Pecans vs. Cashews — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pecans contain more calories and fats than cashews, while cashews contain around 2 times more protein and carbs.
Cashews provide 2 times more Vitamin B6 and 10 times more Vitamin K. On the other hand, pecans contain approximately 2 times more vitamin B1, vitamin B2, and vitamin E.
Compared to pecans, cashews have relatively higher amounts of minerals. Cashews provide 2 times more copper, magnesium, and phosphorus, as well as 3 times more iron. On the other hand, pecans provide 3 times more manganese.
Introduction
Indeed, it's truly amazing that you can enjoy your favorite snacks while also reaping their health benefits. Yes, I'm talking about nuts. According to research, eating nuts is good for your heart, brain, and overall health.
Here comes the question: which nut suits your needs, dietary requirements, and taste?
Today, we will discuss two delicious nuts: pecan and cashew, focusing on their nutritional values and health impact. Both nuts are irreplaceably used in culinary, particularly in baking and dishes.
What's the Actual Difference?
Varieties
The tropics, Central America, and the Caribbean islands are home to cashews. They are commonly used in Asian cuisines, particularly in India and China, and are often eaten roasted. The most popular cashew variety is the W-180, also known as the "King of Cashews," because they are larger and more expensive. W-210 nuts are commonly referred to as "jumbo" nuts.
The pecan tree is indigenous to South America and Mexico. Pecans have oval or elongated dark brown shells. There are over 500 different varieties of pecans, each with slightly different characteristics such as flavor, texture, size, color, shape, etc. Cape Fear, Desirable, Moreland, Stuart, and Natives are the most common types.
Taste and Culinary
The flavor of pecans is both dry and sweet. They are popular as raw ingredients in pastries, candies, salads, cookies, pasta, and other dishes. Furthermore, the nutshells can be utilized for smoking meats, ground up and incorporated into beauty products, and even used to make delicious ice cream.
Cashew milk is now widely used as an alternative to dairy milk, particularly among vegans and lactose-intolerant people. The flavor of cashews is rich and nutty. They are widely used to prepare salads, fresh yogurt, cookies, bread, and other foods worldwide.
Nutrition
In this section, we will be comparing the nutritional compositions of cashews and pecans, with a specific focus on macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
Usually, the serving size for both cashews and pecans is one ounce or 28.35 grams.
Please note that in this section, we will be referring to 100-gram servings of each to make the comparison easier.
Macronutrients and Calories
The macronutrient composition of pecans and cashews is quite different. Although the predominant macronutrient found in both pecans and cashews is fat, pecans contain a significantly higher amount of it compared to cashews.
Pecans consist of 72% fats, while cashews only contain 44%. Moreover, cashews have a higher protein and carb content than pecans.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+64.1%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+98.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+117.8%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+47.7%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+71.6%
Calories
Both pecans and cashews contain high amounts of calories; however, pecans contain more calories than cashews.
In a 1oz serving, pecans contain 196 calories, while cashews contain 157 calories. Per 100-gram serving, pecans contain 138 more calories than cashews.
Fats
Pecans have more overall fat content than cashews. Per 1oz serving of each, pecans provide 20.4 grams of total lipid fat, while cashews provide only 12.4 grams.
Per 100-gram serving, the difference in total lipid fats between the two equals 28.2 grams.
As can be seen in the fat type coverage comparison charts below, both have similar amounts of saturated fats, although the content is slightly higher in cashews. Still, pecans have more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats when compared to cashews.
Monounsaturated fats are the predominant type of fat found in both.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-20.6%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+71.5%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+175.5%
Cholesterol
Cashews and pecans have no cholesterol.
Protein
Cashews contain around 2 times more protein than pecans.
Per 100-gram serving, there are 9.17 grams of protein in pecans and 18.22 grams of protein in cashews.
Carbohydrates
Cashews provide 2 times more carbs than pecans.
Cashews contain 8.56 grams of net carbs, while pecans contain 3.94 grams of net carbs per 1oz serving.
This difference equals 16.33 grams per 100-gram serving.
Vitamins
As you refer to the graphs below to observe the visual differences in vitamin contents, keep in mind that an average serving is only about 30 grams, while the graphs are provided for a 300-gram serving.
The predominant vitamins found in pecans include vitamin B1, vitamin B5, and vitamin B6. On the other hand, cashews encompass all of those vitamins, as well as vitamin K.
Cashews provide 2 times more Vitamin B6 and 10 times more Vitamin K. On the other hand, pecans contain approximately 2 times more vitamin B1, vitamin B2, and vitamin E.
They both have similar amounts of vitamin B5 and vitamin B3.
Cashews also completely lack vitamin A, which is present in pecans in small amounts. Both nuts have no Vitamin B12 and Vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+120%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+55.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+56%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+124.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+98.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+874.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+13.6%
Minerals
Compared to pecans, cashews have relatively higher amounts of minerals.
The predominant minerals found in pecans are copper and manganese. While cashews also contain both copper and manganese, they additionally provide significant amounts of iron, magnesium, and phosphorus.
Cashews provide 2 times more copper, magnesium, and phosphorus, as well as 3 times more iron. On the other hand, pecans provide 3 times more manganese.
Cashews also contain more potassium, zinc, and selenium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+89.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+171.9%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+141.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+61%
Contains
more
IronIron
+164%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+82.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+27.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+114.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+423.7%
Glycemic Index
Both cashews and pecan are considered low glycemic index foods. The glycemic index of pecan is lower than that of cashew.
The GI of pecan is equal to 10, while the estimated glycemic index of cashew is 25.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism. Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of pecans and cashews are both acidic and equal to 2.1 and 8.9, respectively.
Weight Loss & Diets
Both nuts are high in calories and fats, so it is better to avoid them in low-calorie diets. Nevertheless, they are also high in protein, healthy fats, and dietary fiber, making them applicable for a healthy weight-loss diet.
Pecans are a better choice if you are on low carbs diets, such as the Keto diet. Besides, both pecans and cashews have a low glycemic index, which is good in the case of low GI diets.
Health Benefits
This section of the article will discover the health impacts of pecans and cashews.
Cancer
According to studies, nuts are high in antioxidants and hence, provide various anti-cancer properties.
One study found that pecans contain powerful chemicals such as 4-hydroxybenzoic, chlorogenic, vanillic, caffeic, and ellagic acid, which are effective against tumor cell growth and may be used as an alternative to cancer treatment (1).
Another study found that colon cancer survivors who regularly eat nuts have a significantly lower risk for cancer recurrence. People who ate two or more servings of tree nuts per week, such as pecans, cashews, and hazelnuts, were 46 percent less likely to have cancer return and had a 57 percent lower mortality rate (2).
Cardiovascular Health
Pecans and cashews are both delicious nuts with various nutritional benefits, but when it comes to cardiovascular health, pecans might have a slight edge.
Pecans are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are considered heart-healthy as they can help lower LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. They also contain antioxidants like flavonoids and tocopherols (vitamin E), which have anti-inflammatory properties and may decrease the risk of atherosclerosis.
Cashews, on the other hand, are also a good source of healthy fats. They contain vitamins and minerals like magnesium and potassium, which are important for heart health. However, they don't have quite as many of the specific antioxidants found in pecans that are linked to cardiovascular benefits.
One meta-analysis found that consuming one serving of nuts (approximately 28 grams) at least five times per week was associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and coronary heart disease (3).
Both nuts can be part of a heart-healthy diet when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. It's essential to consider overall dietary patterns and lifestyle factors when assessing their impact on cardiovascular health (4).
Diabetes
According to research, nuts like pecans and cashews can help lower blood sugar levels.
In one study, the daily consumption of cashews resulted in lower total insulin levels in diabetic patients, assisting in the management of diabetes mellitus (5).
Pecans have a low glycemic index, so they do not cause blood sugar spikes, even in people with diabetes. When consumed as part of a meal, pecans can even counteract the effects of foods with a higher glycemic index (6).
Improved Brain Function
Firstly, pecans are high in the B-complex vitamins, which are directly linked to proper neurological development and function.
According to one study, the monounsaturated fatty acids found in pecans may aid in the prevention of mental decline and inflammation. Furthermore, pecans are high in potassium, which increases blood flow to the brain and promotes nervous system health.
Moreover, vitamin E helps to reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease. The vitamin E in pecans acts as an antioxidant, protecting brain tissues from being covered with plaques, which is the cause of Alzheimer's disease (7, 8).
Other Health Benefits
Pecans are known to be acne-fighting nutrients. These nuts are high in selenium, which, when combined with vitamin E, acts as an antioxidant, leaving skin hydrated and reducing inflammation. Zinc promotes immune function and cell growth, renewing and replenishing infected or damaged acne zones (9).
Downsides and Risks
Allergies
Although pecans and cashews may have health benefits, they also have some drawbacks to consider.
Patients who are allergic to tree nuts are often allergic to pecans. Symptoms include itching, swelling, and burning in the mouth and throat.
There is also a pollen food allergy syndrome (PFAS), also known as oral allergy syndrome, caused by cashews. Symptoms include an itchy mouth or ears, a scratchy throat, hives on the mouth, or swelling of the lips, mouth, tongue, or throat (10).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28807853/
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa1307352
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5762129/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24398275/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6408729/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26561616/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3098039/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5751107/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18494484/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7811165/
Infographic
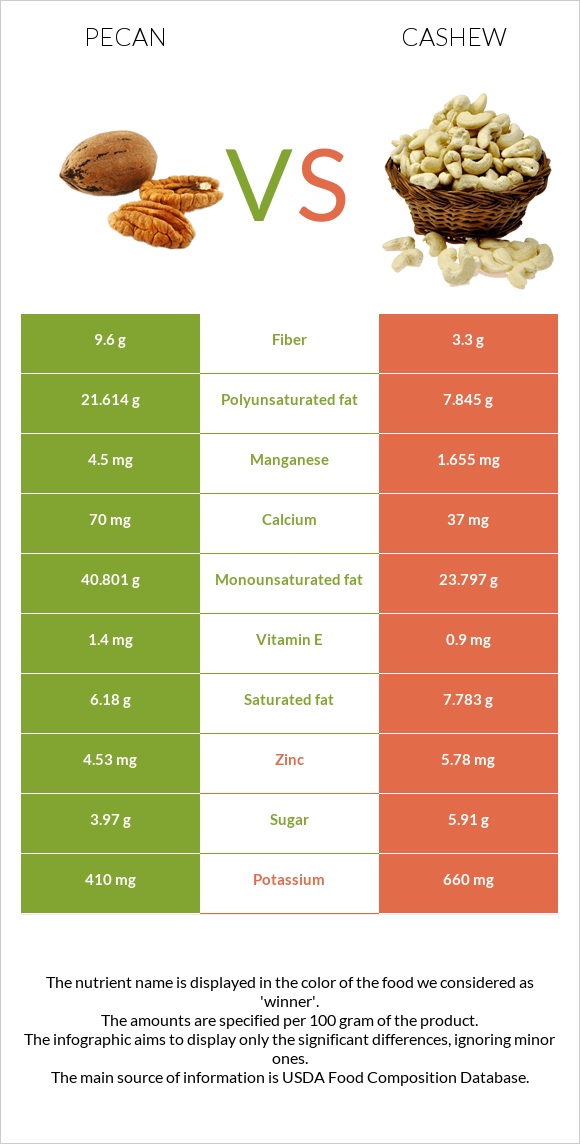
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Manganese | 4.5mg | 1.655mg | 124% |
| Copper | 1.2mg | 2.195mg | 111% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 21.614g | 7.845g | 92% |
| Iron | 2.53mg | 6.68mg | 52% |
| Phosphorus | 277mg | 593mg | 45% |
| Fats | 71.97g | 43.85g | 43% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 40.801g | 23.797g | 43% |
| Magnesium | 121mg | 292mg | 41% |
| Selenium | 3.8µg | 19.9µg | 29% |
| Vitamin K | 3.5µg | 34.1µg | 26% |
| Fiber | 9.6g | 3.3g | 25% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.66mg | 0.423mg | 20% |
| Protein | 9.17g | 18.22g | 18% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.21mg | 0.417mg | 16% |
| Zinc | 4.53mg | 5.78mg | 11% |
| Starch | 0.46g | 23.49g | 9% |
| Calories | 691kcal | 553kcal | 7% |
| Potassium | 410mg | 660mg | 7% |
| Choline | 40.5mg | 7% | |
| Saturated fat | 6.18g | 7.783g | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.13mg | 0.058mg | 6% |
| Carbs | 13.86g | 30.19g | 5% |
| Calcium | 70mg | 37mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 1.4mg | 0.9mg | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 1.1mg | 0.5mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 0mg | 12mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.167mg | 1.062mg | 1% |
| Folate | 22µg | 25µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 4.26g | 26.89g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.97g | 5.91g | N/A |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.863mg | 0.864mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.093mg | 0.287mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.306mg | 0.688mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.336mg | 0.789mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.598mg | 1.472mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.287mg | 0.928mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.183mg | 0.362mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.426mg | 0.951mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.411mg | 1.094mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.262mg | 0.456mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.04g | 0.05g | 0% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +5006.5% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +49% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +25% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +25% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pecan - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170182/nutrients
- Cashew - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170162/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






