Pork belly vs. Pork shoulder — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Pork shoulder is a leaner cut, and it is richer in proteins, selenium, choline, zinc, phosphorus, iron, copper, and vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and D. In comparison, pork belly is higher in total fats and saturated fats and richer in vitamins B3 and B12.
Introduction
This text will compare two different pork cuts; pork shoulder vs. pork belly. These cuts are different cuts based on several aspects. They are different according to taste, tenderness, the content of fat, and the content of lean meat.
The pork shoulder contains a lean portion. However, it's a tougher cut. A pork belly is a juicer and fattier cut than a pork shoulder.
The main focus of this article will be their nutritional content and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
We are going to consider 100g of each cut. Noting that we are considering them in their raw state.
Calories
Since pork belly is a fattier cut, it contains more calories. Pork belly contains nearly 2.2 times more calories compared to pork shoulder. Pork belly contains 518 calories, whereas pork shoulder 238 calories.
Carbs
The carb content of both cuts is negligible.
Proteins
Pork shoulder is a leaner cut and contains double the amount of protein compared to pork belly. Pork shoulder contains nearly 18g of protein, whereas pork belly contains 9g of protein.
Fats
Pork belly is very high in fat and contains 53g of fat compared to pork shoulder, which contains nearly 18g of fat.
It is important to note that pork belly is very high in saturated fats. It contains nearly 20g of saturated fats compared to pork shoulder, which contains 6g.
However, pork belly is richer in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Minerals
Pork shoulder is richer in selenium, choline, zinc, phosphorus, iron, and copper. It is richer in all minerals compared to pork belly.
Below we can visualize their comparative diagrams.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+350%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+200%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+63.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+101.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+61.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+164.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+68.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+83.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+218.8%
Vitamins
Pork shoulder is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and D. Whereas pork belly is richer in vitamins B3 and B12.
Below we can visualize their comparative diagrams.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+105.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+21.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+13.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+133.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+93.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+13.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+180.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+167.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+400%
Health impacts
Pork shoulder and belly come from pork; these cuts can affect health differently since their nutritional content differs.
The pork shoulder is a leaner cut than the pork belly; however, it has tougher meat since it comes from the shoulder, which supports the animal's weight. The shoulder cut is healthier since it is lower in calories and fats. It is richer in proteins, minerals, and vitamins.
Cardiovascular and metabolic health
Pork belly is high in fats and saturated fats which is linked with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases and metabolic diseases.
High saturated fat foods are linked with increased cardiovascular mortality risks such as atherosclerosis and myocardial infarctions. (1)(2)
Anemia
Pork shoulder and belly and rich in iron and vitamin B12: pork shoulder is richer in iron, and pork belly is richer in vitamin B12.
Regular iron-rich food consumption decreases the risk of iron deficiency or microcytic anemia and helps in the treatment. In comparison, vitamin B12 decreases the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency or megaloblastic anemia. (3)(4)
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential to maintain normal immunity, bone health, and calcium homeostasis, among other physiological necessities. Pork shoulder is richer in vitamin D, which improves overall physiology, and it is a necessary vitamin to consume in countries with low sun exposure. (5)
Choline benefits
Choline is an essential element to consider, and pork shoulder contains a rich and highly bioavailable source of choline. Choline is essential in general physiological processes, specifically in the formation of acetylcholine and the regulation of homocysteine metabolism. This choline maintains metabolic physiology and cognitive activity of the nervous system. (6)
Infographic
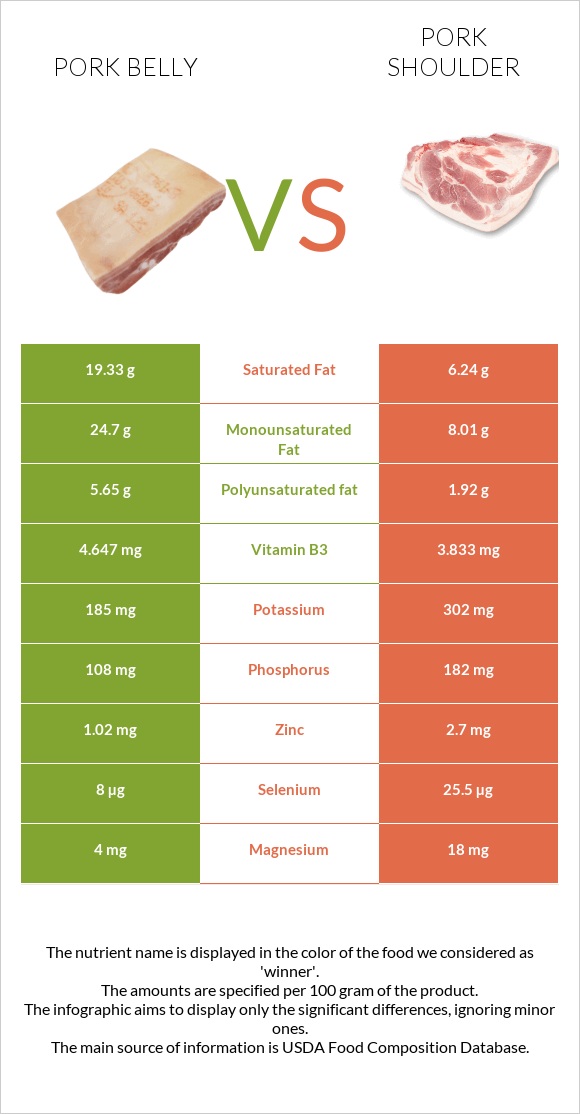
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 19.33g | 6.24g | 60% |
| Fats | 53.01g | 17.99g | 54% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 24.7g | 8.01g | 42% |
| Selenium | 8µg | 25.5µg | 32% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.396mg | 0.767mg | 31% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 5.65g | 1.92g | 25% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.13mg | 0.348mg | 17% |
| Protein | 9.34g | 17.18g | 16% |
| Zinc | 1.02mg | 2.7mg | 15% |
| Calories | 518kcal | 236kcal | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 108mg | 182mg | 11% |
| Choline | 60.6mg | 11% | |
| Vitamin D | 70 IU | 9% | |
| Vitamin D | 1.7µg | 9% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.256mg | 0.719mg | 9% |
| Iron | 0.52mg | 1.05mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.647mg | 3.833mg | 5% |
| Copper | 0.052mg | 0.084mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.84µg | 0.74µg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 4mg | 18mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 185mg | 302mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.242mg | 0.275mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 15mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 32mg | 65mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 0.19mg | 1% |
| Folate | 1µg | 5µg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.3mg | 0.7mg | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 72mg | 71mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 2µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.006mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.208mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.768mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.781mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.36mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 1.531mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.441mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.681mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.921mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.656mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +194.7% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +12.3% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +83.9% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +74.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +208.4% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +194.3% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -67.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pork belly - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167812/nutrients
- Pork shoulder - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167843/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.