Bratwurst vs. Hot Dog — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Hot dogs are relatively thinner and are more processed with preservatives and nitrates than bratwursts.
Bratwursts are relatively richer in vitamins. The amount of Vitamin B1 is five times higher in bratwurst. Bratwurst also contains less sodium and saturated fats. On the other hand, hot dogs contain fewer calories, more calcium, and phosphorus.
Introduction
Sausages are one of the common forms of processed food. In particular, hot dogs are consumed worldwide. The countries with the highest consumption of sausages include Germany, Poland, and many more European Countries. They are also very popular in the United States.
We are going to compare hot dogs and bratwursts, focusing on their nutrition and health impact.
What's the Actual Difference?
Hot dogs and bratwursts have different ingredients, and hence flavor, texture, and appearance.
The most significant difference between hot dogs and bratwurst is the flavor. These products have different spices that give them their unique flavor. For instance, ginger, nutmeg, and garlic are some of the most popular seasonings for bratwurst. Garlic, cumin, and paprika are commonly used in hot dogs.
Also, while both hot dogs and bratwursts are made with ground meat, bratwursts are commonly made with pork or beef, while hot dogs are made with pork, beef, chicken, or turkey.
In general, hot dogs are more processed than bratwurst. Besides, hot dogs may contain more sodium and preservatives. Hot dog meat is emulsified into a paste; therefore, it may have a very smooth texture.
When it comes to their appearance, hot dogs are generally thinner than bratwursts.
Production
During the processing of hot dogs, the meat is mixed with a curing solution to improve the taste and increase the shelf life. The main ingredient is salt. It is used to make the meat easier to handle, improve flavor, and inhibit bacterial growth.
Usually, the meat of bratwurst is crushed, salted, seasoned with spices, and pressed into the intestines in the form of a shell; then, they hang it in a meat cellar to keep it cool.
Varieties
There are many different types of hot dogs and so many ways to serve them. The most popular types are:
- Kuuma Koira (traditional Finnish street food).
- Ripper.
- Reindeer dog ( Alaskan hot dog variety).
Bratwurst has a variety that is called white bratwurst. There are also various Franconian varieties including Kulmbacher bratwurst, Coburger bratwurst, Rote Wurst, and more.
Use
Hot dogs are usually boiled or grilled and served in a bun with ketchup and mustard. Other common condiments include chili, onions, cheese, and spices. Because of its convenience, it is usually eaten on the go.
Unlike hot dogs, bratwursts are thicker. In order to cook them evenly, it is recommended to boil the sausages and then grill them. Like hot dogs, bratwursts are usually served with mustard and a slice of bread, potatoes, or a pretzel on the side. Another popular side dish for both hot dogs and bratwursts is sauerkraut.
Dressing the sausages with whatever ingredients, be it hot dogs or bratwursts, is all up to you and your personal preference.
Nutrition
The food varieties used in this article are bratwurst, beef and pork, smoked, and hot dog Frankfurter meat.
One serving of bratwurst is 66 grams, while one serving of hot dog is 52 grams.
Please keep in mind that we will be discussing the differences in nutritional content per 100 grams (around 1 and a third of bratwurst or 2 hot dogs) for better comparison. To understand the differences in the nutrition of hot dogs and bratwursts, we created nutrition infographics, have a look below.
Macronutrients
Although the macronutrient composition of these two products is quite similar, we can still discuss the differences.
Both hot dogs and bratwurst have similar amounts of fats. A 100-gram serving of bratwurst contains 26.3 grams of total lipid fat, while a similar serving of hot dogs contains 25.8 grams. Hence, hot dogs and bratwurst are considered to be relatively high in fats. When comparing the two, hot dogs contain slightly more polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats.
Also, hot dogs and bratwurst have similar amounts of cholesterol (77mg and 78mg, respectively) as well as protein (10.3g and 12.2g, respectively).
Both contain no fiber or sugars.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+18.9%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+108.5%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+24.6%
Carbs
Hot dogs are higher in carbs compared to bratwursts. Hot dogs contain two times the number of carbs as bratwursts. Despite this, it is important to note that both products are considered to be low in carbohydrates.
Calories
Overall, the calories of hot dogs and bratwursts are pretty similar. They contain 297 calories per 100g, whereas hot dogs contain 290 calories per 100g. Nevertheless, the calorie level of bratwursts is a bit higher than in hot dogs.
Minerals
Although a single serving of neither bratwurst nor hot dog provides as many minerals as are needed to fill the daily need, they still contain adequate amounts of various minerals.
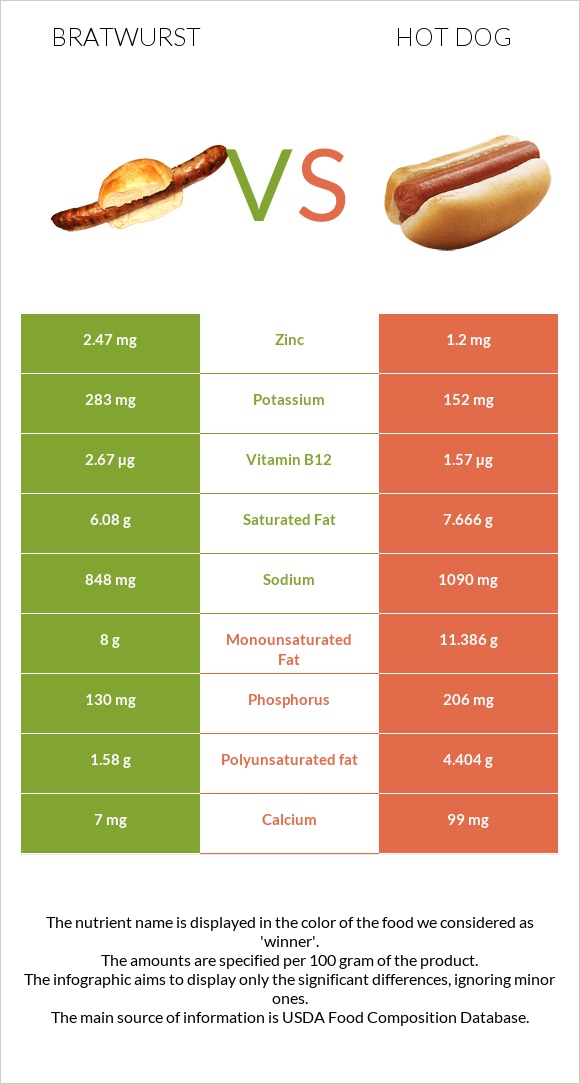
Bratwurst is richer in zinc. On the other hand, hot dogs are richer in phosphorus and calcium. The amount of calcium is 14 times higher in hot dogs. Both have equal levels of magnesium and iron.
The most prevalent mineral in these sausages is sodium. Both have high levels of sodium – 848 mg in bratwurst and 1090 mg in hot dogs. The level of sodium is 22% less in bratwurst than in hot dogs.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+86.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+105.8%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-22.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+12.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1314.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+21.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+58.5%
Vitamins
Generally, bratwursts contain higher concentrations of Vitamin B1, as opposed to hot dogs, although hot dogs also contain high levels of Vitamin B1.
Bratwursts are also high in Vitamin B12, Vitamins B2, Vitamin B5, and Vitamin B6. Bratwursts and hot dogs completely lack Vitamin E, Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Vitamin K, and Vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+590.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+76%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+16.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+122.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+20.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+70.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Glycemic Index
Generally, the glycemic index of a food is a value based on how quickly a food causes increases in blood glucose levels. The glycemic index of bratwursts and hot dogs is equal; it is 28. Both products are considered low glycemic index food.
Acidity
The acidity level of bratwursts is about 4.4, while hot dogs have 7.8. Both are acidic.
Health Impact
Ketogenic (Keto) Diet
The ketogenic diet is a low-carb and high-fat diet that includes foods with high protein. Eating meat, including fatty meats such as pork belly, lamb, and poultry, is recommended if you are on this diet.
Bratwursts contain fewer carbs than hot dogs and are a good source of protein. Hot dogs are more affluent in fats. If you're on this diet, eating hot dogs and bratwursts is not an issue, but in any case, try to combine it with a natural source of healthy fats (1, 2)․
Side Effects
Cardiovascular Health
Comparing bratwurst and hot dogs in terms of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk involves considering several factors:
Nutritional composition: Bratwurst typically contains more fat and calories compared to hot dogs. The higher fat content in bratwurst, especially if it's made from pork, can contribute to higher levels of saturated fat and cholesterol, which are linked to an increased risk of CVD (3).
Processing: Both bratwurst and hot dogs are processed meats, which have been associated with an increased risk of CVD. Processed meats often contain additives such as sodium nitrite, which can contribute to CVD risk (4).
Sodium content: Both bratwurst and hot dogs tend to be high in sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and increase the risk of CVD, especially in individuals who are sensitive to sodium (5).
The daily recommended intake of sodium is 2.3 g. Our body needs only a tiny amount of sodium to function correctly (6).
Serving size: Portion size also matters. Eating excessively large portions of either bratwurst or hot dogs can contribute to obesity and consequently increase the risk of CVD.
Preparation methods: How these meats are cooked also affects their impact on CVD risk. Grilling or frying at high temperatures can produce compounds linked to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are risk factors for CVD (7).
In general, both bratwurst and hot dogs are not considered healthy foods, and their regular consumption may contribute to an increased risk of CVD, especially when part of a diet high in processed and high-fat foods. Moderation and choosing healthier alternatives more often, such as lean cuts of meat or plant-based options, can help reduce cardiovascular risk.
Diabetes
Research shows a link between eating red meat, mainly processed meats, and type 2 diabetes. Compared to women who eat less red meat, women who often eat red meat have an almost one-third higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes (8). According to this study, daily consumption of processed meats is associated with a 43% increased risk of type 2 diabetes in women.
Allergy
Overall, two reasons can cause allergies to hot dogs and bratwursts. One of them is an allergy to red meat and an allergy to paprika.
Red Meat Allergy
Red meat allergy is a common allergy type that may affect any age group and race. People can have an allergic reaction to red meat if they are sensitive to cat serum albumin that cross-reacts with albumin in pork. Symptoms include urticaria, vomiting, and stomach cramps, in rare cases, anaphylaxis (9).
Paprika Allergy
In general, paprika allergy symptoms are rare, but they can lead to anaphylaxis, so it is essential to get tested if you usually have food allergies. Common symptoms include dizziness, hives, and swelling of the throat (10).
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0309174009002514
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1871403X07000816
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20089734/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33787869/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0033062006000831
- https://www.fda.gov/food/nutrition-education-resources-materials/sodium-your-diet
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26457715/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/article-abstract/1697785
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6488443/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4954633/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.67µg | 1.57µg | 46% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.38mg | 0.055mg | 27% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.58g | 4.404g | 19% |
| Zinc | 2.47mg | 1.2mg | 12% |
| Phosphorus | 130mg | 206mg | 11% |
| Sodium | 848mg | 1090mg | 11% |
| Calcium | 7mg | 99mg | 9% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.69mg | 0.31mg | 8% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8g | 11.386g | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.213mg | 0.121mg | 7% |
| Saturated fat | 6.08g | 7.666g | 7% |
| Protein | 12.2g | 10.26g | 4% |
| Potassium | 283mg | 152mg | 4% |
| Selenium | 14.1µg | 12.5µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.11mg | 2.665mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2mg | 0.166mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.08mg | 0.097mg | 2% |
| Fats | 26.34g | 25.76g | 1% |
| Carbs | 2g | 4.17g | 1% |
| Iron | 1mg | 1.09mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.19mg | 1% | |
| Folate | 4µg | 6µg | 1% |
| Calories | 297kcal | 290kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 2g | 4.17g | N/A |
| Cholesterol | 78mg | 77mg | 0% |
| Magnesium | 15mg | 15mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.041mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.107mg | 0.111mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.465mg | 0.474mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.485mg | 0.53mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.81mg | 0.907mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.903mg | 0.963mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.364mg | 0.291mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.405mg | 0.445mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.464mg | 0.555mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.395mg | 0.331mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -20.7% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +42.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +178.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Bratwurst - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172956/nutrients
- Hot dog - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172968/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




