Turkey meat vs. Duck meat — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Turkey meat is richer in proteins and contains less fat and specifically saturated fats. Turkey meat is richer in B vitamins, zinc, and phosphorous. Ducks are richer in copper and iron vitamins B1 and B5.
Turkey meat is healthier meat compared to duck meat. It is rich in proteins, has neutral associations with cardiovascular diseases, and is a good source of tryptophan, that has positive mental health impacts. Duck meat contains higher fat content, which is associated with cardiovascular diseases.
Introduction
This article will compare two types of poultry meats, turkey meat and duck meat. They are both classified as white meat. However, differences do exist between them. We will compare their nutritional aspects, health impacts, and in the end, some general differences between them.
It is essential to understand which meat is healthier in this case. Thus we need to dig deep into the nutritional and health impacts to conclude.
In this article, we consider turkey meat and duck meat to be roasted with the skin.
General differences
Turkey meat and duck meat are both poultry types of meat. One of the main differences is that duck meat has a darker color. This is due to a higher myoglobin content. Turkey meat and duck meat cuts are nearly similar to chicken cuts. Breast, drumstick, wing, thigh. In addition, duck foie gras can be found.
Taste
Duck meat has a stronger taste and flavor, contains more fats, and has a fattier taste than turkey meat. While turkey often has a milder flavor with hardly perceptible nuttiness, duck is famous for its rich, meaty taste with an element of sweetness.
Can you substitute duck for turkey?
Definitely yes! Roasted duck is a great alternative to Thanksgiving turkey if you do not like the taste of turkey meat at all. Also, it is a better source of tryptophan - an essential amino acid.
Nutritional content comparison
In this section, we are considering turkey and duck as a whole. Although some differences exist between each part, we are taking it as a whole. The infographic shown below indicates that turkey meat contains more water and protein, while duck meat is significantly richer in fats. Please, find the details in the corresponding sections.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+50.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+∞%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+22.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+283.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+70.8%
Calories
Duck meat contains higher amounts of calories than turkey meat. It contains 148 calories more. Duck meat is classified as high-calorie food, while turkey meat is considered a low-calorie food.
Proteins
Turkey meat is richer in proteins. Turkey meat is one of the highest protein-containing meats.
Duck meat contains 11g less protein per 100g than turkey meat.
Fats
Duck meat contains 4 times higher amounts of fats compared to turkey meat. Duck meat on its own is very high in fats.
Types of fats
Duck meat contains five times more saturated fats compared to turkey meat.
However, the highest fat available in duck meat is monounsaturated fats.
Cholesterol
Turkey meat contains higher amounts of cholesterol. It contains 25mg more cholesterol than duck meat.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-77.7%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+387.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+72.3%
Carbs
They contain a negligible amount of carbs.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of turkey and duck meats is equal to 0.
Minerals
Turkey meat is richer in zinc and phosphorous.
Whereas duck meat is richer in copper and iron.
The diagram below displays their distribution.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+87.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+27.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+17.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+33.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+42.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+49%
Contains
more
IronIron
+147.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+144.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-42.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+35.7%
Vitamins
Turkey meat is richer in vitamins B2, B3, B6, and B12. on the other hand, duck meat is richer in vitamins B1 and B5.
The diagram below displays their distribution.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+98.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+242.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+240%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+425%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+900%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+286.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+15.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Health impacts
White meat consumption, such as turkey meat and duck meat, positively affects overall health. White meat consumption is inversely related to overall mortality rates (1).
Health impacts of turkey meat
Bodybuilding
Turkey meat is very rich in proteins and is an excellent addition to muscle-building diets (2).
Diabetes and cardiovascular health
Consuming turkey meat has a neutral association with the development of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular health. The consumption of turkey meat is an excellent alternative to red meat (3).
Cancer
Turkey meat consumption in its unprocessed form has neutrally associated with cancer development. In addition, there are lower incidence rates of developing cancer compared with the positive association between red meat and cancer development. This indicates that the consumption of poultry, in this case, turkey meat, instead of red meat decreases the risk of developing cancer (3)(4).
Sleep and mood
Eating turkey and duck meat is usually associated with a sleepy feeling mainly due to the high amounts of tryptophan, an amino acid involved in sleep (5).
Tryptophan is also a serotonin precursor, which increases serotonin levels and provides a feeling of well-being (6).
Negative health impacts of turkey meat
Processed turkey contains preservatives and additives responsible for its negative health impacts.
Processed turkey consumption is positively associated with increased risks of cardiovascular health diseases, type 2 diabetes, and cancer (7)(8).
Health impacts of duck meat
Metabolism
Duck meat consumption decreases basal metabolism by decreasing thyroid hormone activity. This, in turn, can lead to increased weight gain (9).
Cardiovascular health, diabetes, and cancer
Overall there is a decrease in risks of CVD, diabetes, and cancer associated with poultry meat compared to red meat. However, it is essential to mention that duck meat contains a higher amount of saturated fats, which increases the risks of developing these diseases, especially cardiovascular diseases (10).
Overall, consumption of duck meat in moderation has a lower risk of developing cardiovascular diseases than red meat (1).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33672599/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31028659/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462824/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3208759/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6764927/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908021/
- Meat Consumption, Diabetes, and Its Complications
- https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/meat-fish-and-dairy/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23665298/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32723506/
Infographic
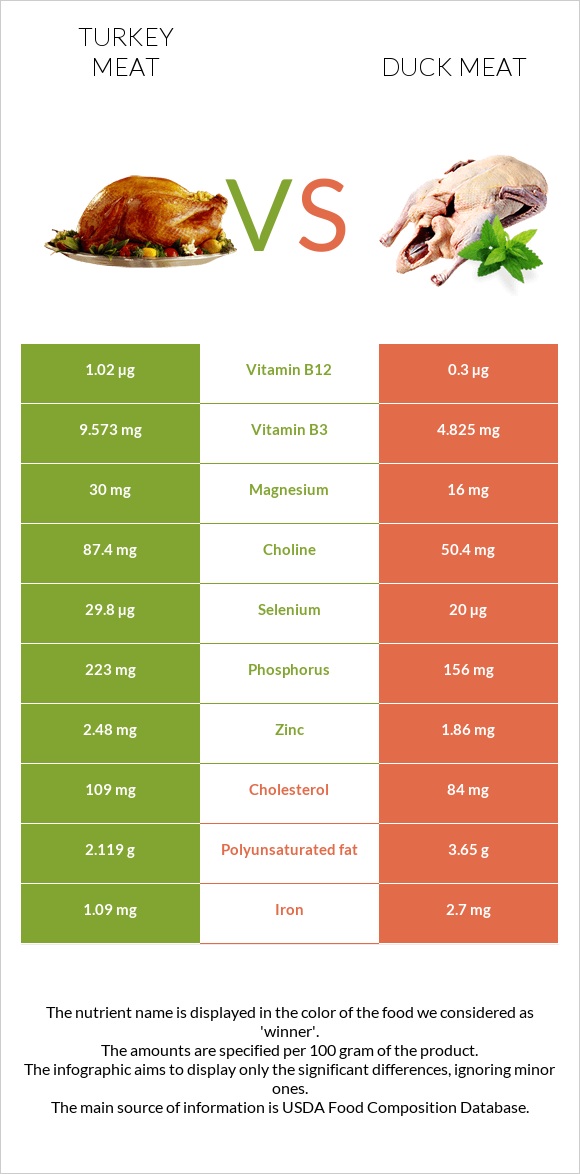
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.616mg | 0.18mg | 34% |
| Saturated fat | 2.155g | 9.67g | 34% |
| Fats | 7.39g | 28.35g | 32% |
| Vitamin B3 | 9.573mg | 4.825mg | 30% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.02µg | 0.3µg | 30% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.647g | 12.9g | 26% |
| Iron | 1.09mg | 2.7mg | 20% |
| Protein | 28.55g | 18.99g | 19% |
| Selenium | 29.8µg | 20µg | 18% |
| Copper | 0.093mg | 0.227mg | 15% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.045mg | 0.174mg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 223mg | 156mg | 10% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.119g | 3.65g | 10% |
| Cholesterol | 109mg | 84mg | 8% |
| Calories | 189kcal | 337kcal | 7% |
| Choline | 87.4mg | 50.4mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 2.48mg | 1.86mg | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 12µg | 63µg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.07mg | 0.7mg | 4% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 5.1µg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 30mg | 16mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.948mg | 1.098mg | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 15 IU | 3 IU | 2% |
| Sodium | 103mg | 59mg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 0.4µg | 0.1µg | 2% |
| Potassium | 239mg | 204mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.281mg | 0.269mg | 1% |
| Folate | 9µg | 6µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0.06g | 0g | N/A |
| Carbs | 0.06g | 0g | 0% |
| Calcium | 14mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.014mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.101g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.291mg | 0.232mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.004mg | 0.773mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.796mg | 0.872mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.925mg | 1.465mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.282mg | 1.486mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.724mg | 0.475mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.903mg | 0.752mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.902mg | 0.938mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.749mg | 0.462mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.008g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.005g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.105g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.008g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.01g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.014g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.841g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Turkey meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171479/nutrients
- Duck meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172409/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


