Turnip vs. Radish — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
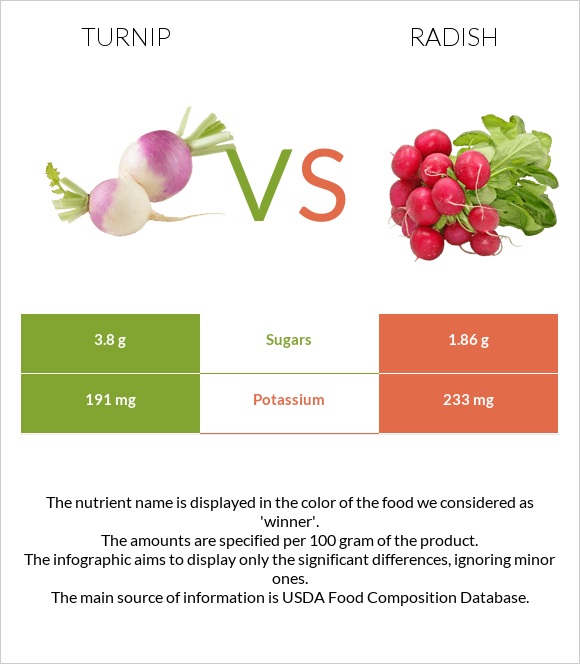
Turnips have a wider range of multisystem health benefits. Turnips are richer in copper, vitamin C, and most B complex vitamins. In comparison, radishes have a lower glycemic index, lower calories, and are cheaper. Radishes are also richer in folate compared to turnips.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- General differences
- Nutritional data comparison
- Calories
- Glycemic index
- Carbs
- Fiber
- Fat and protein
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Bioactive compounds with pharmaceutical effects
- Health impacts
- Cancer
- Antioxidant
- Anti Inflammatory
- Cardioprotective
- Obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome
- Analgesic properties
- Antimicrobial properties
- Cardiopulmonary enhancing properties
- Hepatoprotective properties
- Nephroprotective properties
- Diets and weight loss
- Downsides
- References
Introduction
Turnips and radishes belong to the family of root vegetables, which means that the edible part is the root of the vegetable grown under the soil. It is important to note that the green leaves are also edible.
This article will compare both based on general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Differences and Similarities in Appearance and Taste
Turnips and radishes come in different colors and sizes. This article will consider medium-sized turnips with white and purple colors and small-sized red-colored radishes.
Raw turnips have a spicy and mustardy flavor; however, they give a sweet and earthy flavor when cooked. On the other hand, radish has a zesty and spicy flavor similar to turnips; when cooked, they give a sweet earthy flavor.
Seasonal availability
Turnips are primarily cultivated in temperate climate regions. The harvest takes place during summer.
Radishes, on the other hand, are available throughout the year. There are spring, summer, and winter radishes.
Recipes
Turnips can be consumed in various ways, such as raw ones added to salads to increase flavor and texture.
Turnips can also be boiled, roasted, and mashed. It can also be used to prepare coleslaw preparation instead of cabbage.
A famous middle-eastern pickle is the turnip pickle which is usually done with beetroot and vinegar.
Radishes, similar to turnips, can be consumed similarly. The difference in radishes is that they have a less mustardy flavor. Thus, they are mostly consumed raw or pickled compared to turnips.
Price
Radish is cheaper than a turnip, but the price difference is not very high. They are nearly similar compared to each other.
Nutritional data comparison
Calories
Radishes are lower in calories compared to turnips. 100g of radish contains 16 calories compared to turnips which contain 28 calories. It is important to note that both are classified as low-calorie foods.
Glycemic index
Radish has a lower glycemic index compared to turnip.
Turnips are classified as high glycemic index foods. The glycemic index of turnips is 73. On the other hand, radishes are classified as low glycemic index foods. The glycemic index of radish is 32.
Carbs
Turnips contain more carbs than radishes. Turnips contain two times more carbs compared to radishes.
Fiber
Turnips and radishes have similar amounts of fiber.
Fat and protein
Turnips and radishes have negligible amounts of fats and proteins.
Vitamins
Turnips are richer in vitamin C by 42% compared to radishes.
In addition, turnips are richer in vitamin B6 and most other B-complex vitamins.
On the other hand, radishes are richer in folate.
300g of turnips satisfy 70% of the daily requirement of vitamin C and 21% of vitamin B6. In comparison, 300g of radishes satisfy 50% of the daily requirement of vitamin C and 19% of folate requirements.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+41.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+233.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+57.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+21.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+26.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+30%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1200%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+66.7%
Minerals
Turnips are richer in copper compared to radishes. Turnips contain 70% more copper.
On the other hand, radishes are richer in iron and potassium. Radishes are also lower in sodium compared to turnips by 42%.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+20%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+70%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+35%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+94.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+16.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+22%
Contains
more
IronIron
+13.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-41.8%
Bioactive compounds with pharmaceutical effects
Important chemicals present in turnips that have health importance are glucosinolates, isothiocyanates, phenylpropionitrile, brassica phenanthrene A, flavonoid phenolics, and arvelexin.
On the other hand, radish contains the following important compounds:
Flavonoids, phenols, polyphenols, pelargonidin, and isothiocyanates.
Health impacts
Cancer
Turnips have anti-carcinogenic and anti-tumor properties. The main components in turnips that provide these characteristics are glucosinolates and isothiocyanates. (1)
Radish has anti-carcinogenic properties. Radish metabolites like glucosinolates and isothiocyanates induce apoptosis and cancer cell death. This effect has been manifested in different cancers like liver cancer, colon cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, cervical cancer, and lung cancer. (2) (3)
Antioxidant
The flavonoids and phenolic compounds present in turnips have anti-oxidative characteristics. They are responsible for the scavenging effect of free radicals and reducing overall levels of oxidative stress. (4) (5)
On the other hand, radish also has anti-oxidative properties. Polyphenols provide high scavenging properties of free radicals, which in turn reduces oxidative stress. In addition, pyrogallol and vanillic acid present in radish have anti-oxidative properties. Radish anthocyanins have chemoprotective characteristics on overall stress-induced damage on normal body cells. (6)
Anti Inflammatory
Turnip has anti-inflammatory characteristics, which are due to the activity of arvelexin. (7)
Comparatively, radish contains anti-inflammatory compounds that have a bioactive effect similar to NSAIDs which suppress the activity of COX-2, a pro-inflammatory compound. It is important to note that these anti-inflammatory compounds are also present in radish leaves. (8)
Cardioprotective
In addition to their anti-inflammatory characteristics, arvelexin in turnips has antihypertensive and lipid-decreasing properties. The regulation of blood pressure and the decrease in blood lipid levels overall provide the cardioprotective role of turnips. (7)
While radish is rich in nitrate, it protects vascular tissue and acts as an antiaggregant. These characteristics help maintain healthy cardiovascular homeostasis.
Obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome
Ethanolic extracts present in turnips have anti-obesity properties. (10)
The ethanolic extracts in turnips, also have anti-diabetic properties. It improves blood glucose levels and regulates glucagon and insulin ratios. These extracts regulate hepatic glucose-regulating enzymes. Overall these extracts normalize blood glucose levels. (11)
Radish has anti-diabetic properties. It acts on the synthesis of adiponectin, one of the factors in regulating lipids and glucose in the body. This is also responsible for fatty acid oxidation and mobilization from stored fatty acid deposits all over the body. (12) (13)
Analgesic properties
Alcoholic compounds present in turnips have analgesic properties when consumed in the correct dosage and time intervals. (14)
Antimicrobial properties
Turnip extract has antimicrobial properties against multiple pathogens like staphylococcus, bacillus, and vibrios. In addition, turnip extracts were tested against helicobacter pylori and have beneficial results in treating helicobacter infections. (5)
Radish contains sulfur-containing compounds with antimicrobial characteristics on multiple pathogenic bacterial species, like E Coli and pseudomonas. (15)
Cardiopulmonary enhancing properties
Consumption of turnips has been shown to improve hemoglobin levels in the blood, increasing overall oxygen levels. (16)
Hepatoprotective properties
Flavonoids, phenolics, indoles, and volatiles found in turnip may have hepatoprotective effects by mitigating liver injury caused by hepatotoxic agents. (17)
Radish bioactive compounds may also have hepatoprotective effects due to cytoprotective (cell protection) and antioxidant effects. (18) (19)
Nephroprotective properties
Turnip extract improves kidney functioning and filtration. In addition to that, kidney and overall urinary tract inflammation reduction. (20)
Diets and weight loss
Turnip and radish are low in carbs and rich in fibers. On a caloric deficit diet or overall healthy lifestyle, it is important to include both during daily meals to maintain a healthy digestive tract and add textural complexity to everyday meals.
Vegan
Radish and turnips can be eaten by people who are following vegan diets.
Keto
Turnips are an excellent alternative replacement for potatoes in keto diets. Fried, boiled, mashed, and roasted turnips are a low-carb alternative to potatoes. However, the mustardy flavor might be overpowering for people who don’t like mustardy flavors.
Although fried turnips can replace fried potatoes, it is important to mention that if someone wants to follow a healthy lifestyle, it is recommended to avoid eating fried foods, which means that fried turnips are not a healthy alternative to fried potatoes.
Radishes are also recommended to be consumed in the keto diet and can be a good alternative to potatoes. However, turnips are more versatile in cooking compared to radishes.
Downsides
Drug interaction
Turnips can interact with medications dedicated to high blood pressure by increasing their activity and causing severe hypotension. In moderation, turnips wouldn’t cause these overreactions. However, it is best to take advice from your doctor.
Radishes decrease blood sugar levels. If taken in high amounts associated with anti-diabetic drugs, it might cause hypoglycemia, which means it decreases sugar levels below normal.
Allergies
It is essential to take into consideration turnip allergies. If it’s the first time someone is consuming turnips, it is advised to consume them in lower amounts the first two times if that person is allergic to them.
Radish allergies also exist; however, it is rare.
General Highlights
Turnips can cause bloating and gas. It is best to boil, cook, or bake turnips before consuming them if bloating and gas cause discomfort.
Moderate consumption of radish doesn’t cause any discomfort. However, consuming radishes in high amounts causes stomach irritation.
Radish consumption increases bile flow from the liver and gallbladder. In patients who suffer from gallstones, the flow might cause the stones to block the bile path and cause a painful gallbladder shock.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9751619/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17616135/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24510468/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10956123/
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Amira-Beltagy/publication/287409006
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17935293/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21434881/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5383142/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5986475/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20132043/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17996336/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25685286/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16936205/
- https://hms.gmu.ac.ir/article-1-1713-en.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5066007/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27856303/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30561035/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36501112/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24278606/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22069563/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 21mg | 14.8mg | 7% |
| Copper | 0.085mg | 0.05mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.134mg | 0.069mg | 3% |
| Folate | 15µg | 25µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 0.012mg | 2% |
| Calories | 28kcal | 16kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 6.43g | 3.4g | 1% |
| Calcium | 30mg | 25mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 191mg | 233mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.3mg | 0.34mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 1.8g | 1.6g | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 27mg | 20mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 67mg | 39mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg | 0.039mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.4mg | 0.254mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.2mg | 0.165mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.09mg | 0.071mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 1.3µg | 1% |
| Choline | 11.1mg | 6.5mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.71g | 1% | |
| Protein | 0.9g | 0.68g | 0% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 3.2142857142857144g | 4.25g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 311.1111111111111kcal | 235.2941176470588kcal | N/A |
| Fats | 0.1g | 0.1g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 4.63g | 1.8g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.8g | 1.86g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.27mg | 0.28mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.7µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.011g | 0.032g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.006g | 0.017g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.053g | 0.048g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.009mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.025mg | 0.023mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.036mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.033mg | 0.031mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.036mg | 0.033mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.011mg | 0.01mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.017mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.03mg | 0.035mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +32.4% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +89.1% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +27.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -65.6% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +183.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Turnip - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170465/nutrients
- Radish - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169276/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





