Pomelo vs. Guava — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Guava is higher in protein, fats, net carbs, fiber, and vitamins C and A. It also contains more potassium, calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus.
In contrast, pomelo has fewer calories and oxalates, whereas guava is low-GI and low-GL food.
Table of contents
Introduction
Guava is native to tropical regions of the Americas, including Southern Mexico, Central America, and northern South America. On the other hand, pomelo (shaddock or pummelo) is native to Malaysia and Indonesia. It is also grown in China, Thailand, Vietnam, and some parts of the Americas.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare the nutritional values of raw pomelo and raw guava, concentrating on differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Pomelo has a high water content. Pomelo contains 89% water, whereas guava has 81% water. Pomelo is high in all macronutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+235.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+2275%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+48.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+187.5%
Calories
Guava provides more calories per hundred grams. A hundred grams of pomelo has 38 kcal, whereas guava provides 68 kcal.
Protein
Guava has more protein than pomelo. A hundred grams of pomelo provides 0.76g of protein, whereas guava has 2.55g.
Fats
Guava and pomelo are not good sources of fats and have less than 1g of fat. However, guava has over 24 times more fat. In a 100g serving, pomelo and guava have 0.04g and 0.95g of fat, respectively.
Carbohydrates
Guava is higher in carb content. 100g of pomelo contains 9.62g of carbohydrates, of which 1g is dietary fiber and 8.62g are net carbs. 100g of guava contains 14.32g of carbohydrates, of which 5.4g are dietary fiber and 8.92g are net carbs.
Cholesterol
Guava and pomelo are cholesterol-free.
Vitamins
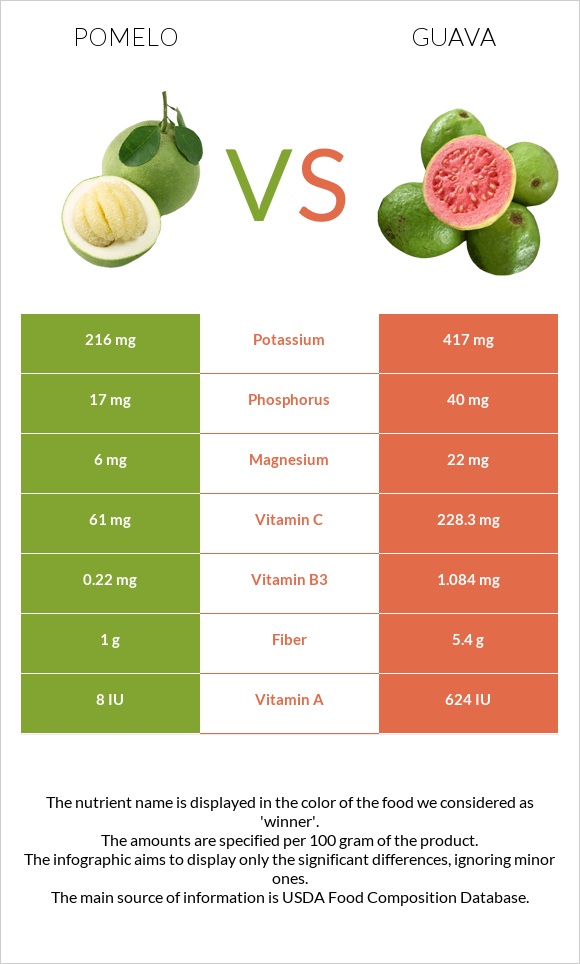
Guava is the winner in this category. It is higher in all vitamins. Guava has 78 times more vitamin A and over four times more vitamin C. In a 100g serving, pomelo and guava have 8IU and 624IU of vitamin A, respectively.
A hundred grams of pomelo provides 61mg of vitamin C, whereas guava has 228mg. Guava has over five times more vitamin B3, three times more vitamin B6, two times more vitamin B1, and 1.5 times more vitamin B2. Guava also provides small amounts of folate and vitamin K.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+274.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+97.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+48.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+392.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+205.6%
Minerals
Guava is the winner in this category. In a 100g serving, pomelo and guava have 216mg and 417mg of potassium, respectively. Guava has more phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, copper, and iron. On the other hand, pomelo has less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-50%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+266.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+350%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+93.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+136.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+379.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+187.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+135.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+782.4%
Oxalates
A hundred grams of guava has 6mg of oxalates, whereas pomelo is oxalate-free.
Glycemic Index
Pomelo has a higher glycemic index (GI) than guava. The glycemic index of pomelo is 78. Guava has a glycemic index of 31. The glycemic index of pomelo falls in the high category, whereas the GI of guava falls in the low category.
Glycemic Load
The glycemic load (GL) of pomelo is 13, whereas guava has a glycemic load level of 2. The glycemic load of pomelo falls in the medium category, while the GL of guava falls in the low category.
Acidity
The way to determine the acidity of a food is by calculating its potential renal acid load (PRAL), which indicates how much acid or base the food can produce in the body. Pomelo has a PRAL value of -3.7, while guava has a PRAL value of -6.8. Both fruits are alkaline-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
The findings suggest that pomelo may prevent obesity. The pomelo peel contains high levels of total dietary fiber, including insoluble and soluble fiber. The pomelo peel dietary fiber (PPDF) may significantly decrease weight gain and fat accumulation in obese mice, improve dyslipidemia, and restore cholesterol levels (1).
The study investigated the effects of guava polysaccharide (GP) on diet-induced obesity in mice. Guava supplementation may reduce weight gain and visceral obesity and improve lipid profiles. It also may prevent hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in adipose tissues (2).
Vegan/ Vegetarian: Pomelo and guava are vegan because they are made entirely of plants and do not contain any animal ingredients. They are also suitable for vegetarians, who avoid all animal products.
Mediterranean: The Mediterranean diet allows you to eat fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Guava and pomelo are excellent for this diet.
Keto: The keto diet includes low-carb, high-fat, and high-protein foods.
Pomelo and guava can be part of the keto diet but in moderation.
Paleo: The paleo diet focuses on consuming natural, unadulterated foods while avoiding synthetic items. Pomelo and guava are paleo-friendly.
Health Impact
Diabetes
Guava leaves (GLP) have strong antioxidant properties and may significantly reduce blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, cholesterol, triglycerides, and other diabetic markers in mice (3).
It may enhance glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Histopathological analysis showed that GPs protect pancreatic islet cells. The findings suggest that GPs could be a beneficial treatment for T2DM and may reduce the risk of associated complications (4).
According to the study, pomelo consumption did not cause significant glucose fluctuations in hospitalized T2D patients. This suggests that despite its high GI, pomelo can be a suitable fruit option for T2D patients when consumed in moderation (5).
The study found that the antidiabetic effect was most significant in the group treated with pomelo juice, followed by fortified paranthas and naringin (6).
Digestive Health
The pomelo peel dietary fiber may improve gut microbiota diversity by increasing beneficial bacteria and decreasing harmful bacteria. It may reduce the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes, increase the presence of Bifidobacterium, Alloprevotella, and Lactobacillus, and lower the levels of Staphylococcus and Corynebacterium_1 (1).
Guava polysaccharide (GP) may normalize the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Clostridium XlVa, Parvibacter, and Enterorhabdus, and reduce levels of the inflammation-related bacteria Mucispirillum (2). This effect is achieved by increasing the production of short-chain fatty acids, notably butyric acid, within the colon.
Antimicrobial Properties
The findings suggest that pomelo seeds and pulp ethanolic extract have antimicrobial properties. Antimicrobial testing against Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli showed that the pomelo extract is more effective than the grapefruit extract, exhibiting larger inhibition zones for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. However, the pomelo extract showed no activity against Candida albicans, possibly due to differences in the testing method (7).
The studies suggest that ethanol and methanol are more effective than n-hexane and water for extracting the antibacterial properties of guava. Although these extracts didn't exhibit any antibacterial activity against Gram-negative bacteria, they did demonstrate a reduction in the growth of Gram-positive bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus (8).
Cancer
The various components of guava, including leaves, fruits, seeds, peels, pulp, bark, and oil, are rich in nutrients and antioxidants with medicinal properties. Research indicates that these bioactive compounds may have cancer-preventive and anticancer effects through various mechanisms (9).
According to the study, guava extracts can selectively inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells without harming normal cells (10).
Flavonoids, such as neohesperidin and naringin, and other compounds like hesperidin, naringin, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, vanillic acid, and buntanbismine in pomelo, have anticancer effects. Flavonoids play a role in cancer prevention by influencing cell proliferation and angiogenesis through signal transduction pathways (11).
Classification
Pomelo (Citrus maxima) belongs to the family Rutaceae and the genus Citrus. Guava (Psidium guajava) belongs to the family Myrtaceae and the genus Psidium.
Appearance
Guava is typically smaller, ranging from the size of an apple to that of a grapefruit. They have green or yellow skin and pink or white flesh. In contrast, pomelo is a larger citrus fruit, often comparable to a small melon, characterized by thick, rough, pale green to yellow skin. Pomelo has a spongy and thicker rind that encases juicy flesh. The flesh is firm, similar to a grapefruit, but less tart, and is divided into slices like other citrus fruits. Guava has a thin, smooth skin that is green when unripe and may turn yellow, maroon, or remain green when ripe. The flesh of guava is typically pink, white, or yellow, with small and edible seeds in the center.
Guava is generally round or oval, whereas pomelo is round or slightly pear-shaped.
The texture of pomelo flesh is juicy and somewhat coarse, with a refreshing, citrusy taste. Guava has a unique texture that varies depending on the variety and ripeness. When ripe, guava has soft, creamy flesh that is juicy and fragrant, with a texture similar to a very ripe pear. The edible seeds add a crunchy texture. Unripe guavas are firmer and tarter, with a texture similar to a crisp apple.
Taste and Use
Pomelo has a sweet and mild flavor with a hint of tartness, similar to a mild grapefruit. The taste is refreshing, citrusy, and less acidic than a grapefruit, making it a popular choice for those who find grapefruit too tart.
Guava is sweet and tropical, with a strong, fruity aroma. The taste is characterized as a combination of pear, strawberry, and lemon with a floral undertone.
Guava is often eaten fresh, juiced, or used in jams, jellies, and desserts. On the other hand, pomelo is eaten fresh, added to salads, or used in fruit cocktails.
Varieties
Chandler, Tahitian, Thong dee, and Siamese sweet pomelo are varieties of pomelo.
Common types of guava are apple guava (Psidium guajava), strawberry guava (Psidium littorale), pineapple guava (Feijoa sellowiana), and lemon guava (Psidium cattleianum).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38144811/v
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35605721/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30959759/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28347786/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29058284/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33864254/
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/acp/article/1933/1/030002/791645/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817707/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10408398.2021.1945531
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36836712/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3195351/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 61mg | 228.3mg | 186% |
| Copper | 0.048mg | 0.23mg | 20% |
| Fiber | 1g | 5.4g | 18% |
| Folate | 49µg | 12% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.451mg | 9% | |
| Potassium | 216mg | 417mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.017mg | 0.15mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.036mg | 0.11mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.73mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.22mg | 1.084mg | 5% |
| Protein | 0.76g | 2.55g | 4% |
| Magnesium | 6mg | 22mg | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 17mg | 40mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 31µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.034mg | 0.067mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.401g | 3% | |
| Calories | 38kcal | 68kcal | 2% |
| Carbs | 9.62g | 14.32g | 2% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 0.26mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.6µg | 2% | |
| Fats | 0.04g | 0.95g | 1% |
| Calcium | 4mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.08mg | 0.23mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 1% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 1% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.272g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 8.62g | 8.92g | N/A |
| Sugar | 8.92g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 1mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.087g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.022mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.096mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.093mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.171mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.072mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.016mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.006mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.087mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.022mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pomelo - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167754/nutrients
- Guava - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173044/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






