glycemic index of both palm oil and sunflower oil is 0)
- Minerals
Fats
Compared to sunflower oil, which has more unsaturated fats, palm oil has a higher concentration of saturated fats. It means that sunflower oil is healthier than palm oil.
Many foods consumed as part of a healthy diet plan contain some saturated fat. However, it's crucial to limit intake; a general guideline is to strive for less than 20 grams each day. It should be noted that people who consume fewer than 2,000 calories per day may need to keep their daily intake of saturated fat to under 20 grams (1).
Limiting saturated fats is important, but replacing them with healthier unsaturated fats is the best way to safeguard your health. Based on this, we may offer to replace palm oil with sunflower oil.
Vitamins
Only two vitamins are available in both oils. Vitamin E is higher in sunflower oil, and vitamin K, is higher in palm oil.
As an antioxidant, vitamin E disarms unstable chemicals that can harm cells. Vitamin E-rich diets may aid in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease. Both wrinkle prevention and other aging processes are not slowed by vitamin E. Meanwhile, proteins and calcium necessary for blood coagulation are activated by vitamin K (2).
Calories
They have equal amounts of calories, which is 884 calories per 100g.
Diets and weight-loss
As mentioned above, it’s important to cook with and buy items prepared with oils high in polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat (e.g., canola, maize, olive, peanut, safflower, soybean, and sunflower) rather than butter, shortening, coconut, or palm oils.
Palm oil and sunflower oil are high in calories. While being on a weight-loss diet or healthy lifestyle, it is always recommended to avoid frying foods; It is recommended to add oil to cooked food and not to heat the oil.
Let's discuss the use of these products in various diets.
- Keto diet. Palm oil and sunflower oil have 0 amounts of carbs, so they can be used to prepare keto-friendly meals.
- Vegan diet. Both palm oil and sunflower oil are suitable for vegan consumption. However, vegans usually prefer to avoid palm oil due to its negative effects on the environment.
- The Mediterranean diet is high in fat; however, it is low in dangerous saturated fats such as palm oil, as opposed to sunflower oil, which is suggested throughout this diet.
- Sunflower and palm oils are not recommended on the Paleo diet. Overall, there are far better ways to obtain healthy fats. Oils such as coconut oil, olive oil, nuts and seeds, and animal fats like lard or fatty fish, which are less processed or refined and have longer shelf lives, are better alternatives overall.
- The intermittent fasting method regulates when you eat, just like an eating pattern rather than a diet. As a result, both of these products can be used in this diet. However, it is preferable to use sunflower oil rather than palm oil.
- The DASH diet was created to help treat or prevent high blood pressure (arterial hypertension). Unlike palm oil, sunflower oil is recommended during this diet.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular Health
As previously said, it is important to replace saturated fats with healthy unsaturated fats. Switching to unsaturated fats may lower LDL cholesterol (the "bad" type of cholesterol) levels in the blood. Cutting the LDL level is crucial for people with coronary artery disease or who have had a myocardial infarction (3.4.5). Based on this, we offer to replace palm oil with sunflower oil.
According to this rat study, fresh palm oil has no negative effects on blood pressure or cardiac tissue, but repeated heating may increase blood pressure and necrosis cardiac tissue (6). Sunflower oil, on the other hand, can be employed in dietary patterns that have been shown to decrease blood pressure (7).
On the other hand, compared to sunflower oil, palm oil is richer in vitamin K, whose consumption is important during anticoagulation drug use (2).
Diabetes Mellitus
An unbalanced intake of fats and oils, especially palm oil, can potentially have negative metabolic and glycemic consequences and thus contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. More research is required for more accurate information, particularly in developing countries (8).
Digestive and Liver Health
In a double-blind, randomized experiment on overweight people, it was found that eating too much saturated fatty acid from palm oil caused significant liver fat formation. Both circulating liver enzymes and ceramides increased concurrently, indicating hepatocellular damage. Overeating polyunsaturated fatty acid from sunflower oil, on the other hand, fully inhibited liver fat accumulation and even improved the blood lipid profile despite equal weight gain (9).
The effects of vegetable oils (corn, olive, and sunflower oils) and Vitamin E on antioxidant defense systems in rat stomach tissues against oxidative damage were discovered. These findings demonstrate that indomethacin and other NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines) have no negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract when combined with vegetable oils and vitamin E or as oil formulations (10). This effect on palm oil is unknown.
In addition, sunflower oil may be useful during constipation. For the best results, it should be taken on an empty or almost empty stomach.
Cancer
Two compounds, MCPD and glycidyl esters, are formed during oil production. These substances are associated with the development of cancer. Unlike sunflower oil, palm oil produces these substances in large quantities (11).
On the other hand, sunflower oil contains acylglycerols, which have protective characteristics against the development of colon cancer (12).
Nervous system
Sunflower and palm oils are two of the most plentiful natural sources of tocotrienol (sunflower oil is richer than palm oil), which has distinct neuroprotective effects not shared by other members of the vitamin E family. Oral supplementation with tocotrienol produced from palm oil reaches the brain in sufficient quantities to reduce stroke-induced neuropathy (13).
Allergies
Some people who are allergic to the Asteraceae plant family, such as daisies, might also be allergic to sunflower oil (14),
References
- https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2021-11/DGA_FactSheet_SaturatedFats-07-09_508c_0.pdf
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/listing_of_vitamins
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28620111/
- https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/145/7/1549/4616780
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15983523/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0188440908001331
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMct0911013
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07315724.2010.10719844
- https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/104/12/6207/5540968?login=false
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18621042/
- https://www.fda.gov/food/process-contaminants-food/3-monochloropropane-12-diol-mcpd-esters-and-glycidyl-esters
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27007804/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3065441/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5806758/
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +48.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +157.7% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
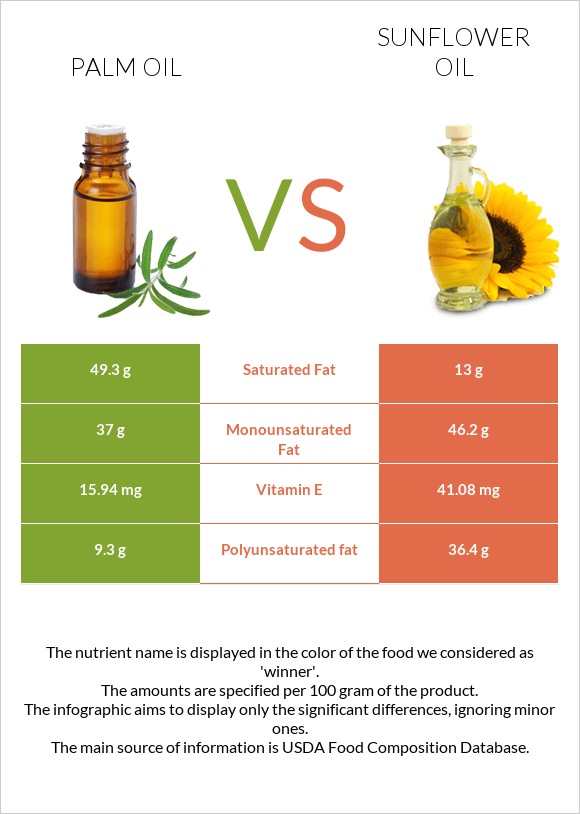
| Polyunsaturated fat | 9.3g | 36.4g | 181% |
| Vitamin E | 15.94mg | 41.08mg | 168% |
| Saturated fat | 49.3g | 13g | 165% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 37g | 46.2g | 23% |
| Vitamin K | 8µg | 5.4µg | 2% |
| Calories | 884kcal | 884kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 100g | 100g | 0% |
| Iron | 0.01mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Choline | 0.3mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -73.6% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +24.9% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +291.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Palm oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171015/nutrients
- Sunflower oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172328/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




