Provolone vs. American cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Provolone contains more protein than American cheese, which is higher in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats compared to Provolone. Both of them are low in carbs.
Provolone is higher in soluble B-group vitamins, whereas American cheese is high in unsoluble vitamins like vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
In comparison to Provolone, which is high in zinc, American cheese contains more calcium, sodium, and other minerals.
Introduction
Provolone is a cow's milk-based Italian cheese with Southern Italian origins, whereas American cheese is made from a mixture of milk, milk fats, and additional lipids; previously, it was produced with a combination of cheeses, most often Colby and Cheddar.
This article will compare the two types of cheeses according to their nutritional content and health impacts. By the end of this article, the reader will understand the nutritional profile of each cheese.
Appearance and Taste
The flavor of Provolone ranges from sharp to very mild. The texture is homogeneous and slightly smooth. The skin is smooth and golden. In contrast, the taste and texture of American cheese vary depending on the other components used; it ranges in color from yellow to white.
There are several varieties of provolone:
- Provolone Dolce (two to three months old) is a sweet cheese. Use it as an aperitif or dessert.
- Provolone Piccante (aged for four months) is a salty cheese. It is grated (rather than parmesan).
- Provolone Affumicato is a smoked cheese.
There are three forms of processed American cheese available for purchase: huge blocks, little pre-sliced blocks, and individually wrapped cheese slices, whereas Provolone comes in a ball shape, a pear with vertical constrictions, a huge sausage, etc.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we will consider 100g of each cheese.
Calories
American cheese has more calories than provolone cheese. American cheese has 371 calories, whereas provolone has 351 calories.
Proteins
Provolone has more protein than American cheese. Provolone provides 25g of protein, while American cheese has 18g.
Fats
Provolone is lower in fat compared to American cheese. Provolone contains 26.62g of fat, whereas American cheese contains 31.79g of fat. In addition, most of the fats are saturated fats. American cheese contains more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats than Provolone. American cheese contains omega-3 and omega-6, unlike Provolone.
Carbs
Both these kinds of cheese are low in carbs. Provolone cheese contains 2.14g of carbs. American cheese is slightly higher in carbs and contains 3.7g.
Minerals
In comparison to Provolone, which is high in zinc, American cheese contains more phosphorus, selenium, calcium, copper, manganese, iron, and sodium (see the diagram below).
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+29.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-47.6%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+38.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+21.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+76.9%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+29.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+310%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+39.3%
Vitamins
Provolone is higher in soluble B-group vitamins than American cheese, which is higher in unsoluble vitamins such as vitamins D, E, and K. Both of them contain equal quantities of vitamin A and vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+26.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+37.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+105.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+18.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+35.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+247.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+20%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+18.2%
Weight loss and Diets
American cheese and Provolone are keto-friendly since they are low in carbs and high in fat and protein.
In contrast to highly processed American cheese, Provolone can be used in moderation in the Mediterranean diet.
Both of these cheeses are allowed during intermittent fasting because it regulates the timing of eating rather than the energy quality.
Thus, when following a weight-loss diet, Provolone and American cheese should be ingested in moderation.
Health impacts
This section will focus on the different health impacts each cheese provides.
Cardiovascular health
Sodium is an essential mineral that contributes to the regulation of normal blood pressure. As previously stated, American cheese contains nearly twice as much sodium as Provolone (1671mg vs. 876mg). Although a healthy adult can ingest up to 2300 mg of salt, certain people are advised to follow a reduced sodium diet due to a pre-existing health condition such as heart failure, high blood pressure, renal failure, and so on (1).
Based on the above, we recommend that people with arterial hypertension and heart failure limit their consumption of American cheese, as opposed to Provolone, which contains Lactobacillus helveticus, which, like some antihypertensive drugs (Captopril, Perindopril, et al.), may reduce arterial blood pressure by inhibiting angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) (2.3).
In addition, tyramine-containing cheeses (such as Provolone and American cheese) may cause a hypertensive crisis (blood pressure of 180/120 mm Hg or higher; a hypertensive crisis is a potentially fatal medical condition that can result in a heart attack, stroke, or other potentially fatal health complications) in patients taking MAO inhibitors (particularly antidepressants). It should be noted that American cheese contain more tyramine than Provolone (4.5).
Both kinds of cheese contain saturated fats, whose consumption may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, and this effect is assumed to be mediated mostly by higher LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in the blood (6).
On the other hand, given that loop diuretics (Furosemide, Bumetanide, and Torsemide), which are mainly prescribed in heart failure, increase calcium loss by limiting reabsorption in the loop of Henle, we recommend that people who take loop diuretics increase (in moderation) consumption of dairy products (including these ones), unless contraindications exist (7).
It should be noted that loop diuretics have the opposite impact of thiazide diuretics (Chlorothiazide, Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide, Indapamide, and Metolazone), which lower calcium excretion and may improve bone mineral density (for more information about calcium, see below) (7).
Digestive Health
Provolone and American cheese are high in threonine, an amino acid that contributes to the integrity of the intestinal mucosa and is important for the digestion and absorption of nutrients (8).
Lactose intolerance is characterized by a deficiency of the enzyme lactase (which destroys or aids in the digestion of the milk sugar lactose). Individuals who are lactose intolerant may have symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, and flatulence when they ingest cheeses such as Provolone, American cheese, etc. (9).
However, Provolone has a significantly lower lactose level than American cheese. Even in the tiniest quantity, some people who are particularly sensitive to provolone can have a significant response. In view of the foregoing, all such individuals should avoid cheeses such as provolone and American cheese or stick to lactose-free varieties (10).
Casein is a milk protein found in all dairy products, including provolone cheese. Casein intolerance is a disorder in which your body becomes allergic to the milk protein casein. People who are allergic to casein may experience dangerous symptoms after consuming casein-rich foods (such as cheese or other dairy products), such as wheezing, difficulty breathing, anaphylaxis (a life-threatening acute allergic response), extreme pain, vomiting, rashes, and so on.
Casein allergy affects approximately 3% of children under the age of one year. In most cases, the allergy resolves by the time the child reaches the age of five, but it may resurface later in life. Adults have a 2% prevalence of casein allergies. In view of the above, all such people should avoid cheeses, including these ones, or consume plant-based cheeses (11.12).
Histamine is a naturally occurring substance (or neurotransmitter) that is created in your body to help with digestion by releasing enzymes and acid in the stomach. Aside from internal production, a variety of foods, such as cheese, are high in histamine.
Some people have histamine intolerance; they are genetically predisposed to severe reactions caused by increased histamine sensitivity of the tissues.Inadequate histamine metabolism or excessive histamine intake as a result of eating specific foods (such as cheese, including these ones) can cause a variety of symptoms such as headaches or migraines, nausea, exhaustion, vomiting, and ect. (13).
Histamine levels in aged and fermented cheeses are higher than in fresh cheeses. Although both of these cheeses are high in histamine, American cheese is richer than Provolone.
Diabetes mellitus
According to this study, full-fat and nonfermented cheeses raise the risk of type 2 diabetes in healthy people (14). The development of the metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by the death quartet (abdominal obesity, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension), could be one reason for this. Limited consumption of fatty foods, particularly American cheese (in this content), as well as physical activity, are important in preventing the latter (15).
Bone Health
Bone size and mass grow fast in late childhood and adolescence, lasting into the third decade of life. This is a period of potential and susceptibility for building bone mass, which is necessary for bone health throughout life.
The Recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for calcium is 1300 mg for boys and girls aged 9 to 18. Extremely low calcium intakes, such as <400 mg/day, increase the risk of rickets and fractures, especially when paired with low vitamin D status. This clinical picture may be seen in patients with anorexia nervosa or other forms of malnutrition who have rigorous dairy avoidance without adequate alternative sources of calcium and vitamin D (16).
Adequate calcium intake (the RDA for calcium is 1000–1200 mg for adults) and weight-bearing physical exercise are required to achieve peak bone mass and reduce the development of osteoporosis in adulthood (17).
Both of these cheeses are high in calcium, although American cheese contains more than Provolone.
Cancer
According to this study, Lactobacillus helveticus, which is used in the production of certain Italian cheeses such as Provolone, has numerous health benefits, including preventing the growth of colon cancer cells and breast cancer cells in vivo (18). This effect is unknown for American cheese.
References
- https://journals.lww.com/co-cardiology/Abstract/2002/07000/Sodium_and_blood_pressure.7.aspx
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022030218311184
- https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/AEM.66.4.1259-1265.2000
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/1163613
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22951238/
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/91/3/502/4597078
- https://pro.uptodatefree.ir/Show/2036
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Xiangfang-Zeng/publication/51174299_Specific_roles_of_threonine_in_intestinal_mucosal_integrity_and_barrier_function/links/550158790cf2aee14b594012/Specific-roles-of-threonine-in-intestinal-mucosal-integrity-and-barrier-function.pdf
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2002/0501/p1845.html
- https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/9/12/1730
- https://pro.uptodatefree.ir/show/2386
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924224421005604
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7463562/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29498341/
- https://pro.uptodatefree.ir/show/1784
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29265106/
- https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/menopause-and-bone-loss
- https://www.proquest.com/openview/b9c0abf7edf916daa82acfe6cc31a9d9/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=49113
Infographic
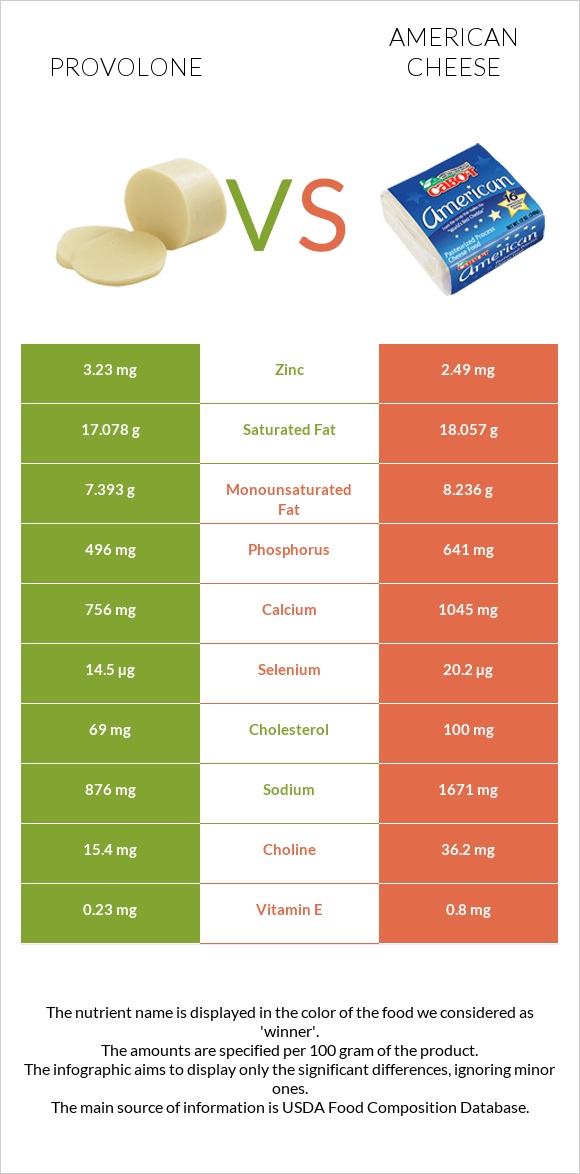
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Sodium | 876mg | 1671mg | 35% |
| Calcium | 756mg | 1045mg | 29% |
| Phosphorus | 496mg | 641mg | 21% |
| Protein | 25.58g | 18.13g | 15% |
| Cholesterol | 69mg | 100mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 14.5µg | 20.2µg | 10% |
| Fats | 26.62g | 31.79g | 8% |
| Zinc | 3.23mg | 2.49mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.321mg | 0.234mg | 7% |
| Vitamin E | 0.23mg | 0.8mg | 4% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 36.2mg | 4% |
| Saturated fat | 17.078g | 18.057g | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.769g | 1.286g | 3% |
| Copper | 0.026mg | 0.046mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 236µg | 250µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.46µg | 1.5µg | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 7.393g | 8.236g | 2% |
| Calories | 351kcal | 371kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 2.14g | 3.7g | 1% |
| Iron | 0.52mg | 0.63mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.5µg | 0.6µg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.01mg | 0.041mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.156mg | 0.076mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.476mg | 0.403mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.073mg | 0.054mg | 1% |
| Folate | 10µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 2.14g | 3.7g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 20 IU | 23 IU | 0% |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 26mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 138mg | 132mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.56g | 2.26g | N/A |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.019mg | 0.015mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 2.2µg | 2.6µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 1.144g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.345mg | 0.232mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.982mg | 0.772mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.091mg | 0.938mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.297mg | 1.716mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.646mg | 1.516mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.686mg | 0.475mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.287mg | 0.939mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.64mg | 1.187mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 1.115mg | 0.546mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.012g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.006g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.137g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.021g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.033g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.009g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.79g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +41.1% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +19.4% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +72.9% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +43.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +11.4% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +67.2% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Provolone - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170850/nutrients
- American cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171290/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.