Cream cheese vs. Goat cheese — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Goat cheese is richer in proteins, iron, calcium, copper, phosphorus, vitamins B2 and A. Instead, cream cheese is lower in sodium and richer in vitamin B5. Both contain high amounts of saturated fats.
Goat cheese and cream cheese are recommended to be consumed in moderation; however, in high amounts, they both increase the risks of cardiovascular diseases since they are high in saturated fats. Goat cheese has additional positive bone health impacts. Goat cheese has overall healthier impacts than cream cheese.
Introduction
This article will cover the differences between goat cheese and cream cheese, focusing on their nutritional differences and health impacts.
General differences
General differences exist between these cheeses. The main difference is the milk source used to prepare these cheeses. Goat milk is used for goat milk, and cow's milk is used for cream cheese.
Cream cheese has a shorter shelf life and has undergone more processing. In contrast, goat cheese is the product of normal cheese fermentation.
Taste
These types of cheese differ in flavor too. Goat cheese usually has an earthy, mild, and tart but slightly buttery flavor. The taste becomes more pronounced as the cheese ripens.
In contrast, cream cheese is a smooth, creamy cheese that has a taste described as sweet and mild, with a note of tanginess.
Nutritional content comparison
Calories
Goat cheese and cream cheese have almost similar amounts of calories. Both are classified as high-calorie foods.
However, goat cheese is higher in calories containing 14 calories more than cream cheese.
Macronutrients
Looking at the chart below, you can see that cream cheese is richer in water and carbs, thus having a creamier texture and sweeter taste. In contrast, goat cheese is higher in protein. Please, read more about macronutrients in the corresponding paragraphs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+15.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+4500%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+15.6%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+250.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+131.5%
Carbs
Goat cheese has negligible amounts of carbs. At the same time, cream cheese contains higher amounts of carbs. Cream cheese contains 5.52g of carbs per 100g, 3.76g of which are sugars.
Fats
Goat cheese and cream cheese are high in fats. Cream cheese contains higher amounts of fat compared to goat cheese. It has 4.6g more fat than goat cheese.
Saturated fats
Goat cheese and cream cheese contain equal amounts of saturated fats. The amount of saturated fats is relevantly high enough to take into consideration.
Cholesterol
Goat cheese and cream cheese contain significant amounts of cholesterol. Goat cheese is lower in cholesterol, containing 79mg of it, compared to 101mg in cream cheese.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+30.8%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+109.2%
Proteins
Goat cheese is more than three times richer in proteins compared to cream cheese. The amount of protein in goat cheese is remarkable - 21.5g per 100g.
Minerals
Goat cheese has a richer mineral profile compared to cream cheese.
Goat cheese is richer in iron, calcium, copper, and phosphorus.
Cream cheese contains lower amounts of sodium.
Below we can visualize the mineral distribution of each food.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-24.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+126.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+222.2%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+207.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+19.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1372.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+3033.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+32%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+250.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+745.5%
Vitamins
Goat cheese is richer in vitamins A and B2.
Whereas cream cheese is richer in vitamin B5.
Below we can visualize the vitamin distribution of each food.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+230.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+172.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+350%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+32.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+213%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+193.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+1161.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+19%
Glycemic index
The glycemic indices of both kinds of cheese are equal to 0. Check our glycemic index chart page for more information about the GI values of other foods.
Health impacts
Probiotics
Cream cheese and goat cheese contain friendly species of bacteria such as Lactobacillus. These kinds of probiotics offer a lot of health benefits, such as supporting digestion and boosting the immune system (9).
Goat cheese may contain L. acidophilus or L. plantarum, depending on its variety, while cream cheese usually has L. chungangensis (10) (11). L. chungangensis consumption may lead to higher levels of short-chain fatty acids, which may be beneficial in fighting inflammation.
Goat cheese health impacts
Positive health impacts of goat cheese
Moderate consumption of dairy has neutral to positive effects on cardiovascular health. Moderate consumption is important since goat cheese contains sodium and saturated fats and can negatively impact overall cardiovascular health (1).
Goat cheese increases satiety and maintains a sensation of fullness for a longer time; thus, we would have an overall reduction in food consumption which positively affects overall health (2).
Dairy consumption reduces the risks of cancer, specifically lung cancer (2).
Goat cheese is rich in calcium, and overall, it has beneficial effects during growth and older ages. During growth, it increases bone mass, forming a stronger bone structure. In addition, it prevents osteoporosis and numerous chronic diseases during older ages (3).
Negative health impacts of goat cheese
Goat cheese contains high amounts of fats, specifically saturated fats, which increase cardiovascular disease risks by increasing blood lipid levels. In addition to that, goat cheese contains higher amounts of sodium than cream cheese, increasing the risks of hypertension and its complications (4).
Calcium-rich foods increase the risk of developing prostate cancer (5).
Cream cheese health impacts
Positive health impacts of cream cheese
Cream cheese is beneficial to the digestive tract. It includes probiotic lactobacilli, which aid in the improvement of gut flora. As a result, there are benefits to general health (6).
Lactose-intolerant people can consume cream cheese in small amounts since it is low in lactose (7).
In moderation, cream cheese has neutral to positive impacts on cardiovascular health. However, if the consumed amounts exceed moderation, saturated fats increase the risks of cardiovascular diseases (1).
Negative health impacts of cream cheese
Lactose-intolerant people who overeat cream cheese will have bloating and diarrhea, but only in extreme circumstances. Cream cheese is processed cheese, and most cream cheese available in stores is processed and contains preservatives. Consuming these cheeses may have negative consequences on one's general health (8).
Cream cheese is high in saturated fats, which have adverse effects on cardiovascular health and metabolic health, increasing the mortality rate from cardiovascular diseases (3).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5867544/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579670/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4505966/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5577766/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12869397/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23126664/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4586575/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12018807/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23894906/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28631434/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6345912/
Infographic
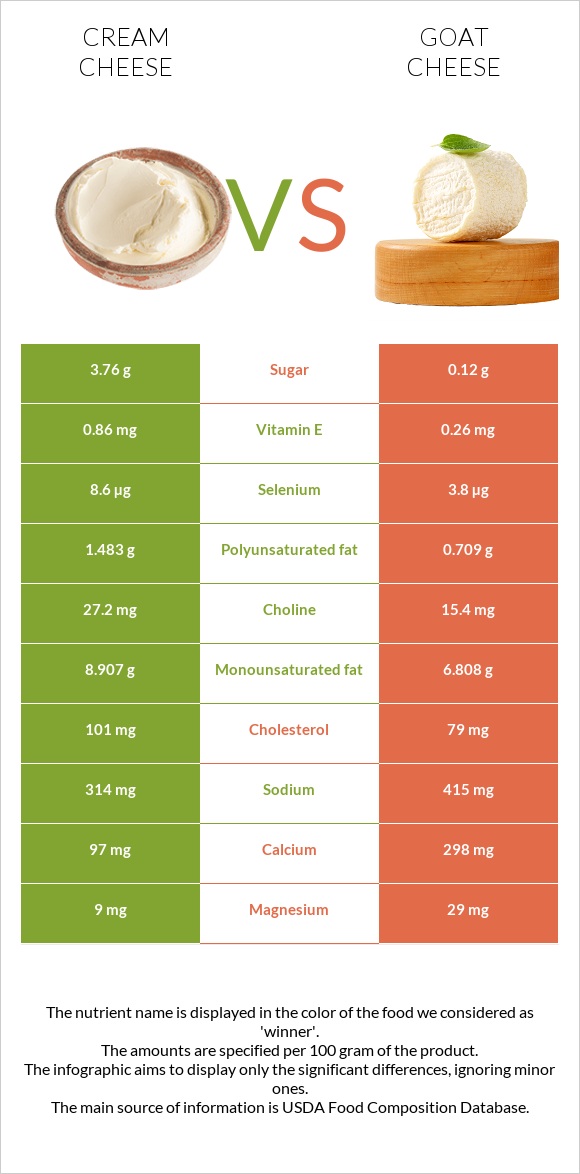
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 0.018mg | 0.564mg | 61% |
| Phosphorus | 107mg | 375mg | 38% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.23mg | 0.676mg | 34% |
| Protein | 6.15g | 21.58g | 31% |
| Calcium | 97mg | 298mg | 20% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 1.62mg | 19% |
| Vitamin A | 308µg | 407µg | 11% |
| Selenium | 8.6µg | 3.8µg | 9% |
| Fats | 34.44g | 29.84g | 7% |
| Cholesterol | 101mg | 79mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.091mg | 1.148mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.517mg | 0.19mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 9mg | 29mg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.907g | 6.808g | 5% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.483g | 0.709g | 5% |
| Sodium | 314mg | 415mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.86mg | 0.26mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.011mg | 0.093mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.023mg | 0.072mg | 4% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 22 IU | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.5µg | 3% |
| Carbs | 5.52g | 0.12g | 2% |
| Folate | 9µg | 2µg | 2% |
| Choline | 27.2mg | 15.4mg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 20.213g | 20.639g | 2% |
| Calories | 350kcal | 364kcal | 1% |
| Potassium | 132mg | 158mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.5mg | 0.66mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 5.52g | 0.12g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.76g | 0.12g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.35g | 0% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.056mg | 0.06mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.22µg | 0.22µg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 2.1µg | 2.5µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.069mg | 0.227mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.233mg | 0.805mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.324mg | 0.893mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.657mg | 1.861mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.567mg | 1.549mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.191mg | 0.575mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.291mg | 0.859mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.395mg | 1.485mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.175mg | 0.589mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.01g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.125g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.02g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.036g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.807g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cream cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173418/nutrients
- Goat cheese - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173433/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






