Green bean vs. Yardlong bean — Nutrition Comparison and Health Impact


Summary
Yardlong beans are richer in proteins, vitamins C, A, and B1, and minerals than green beans. They also contain lower sodium.
On the other hand, green beans are richer in vitamins B3, B5, B6, and fiber. The GI of green beans is also lower.
Introduction
Yardlong bean vs. green bean is what we are going to talk about in this article, focusing on their nutrition and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Even though long beans and green beans are members of the same legume family, there are some subtle differences between them. The main difference is texture and appearance. Green beans, for example, taste good when steamed or boiled. When long beans are treated with water, they typically become soggy and bland. Besides, green bean pods are 6-8 inches long, while yardlong beans can reach 24 and 26 inches long.
Nutrition
You can find nutritional infographics at the bottom of this page that visually show the differences between yardlong beans and green beans.
Calories
Green beans have 31 calories per 100g, whereas yardlong bean contains 47 calories per 100g. Both are considered low-calorie food.
Carbs
Yardlong beans are extremely low in carbohydrates. They have 8g of carbs per 100 g serving. However, they are deficient in dietary fiber. Green beans have 6.97g of carbs per 100g, of which 2.7g is fiber, and 4.27g is net carbs.
Minerals
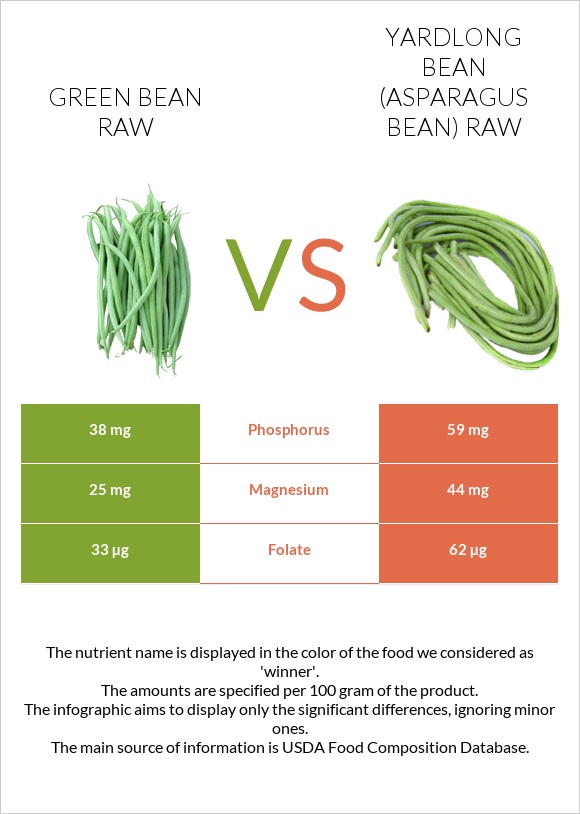
Yardlong beans have more calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, potassium, and less sodium than green beans.
However, green bean provides more iron and copper.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+119.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+43.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+76%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+35.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+13.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+54.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+55.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-33.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+150%
Vitamins
Green bean contains a significantly higher amount of Vitamin B3, three times more B5, and four times more B6.
Yardlong bean provides more Vitamin A, C, B1, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+79%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+309.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+487.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+54.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+22.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+30.5%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+87.9%
Glycemic Index
Green beans are lower in GI than yardlong beans. Despite having a low sugar content, yardlong beans have a high glycemic index. The GI of green beans is 20, which is considered a low glycemic index.
Acidity
The pH value of yardlong and green beans, generally, has been calculated to be equal to 3.3, making them alkaline food.
Health Benefits
Diabetes
Almost all vegetables, including yardlong beans, can help control blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes.
Yardlong beans contain chemical compounds that may help increase insulin production and glucose absorption, which aids in managing diabetes.
Because yardlong beans are low in calories and sugar, they are suitable for diabetic diets [1].
Cancer
Both yardlong and green beans contain a lot of antioxidants. They are high in Vitamin C, beta-carotene, a variety of carotenoids such as lutein, beta-carotene, violaxanthin, and neoxanthin, and flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol, catechin, epicatechins, and procyanidins, all of which have antioxidant properties and may help prevent certain types of cancer [2].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
People with favism or immune allergies to legumes should avoid consuming them.
Some people who are allergic to legumes are sensitive to all types of legumes. In contrast, others may consume various legumes and experience symptoms from only one or two types of legumes. Symptoms of a legume allergy include abdominal pain and vomiting, itching, redness of the skin, and hives, which often appear around the mouth. Wheezing and anaphylaxis are symptoms of severe cases [3].
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 43µg | 36% | |
| Fiber | 2.7g | 11% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.141mg | 0.024mg | 9% |
| Vitamin C | 12.2mg | 18.8mg | 7% |
| Iron | 1.03mg | 0.47mg | 7% |
| Folate | 33µg | 62µg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 25mg | 44mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 38mg | 59mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.41mg | 3% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.225mg | 0.055mg | 3% |
| Choline | 15.3mg | 3% | |
| Protein | 1.83g | 2.8g | 2% |
| Copper | 0.069mg | 0.048mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 1.5µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.082mg | 0.107mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.734mg | 0.41mg | 2% |
| Fructose | 1.39g | 2% | |
| Calories | 31kcal | 47kcal | 1% |
| Calcium | 37mg | 50mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 211mg | 240mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.24mg | 0.37mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 35µg | 43µg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.22g | 0.4g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 4.27g | 8.35g | N/A |
| Carbs | 6.97g | 8.35g | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.26g | N/A | |
| Starch | 0.88g | 0% | |
| Sodium | 6mg | 4mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.216mg | 0.205mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.104mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.05g | 0.105g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.01g | 0.036g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.113g | 0.169g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.019mg | 0.032mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.079mg | 0.104mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.066mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.112mg | 0.2mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.088mg | 0.184mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.022mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.067mg | 0.154mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.09mg | 0.162mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.034mg | 0.09mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +53% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +81.8% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +19.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -52.4% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +260% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +49.6% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Green bean raw - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169961/nutrients
- Yardlong bean (Asparagus bean) raw - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169222/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
