Tomato vs. Cucumber — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cucumbers are richer in vitamin K, containing 16.4 g, approximately twice the amount found in tomatoes, which contain 7.9 g. However, tomato surpasses cucumber in vitamin C content, making it 12% higher in daily vitamin C coverage. Tomatoes are slightly richer in calories and almost as rich in fiber.
Introduction
Tomatoes and cucumbers are common and well-known foods. We'll review the key distinctions and similarities between cucumbers and tomatoes, emphasizing their effects on health and nutrition.
Classification
While tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is a fruit native to South America, cucumber (Cucumis sativus) is a member of the Cucumis genus. Both are typically consumed and served like vegetables, even though they are technically fruits.
Appearance
While green cucumbers are the most prevalent, cucumbers can also be found in white, yellow, and orange varieties, typically distinguished by their varying skin colors. In contrast, tomatoes, usually red when ripe, showcase a wide spectrum of colors, including yellow, orange, green, and purple.
Taste and Use
Tomatoes are frequently used to add a burst of rich flavor and a hint of acidity. They are also commonly used as a main ingredient in pizzas, salsas, and pasta meals. On the other hand, because of their crisp, chilly texture and somewhat pleasant flavor, cucumbers are frequently used in salads, sandwiches, and pickles. In addition, cucumbers are utilized in various appetizers and cool drinks like cucumber-infused water or cocktails.
Varieties
Cucumbers are available in various types, including the English cucumber, Persian cucumber, Kirby cucumber, lemon cucumber, Armenian cucumber, and sliced cucumber. On the other hand, the tomato family boasts an array of varieties, such as beefsteak tomato, Roma tomato, cherry tomato, grape tomato, heirloom tomato, and plum tomato. These diverse types offer unique flavors, textures, and uses, making them versatile options for various culinary creations.
Nutrition
This article presents the nutritional values of raw tomatoes and raw cucumbers.
Macronutrients and Calories
Although neither of these foods is especially high in macronutrients, potatoes provide more protein than cucumbers. Both veggies contain small levels of essential amino acids. Additionally, they include a deficient fat level. They are not present in trans fats or cholesterol. The carbohydrate content of tomatoes and cucumbers is equal; each has about 3.89 grams of carbs. They both contain roughly 94.52% water, which is another similarity between them.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+35.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+81.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+34.2%
Calories
Cucumbers and tomatoes are low in calories. Cucumbers with peels give 15 calories per 100g serving; cucumbers without peels only have 10 calories. A serving of tomato containing 100 grams has 18 calories.
Vitamins
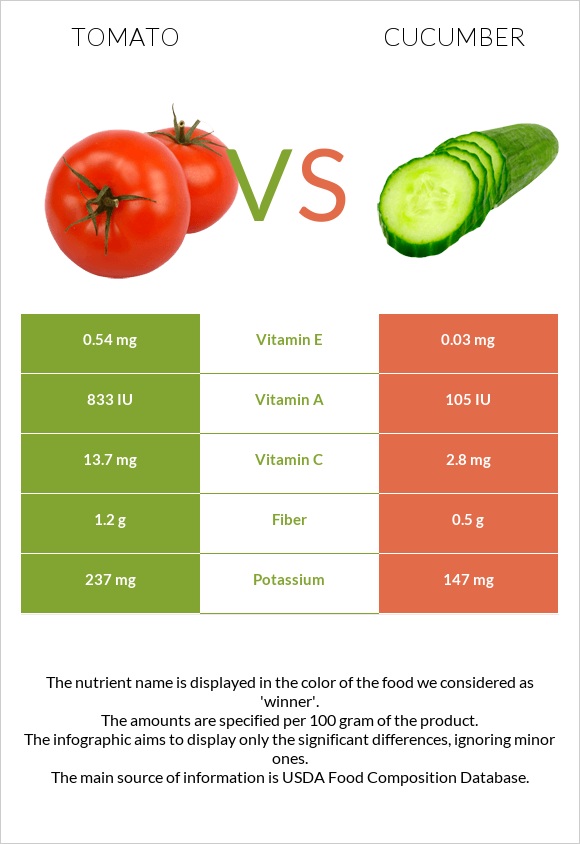
Cucumbers contain significantly more vitamin K than tomatoes, with 16.4 g in cucumbers compared to 7.9 g in tomatoes. On the other hand, tomatoes are notably richer in vitamin A, with 833 IU compared to 105 IU in cucumbers.
Tomatoes also provide more Vitamin A, RAE, Vitamin E, Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B3, and Vitamin B6 compared to cucumbers. However, cucumbers have a higher content of vitamin B2 and vitamin B5 when compared to tomatoes. Additionally, tomatoes contain more folate than cucumbers.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+389.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+740%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1700%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+37%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+506.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+100%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+114.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+73.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+191%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+107.6%
Minerals
Cucumber contains more calcium and sodium compared to tomatoes. Selenium content was not detected in tomatoes, while cucumber contains a minimal amount of 0.3µg. On the other hand, tomatoes contain higher levels of potassium (237mg). Cucumbers and tomatoes are equal in iron, phosphorus, zinc, magnesium, and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+61.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+43.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+44.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+18.2%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+60%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+17.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-60%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Fiber
Tomatoes contain a higher fiber content, providing 1.2 grams compared to the 0.5 grams found in cucumber.
Oxalates
The amount of oxalates in cucumbers is 4 mg, whereas the amount of oxalates in tomatoes is 5 mg.
Glycemic Index
Tomatoes and cucumbers are low-GI, diabetes-friendly foods. The glycemic index of a tomato is 23, and the glycemic index of a cucumber is 21.
Acidity
Vegetables are both acidic. Cucumbers range in pH from 5.12 to 5.78. Cucumber pickles range in pH from 4.20 to 4.60. Tomatoes range in pH from 4.3 to 4.9. Cucumber has a potential renal acid load value of -2.4, while tomato has a higher alkaline PRAL value of -4.1. These foods are base-producing due to their negative PRAL ratings.
Weight Loss and Diets
Both cucumber and tomato are relatively low in carbs and can be included in Keto and Atkins diets. Cucumbers and tomatoes are suggested during the Mediterranean diet, which is based on traditional cuisine from Greece, Italy, and other Mediterranean Sea countries. Tomatoes and cucumbers are excellent choices for the Paleo diet. Additionally, both work well with vegetarian, vegan, and pescatarian diets. Both cucumbers and tomatoes are recommended in the Dukan diet, particularly during the cruise phase. Cucumbers and tomatoes are naturally low in fat and calories, making them suitable for low-fat and low-calorie diets. Tomatoes' antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties make them a good choice for anti-inflammatory diets. Cucumbers also have anti-inflammatory potential. Cucumbers can be suitable for the BRAT diet (bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast) due to their mildness and digestibility. Tomatoes may not be recommended due to their acidity.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Both tomatoes and cucumbers offer various health benefits, particularly those related to heart health. Rich in lycopene and beta-carotene, tomatoes have reduced the risk of heart attacks and strokes (1, 2). Clinical trials have indicated that lycopene supplementation might help lower LDL (harmful) cholesterol levels. At the same time, tomato products have displayed anti-inflammatory properties and protection of blood vessels, potentially decreasing the risk of blood clotting (3, 4, 5). Conversely, cucumbers have been linked to lowering systolic and diastolic blood pressure, likely due to their diuretic effect, which reduces the heart's workload (6, 7). Their consumption may also lead to decreased levels of 'bad' cholesterol and triglycerides, potentially preventing or slowing down the development of atherosclerosis, a primary cause of severe cardiovascular diseases (8, 9). Additionally, cucumbers contain cucurbitacin I and B, which may offer protection against cardiac hypertrophy and oxidative stress. However, some studies suggest a potential risk of cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac cell death from cucurbitacin I (10, 11, 12, 13).
Diabetes
Tomatoes contain lycopene, which is linked to a reduced risk of obesity and diabetes due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Additionally, lycopene has shown efficacy in managing diabetic neuropathy, nephropathy, and other related complications (14). On the other hand, cucumbers, known for their low glycemic index and dietary fiber content, are often included in weight-loss diets. Their low glycemic index values contribute to a decreased risk of developing type 2 diabetes or the need for medication (15). Studies have revealed that cucumbers contain active components with anti-diabetic, anti-hyperglycemic, and hypoglycemic effects, suggesting their potential use in treating and managing diabetes mellitus (16, 17, 18). Furthermore, cucumber extracts have demonstrated the ability to protect the liver and pancreas from the detrimental effects of diabetes (19).
Cancer
Cucumbers have been found to possess anticancer effects that can aid in preventing and treating cancer. Cucurbitacins present in cucumbers have the potential to impede the development of tumor cells and signaling pathways, leading to the death of cancer cells. Various groups of cucurbitacins have exhibited antitumor activity against various cancers, including lung, pancreatic, colon, breast, liver, and cervical cancers (20, 21, 22, 23). In contrast, observational studies have indicated a connection between tomatoes and tomato products and reduced prostate, lung, and stomach cancer incidence (24, 25). While the high lycopene content in tomatoes is considered responsible for these benefits, further high-quality human research is required to confirm the causal link (26, 27). Additionally, a study in women has suggested that high concentrations of carotenoids found abundantly in tomatoes may offer protection against breast cancer (28, 29).
Skin Health
Cucumbers are crucial in maintaining hydrated and healthy skin due to their polysaccharide content, which helps retain skin elasticity and firmness.
Cucumbers, with a water content of around 96%, provide great hydration, reducing dryness and flakiness, which can lead to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles (30). Tomatoes, on the other hand, are known for their skin-health benefits. Tomato-based diets, which are high in lycopene and other plant chemicals, have been linked to sunburn protection (31, 32).
Notably, research indicates that individuals consuming tomato paste with olive oil daily experienced 40% fewer sunburns, highlighting the potential skin benefits of tomatoes and their derivatives (33).
Downsides and Risks
Cucumbers and tomatoes have the potential to trigger allergic reactions in certain individuals. Cucurbit allergy, also known as oral allergy syndrome, can lead to various symptoms, including itching, burning, redness, and swelling of the lips, mouth, tongue, and soft palate. Additionally, it may cause nausea, diarrhea, asthma, rhinitis, watery eyes, or contact urticaria (34, 35). Individuals allergic to aspirin containing salicylate may need to avoid cucumbers, tomatoes, and other foods such as apples, almonds, oranges, and berries (36). While tomato allergies are rare, people allergic to grass pollen may experience allergic reactions to tomatoes due to pollen-food allergy syndrome or oral allergy syndrome (37, 38). Individuals with latex allergies might also experience cross-reactivity to tomatoes (39).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22158914/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23045517/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22965217/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16569044
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16929242/
- http://perpustakaan.poltekkes-malang.ac.id/assets/
- https://www.banglajol.info/index.php/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16407729/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29682157/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26296085/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28390176/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27836799/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33966619/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8569244/
- https://academicjournals.org/journal/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33214339/
- https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/srep36594
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10050865/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12424325/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23883692/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12010859/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22760559/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23098877/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16465309/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15830922/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11340098/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/sdfe/pdf/download/eid/1-s2.0-S2213219821011053/first-page-pdf
- https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/allergolint/64/1/64_S1323-8930-14-00013-6/_article/-char/ja/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1805260/pdf/bullnyacadmed00102-0098.pdf
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20306812/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7943997/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12440950/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 13.7mg | 2.8mg | 12% |
| Vitamin K | 7.9µg | 16.4µg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 42µg | 5µg | 4% |
| Potassium | 237mg | 147mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 1.2g | 0.5g | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.54mg | 0.03mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.594mg | 0.098mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.089mg | 0.259mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08mg | 0.04mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.059mg | 0.041mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.114mg | 0.079mg | 2% |
| Folate | 15µg | 7µg | 2% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 0.3µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.037mg | 0.027mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.019mg | 0.033mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 1.37g | 0.87g | 1% |
| Calories | 18kcal | 15kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 0.88g | 0.65g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.2g | 0.11g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2.69g | 3.13g | N/A |
| Carbs | 3.89g | 3.63g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 13mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.27mg | 0.28mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.63g | 1.67g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 0.2mg | 0% |
| Starch | 0g | 0.83g | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 24mg | 24mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 5mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Choline | 6.7mg | 6mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.028g | 0.037g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.031g | 0.005g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.083g | 0.032g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.006mg | 0.005mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.027mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.018mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.025mg | 0.029mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.027mg | 0.029mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.006mg | 0.006mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.027mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.018mg | 0.022mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -24.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +520% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +159.4% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +64.5% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +57.5% |
| Contains more StarchStarch | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +∞% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +∞% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Tomato - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170457/nutrients
- Cucumber - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168409/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




