Avocado oil vs. Butter — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Butter, a dairy product, is rich in saturated fats, offering a creamy texture and a robust flavor, but is associated with higher cholesterol levels. In contrast, avocado oil, derived from the flesh of avocados, is rich in monounsaturated fats like oleic acid, which promote heart health by improving lipid profiles. While butter contains vitamins like A and E, avocado oil is packed with antioxidants, including lutein, which benefits cardiovascular, skin, and hair health.
Butter has a lower smoke point, making it suitable for medium-heat cooking, whereas refined avocado oil, with its high smoke point, is ideal for high-heat applications. Though both are calorie-dense, avocado oil provides a plant-based, nutrient-rich alternative with added versatility in culinary and cosmetic uses, contributing to long-term health when included in a balanced diet.
Introduction
Butter and avocado oil are fats widely used in kitchens worldwide, yet their nutritional composition, cooking properties, and health benefits distinguish them. This article compares their nutritional profiles, actual differences, and health impacts to help you choose the right option for your needs.
Actual Differences
Classification, Taste, and Appearance
Butter is a dairy product made by churning cream to separate the butterfat (1). Avocado oil, on the other hand, is a plant-based oil derived from the flesh of avocados (2).
Butter has a rich, creamy flavor and pale yellow color, while grass-fed butter is deeper yellow due to beta-carotene. Avocado oil has a subtle, nutty taste and a light green hue when unrefined, but refined versions are almost flavorless.
Production Methods
Butter is produced by churning cream or milk, resulting in a rich, creamy fat that is solid at room temperature. Avocado oil is extracted by pressing the flesh of ripe avocados. Extra-virgin avocado oil, similar to extra-virgin olive oil, is cold-pressed and retains its natural flavor and nutrients. Refined avocado oil undergoes additional processing for a neutral taste and higher smoke point, making it ideal for high-heat cooking.
Smoke Points and Usage Versatility
Butter has a lower smoke point of about 150°C (302°F), making it suitable for medium-heat cooking like baking and sautéing. Clarified butter, or ghee, has a higher smoke point of around 250°C (482°F) and is used in high-heat cooking and frying.
Avocado oil is one of the best oils for high-heat cooking due to its high smoke point, which can reach 271°C (520°F) when refined. It’s excellent for searing, roasting, and stir-frying. Unrefined avocado oil, with a lower smoke point, is better suited for dressings and dips.
Nutrition
The infographics below are presented for 100g servings of butter and avocado oil.
Macronutrients and Calories
Regarding macronutrients, butter and avocado oil are generally made of fats. However, avocado oil contains 100% fat, while butter contains only 81%. The remaining portion is water.
Both butter and avocado oil are calorie-dense fats. Butter contains about 717 calories per 100 grams, while avocado oil provides 884 calories per 100 grams.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+23.3%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+∞%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+∞%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+∞%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Fat Types
Saturated Fat
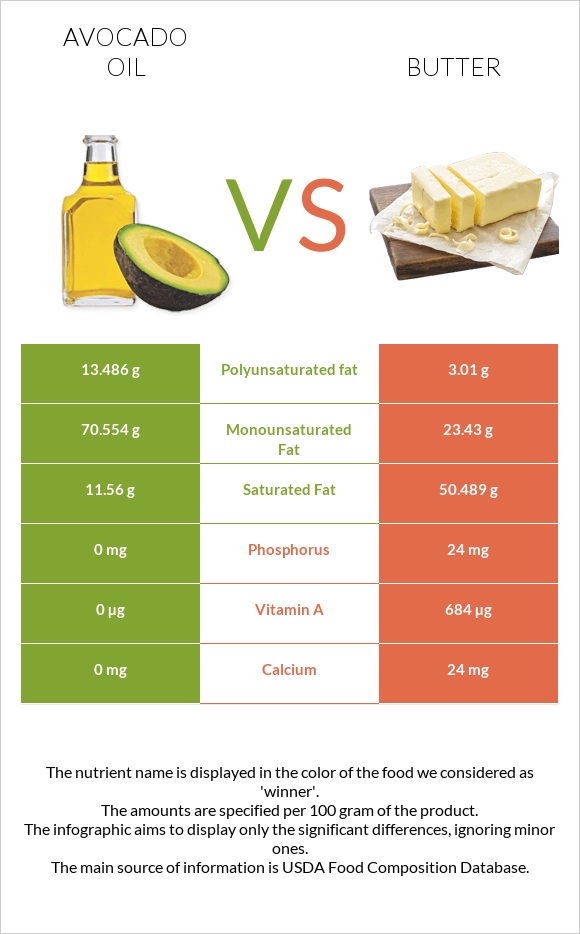
Butter is higher in saturated fats, containing about 50.5g per 100g. These fats contribute to its creamy texture but are associated with increased cholesterol levels.
Monounsaturated Fat
Avocado oil excels in monounsaturated fats (MUFA), providing around 70g per 100g. Its primary MUFA is oleic acid, which supports heart health by lowering LDL cholesterol.
Polyunsaturated Fat
Both foods contain smaller amounts of polyunsaturated fats. Avocado oil has about 13g per 100g, including omega-6 linoleic acid, while butter contains only 3g per 100g.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-77.1%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+201.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+348%
Cholesterol
Butter contains a noticeably high amount of cholesterol. It provides 215mg of cholesterol per 100g, while avocado oil does not contain any amounts of it.
Vitamins
Butter is rich in vitamin A, with 684µg per 100g, supporting vision and immune health. It also provides significant amounts of vitamin E and tocopherols, offering antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Carbs and Proteins
Butter and avocado oil do not provide any amounts of carbohydrates and proteins.
Glycemic index
Most of the oils and fats, including butter and avocado oil, lack carbohydrates. Hence, they have a glycemic index of 0.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Butter’s impact on heart health has been a subject of scientific debate and evolving research. Historically, it has been viewed with caution due to its high saturated fat content, which has been associated with increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease (3). The American Heart Association has long recommended limiting saturated fat intake to reduce the risk of heart disease (4). However, recent evidence suggests that the link between saturated fat and heart health is more nuanced than previously believed.
A 2016 meta-analysis published in PLOS ONE found that butter consumption has a neutral association with total mortality, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. While it does not appear to provide significant cardiovascular benefits, moderate consumption was not strongly linked to adverse outcomes in healthy individuals (5).
Additionally, butter contains bioactive components such as butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that may have anti-inflammatory properties, and fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, which contribute to overall health (6).
However, butter’s role must be considered in the context of the entire diet. A large-scale study highlighted the importance of dietary patterns over individual nutrients. Diets rich in whole, unprocessed foods, including healthy fats from sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, were associated with better cardiovascular outcomes than diets high in processed foods and saturated fats (7).
On the other hand, Avocado oil has gained recognition for its potential benefits to heart health, primarily due to its high content of monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid (8). These heart-healthy fats are known to improve lipid profiles by reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, both of which support cardiovascular health (9).
Additionally, avocado oil contains antioxidants such as lutein, which help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation—key contributors to heart disease (10). A study highlighted that diets rich in monounsaturated fats, like those in avocado oil, were associated with reduced risk of coronary artery disease (11). Its high smoke point also makes it a versatile and stable choice for cooking, ensuring nutrient retention.
Skin and Hair Health
Avocado oil offers a wealth of scientifically backed benefits for both skin and hair due to its rich composition of monounsaturated fats, vitamins, and antioxidants.
For skin, avocado oil is renowned for its moisturizing properties, as it helps to improve the skin’s hydration by replenishing the lipid barrier (12). Rich in carotenoids, such as lutein, it also provides antioxidant protection, neutralizing free radicals that contribute to premature aging and skin damage.
Research has shown that avocado oil can enhance collagen production, helping to maintain skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles (12). Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties may help soothe skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis. In terms of hair care, avocado oil is effective in promoting scalp health and preventing dandruff due to its antifungal and antibacterial properties. Its nourishing fats help strengthen hair strands, reduce breakage, and enhance shine, making it a popular ingredient in treatments aimed at improving hair texture and promoting growth. Clinical studies have demonstrated that avocado oil can penetrate the hair shaft more deeply than many other oils, providing essential moisture and promoting overall hair health (13).
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301702518_Butter_Manufacture
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352546850_Avocado_oil_Production_and_market_demand_bioactive_components_implications_in_health_and_tendencies_and_potential_uses
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002916523125007
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3070119/
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(17)32241-9/abstract
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/avocado-oil
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3546618/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464624004961
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23363996/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9786235/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6356572/
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -100% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +∞% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +∞% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +∞% |
| Contains more IronIron | +∞% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +∞% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +∞% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +∞% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +∞% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +∞% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 11.56g | 50.489g | 177% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 70.554g | 23.43g | 118% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 684µg | 76% |
| Cholesterol | 215mg | 72% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 13.486g | 3.01g | 70% |
| Fats | 100g | 81.11g | 29% |
| Vitamin E | 2.32mg | 15% | |
| Calories | 884kcal | 717kcal | 8% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.17µg | 7% |
| Vitamin K | 7µg | 6% | |
| Phosphorus | 0mg | 24mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0mg | 0.034mg | 3% |
| Choline | 18.8mg | 3% | |
| Protein | 0g | 0.85g | 2% |
| Calcium | 0mg | 24mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0mg | 0.016mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0µg | 1µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0mg | 0.11mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 0mg | 24mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0mg | 0.09mg | 1% |
| Folate | 0µg | 3µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 0g | 0.06g | N/A |
| Carbs | 0g | 0.06g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 0mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.06g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 0mg | 11mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0mg | 0.004mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0mg | 0.005mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0mg | 0.003mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.012mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.038mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.051mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.083mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.067mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.021mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.041mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.057mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.023mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.315g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.166g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Avocado oil - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173573/nutrients
- Butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






