Paprika vs. Cayenne Pepper — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
The cayenne pepper spice is derived from cayenne peppers, while paprika is derived from a variety of sweet peppers. Since both are used as spices and seasonings, their serving sizes are very small. Hence, their contribution to your daily macronutrient, vitamin, and mineral content is insignificant.
Nevertheless, paprika contains slightly higher levels of Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B3, while cayenne peppers provide more Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and folate. When it comes to minerals, paprika provides 3 times more iron as well as 2 times more zinc and copper, while cayenne pepper provides slightly more manganese and selenium.
Introduction
This article will discuss the main differences in the nutrition of paprika and cayenne pepper while also focusing on their health impact.
What's the Actual Difference?
The cayenne pepper spice is derived from cayenne peppers, whereas paprika is derived from a variety of sweet peppers.
Cayenne's color range is limited to an orange-red, with slight variations due to the cayenne color when dried and smoked. Cayenne pepper is typically spicier than paprika. Most paprika varieties have a sweet and fruity flavor as well.
Nutrition
In this section, we are going to present the nutritional differences between paprika and cayenne peppers.
The serving sizes for both spices are usually about 0.5g-2g, but depending on the dish, you might add more. One teaspoon of cayenne pepper and one teaspoon of paprika is around 2 grams.
However, to keep the comparison between the two spices simple, we will sometimes refer to 100-gram servings of each.
Macronutrients and Calories
As can be seen from the macronutrient comparison charts below, both paprika and cayenne peppers are mostly made of carbs, which make up 54% and 57% of the entire macronutrient compositions, respectively.
Given that the serving sizes for the spices are extremely small, the differences in macronutrients are not relevant in the context of the daily recommended amount of nutrients and calories. However, we will still discuss these differences and similarities.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+17.7%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+39.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+28.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+34%
Calories
Cayenne pepper and paprika provide similar amounts of calories.
One teaspoon serving of cayenne peppers (1.8 grams) and one teaspoon of paprika (2.3 grams) both provides around 6 calories.
Per 100-gram serving, cayenne pepper contains 318 calories, while paprika contains 282 calories.
Fats
One teaspoon of paprika provides around 0.297 grams of total lipid fat, while one teaspoon of cayenne peppers provides around 0.311 grams of total lipid fat.
Per 100-gram servings, the total lipid fats in cayenne pepper equal 17.27g, whereas in paprika, 12.89g.
Both paprika and cayenne pepper contain no cholesterol.
Carbohydrates and Fiber
Cayenne peppers and paprika contain similar amounts of carbs; however, the amount of fiber is 2 times higher in paprika.
The carbohydrate content in these spices is also very similar. One teaspoon serving of paprika (2.3 grams) provides 1.24 grams of carbs and 0.803 grams of fiber, while one teaspoon of cayenne peppers (1.8 grams) provides 1.02 grams and 0.49 grams of fiber.
Vitamins
Paprika contains slightly higher amounts of Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B3 than cayenne peppers. On the other hand, cayenne peppers provide more Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and folate.
Specifically, the most significant difference found in vitamin content comparison is the differences in amounts of Vitamin C. Cayenne peppers provide around 85 times more Vitamin C than paprika.
Additionally, both of these spices have equal amounts of Vitamin E, Vitamin B1, and Vitamin K.
Both cayenne peppers and paprika completely lack Vitamin D and Vitamin B12. Moreover, whereas paprika has some levels of Vitamin B5, the vitamin is completely absent in cayenne peppers.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+18.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+33.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+15.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+8388.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+14.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+116.3%
Minerals
Single servings of these spices do not contribute any significant amounts of minerals to your daily need as well; however, we can still discuss their differences.
Paprika provides more magnesium, potassium, zinc, iron, and copper, while cayenne pepper provides slightly more manganese and selenium.
Specifically, paprika provides 3 times more iron as well as 2 times more zinc and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+17.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+54.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+13.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+171%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+91.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+74.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-55.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+25.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+39.7%
Glycemic Index
The estimated glycemic index of cayenne pepper is 32, while for paprika, it is 0. Both are considered low-GI foods.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL values of cayenne peppers and paprika are -31.4 and -36.9, respectively, which means paprika has greater potential to alkalize the body.
Health Benefits
Diabetes and Cancer
Both paprika and cayenne peppers contain a high amount of capsaicin, which has many health benefits.
Capsaicin was first isolated from chili peppers. It is used to treat psoriasis and diabetic neuropathy as a topical treatment (1).
One study revealed that subjects who ate a cayenne-containing meal had lower blood glucose levels (2). Lower blood insulin levels were also observed, particularly in a subgroup that had eaten a cayenne-rich diet for a month before the test. This suggests that cayenne consumption may improve tissue insulin sensitivity, requiring less insulin to move glucose from the blood to the tissues.
According to another research, capsaicin has antioxidant properties that can help reduce the risk of cancer and heart disease while improving immunity (3).
It also may help protect against cellular damage caused by oxidative stress, which is an imbalance in the body's antioxidant defenses and damaging molecules called free radicals.
Cardiovascular Health
Both paprika and cayenne pepper contain antioxidants, but cayenne pepper's capsaicin has more pronounced effects on metabolism and cardiovascular health.
A 2019 Italian study of 22,811 adults discovered that regular capsaicin consumption was linked to a lower risk of death from heart disease (4). Some researchers say capsaicin may improve certain aspects of cardiovascular health, including blood vessel function, but more research is needed to confirm this potential benefit.
Another three-month study discovered that capsaicin significantly reduced the risk factors for heart disease in adults with low HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol) (5).
Inflammation: Both spices have anti-inflammatory properties, but capsaicin in cayenne pepper has been shown to have a more significant impact on inflammation and vascular health.
Incorporating either into your diet can be beneficial, but cayenne pepper may have a more pronounced impact on cardiovascular risk factors.
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Paprika allergy symptoms are usually moderate, but severe paprika allergies can cause anaphylaxis, so if you have a history of food allergies, you should get tested.
Cayenne pepper, also known as capsicum, is a type of red pepper with savory to hot and spicy flavors. Itchiness near and around the mouth, eyes, and other body parts, as well as diarrhea, are common symptoms (6).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29083760/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986509/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7794743/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109719382063
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5622797/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30883393/
Infographic
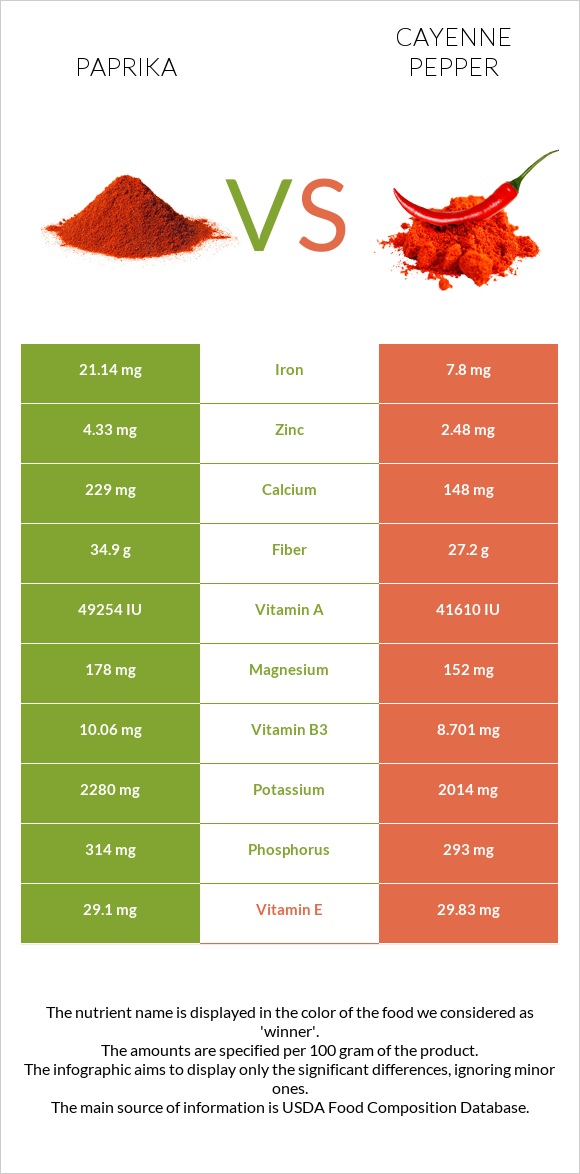
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 21.14mg | 7.8mg | 167% |
| Vitamin C | 0.9mg | 76.4mg | 84% |
| Vitamin B5 | 2.51mg | 50% | |
| Vitamin A | 2463µg | 2081µg | 42% |
| Copper | 0.713mg | 0.373mg | 38% |
| Fiber | 34.9g | 27.2g | 31% |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.23mg | 0.919mg | 24% |
| Vitamin B6 | 2.141mg | 2.45mg | 24% |
| Manganese | 1.59mg | 2mg | 18% |
| Zinc | 4.33mg | 2.48mg | 17% |
| Folate | 49µg | 106µg | 14% |
| Calcium | 229mg | 148mg | 8% |
| Potassium | 2280mg | 2014mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 10.06mg | 8.701mg | 8% |
| Fructose | 6.71g | 8% | |
| Fats | 12.89g | 17.27g | 7% |
| Magnesium | 178mg | 152mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 29.1mg | 29.83mg | 5% |
| Selenium | 6.3µg | 8.8µg | 5% |
| Saturated fat | 2.14g | 3.26g | 5% |
| Protein | 14.14g | 12.01g | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 7.766g | 8.37g | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 314mg | 293mg | 3% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1.695g | 2.75g | 3% |
| Calories | 282kcal | 318kcal | 2% |
| Sodium | 68mg | 30mg | 2% |
| Carbs | 53.99g | 56.63g | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 5.01418439716312g | 3.7767295597484276g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 199.43422913719942kcal | 264.77935054121565kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 19.09g | 29.43g | N/A |
| Sugar | 10.34g | 10.34g | N/A |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.33mg | 0.328mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 80.3µg | 80.3µg | 0% |
| Choline | 51.5mg | 51.5mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.07mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.49mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.57mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.92mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.69mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.2mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.61mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.75mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.25mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.453g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -34.4% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +62.2% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Paprika - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171329/nutrients
- Cayenne pepper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170932/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.