Chicken thigh vs. Chicken breast — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Chicken breast is lower in calories and fats and richer in proteins, selenium, phosphorus, and vitamins B3, B6, and B12. The chicken thigh is richer in iron, zinc, and vitamins B2 and B5. Chicken breast is dry. Chicken thigh is overall fattier and juicier meat.
Introduction
This article will compare fried chicken cuts: the chicken breast and the chicken thigh. We will compare cooked versions, specifically fried without the skin and bones.
Chicken meat is a great source of protein that is consumed around the world. However, there is a difference between the breast and the thigh regarding several aspects in regards to some general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Chicken breast can be found with the bones or filleted, with or without skin. The skin can have an impact on the nutritional content and health impacts.
In comparison, chicken thighs usually come with skin and bones; however, we can find boneless thighs aswell.
Being classified as poultry, chicken breast meat is considered to be white meat. In contrast, chicken thigh meat tends to be dark meat due to higher myoglobin content.
Both cuts are used in various recipes: breast meat is usually flavored with different spices, poached, grilled, baked, or pan-fried with vegetables, pasta dishes, etc. On the other hand, thigh meat can be roasted, braised, fried, or grilled.
Taste and texture
Chicken thigh is fattier and juicier compared to chicken breast. Chicken breast is a lean part and is primarily white and dry. In comparison, the chicken thigh is darker; however, it is still categorized as white meat.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare nutrients in 100g servings of fried skinless chicken breasts and skinless chicken thighs. As you can see in the infographic below, the main differences are shown in protein and fat content: the breast is richer in proteins, while the thigh is higher in fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+118.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+131.4%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+18.7%
Calories
Chicken breast has lower calories compared to chicken thighs. Chicken breast is leaner and contains 187 calories. In comparison, chicken thigh contains 218 calories.
Carbs
Their carb content is negligible. However, chicken thigh contains slightly more carbs.
Fats
Although we are considering skinless here for both, chicken thighs contain nearly double the amount of fat compared to chicken breast. Chicken breast contains 4.7g of fats. In comparison, chicken thighs contain 10.3g of fats.
Chicken thighs are richer in both saturated and unsaturated fats. Besides, they contain 11 mg more cholesterol than breasts.
Below we can visualize the distribution of their fat content.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+122.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+127.1%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-53.6%
Protein
Chicken breast is one of the most common high-protein foods that athletes and bodybuilding eat because it is high in protein and low in fats.
Chicken breast contains 33.4g of proteins in comparison, and chicken thighs contain 28.2g of proteins. The difference is quite significant.
Chicken thighs are often with bones. It is important not to confuse the serving sizes from boneless to regular ones. This article considered skinless and boneless chicken thighs and breasts.
Chicken thighs with skin and bones have a different nutritional profile considering that some of their weight is bone and skin. Similarly, chicken breast often comes with the skin and sometimes the bone, so their nutritional content would be different.
Minerals
Chicken breast is richer in calcium, potassium, selenium, and phosphorus. Chicken breast covers 106% of the daily value of phosphorus. In comparison, the chicken thigh is richer in zinc and iron.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+28.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+66.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+158.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+28.6%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+19.2%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+23.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+23.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-16.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+27.8%
Vitamins
Chicken breast is richer in vitamins B3, B6, and B12. In comparison, the chicken thigh is richer in vitamins B2 and B5.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+11.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+104%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+23.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+125%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+107.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+68.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+12.1%
Health impacts
Although chicken thigh is darker meat, however, it is also considered white meat. So both chicken breast and chicken thigh are white meat.
Overall nutrition
Chicken breast is a cut of chicken that is highly consumed within the athletic and bodybuilding communities as an essential part of a healthy diet. White meat is highly rich in protein and relatively lower in calories.
Chicken skin and carcinogens
Some hypothesis link consumption of chicken skin which, when it gets overcooked, will have high levels of HCA- Heterocyclic amines and PAH polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
In animal experiments, high doses of HCA and PAH increased the risks of different types of cancers, such as breast and colon.
No concrete scientific data states that consuming chicken skin, even when cooked at higher temperatures, increases the risks of various types of cancer in humans.
Most of the data is derived from rodents exposed to megadoses of HCA and PAH. Although these compounds are mutagenic but are the doses enough to harm humans (1)(2)?
Cardiovascular health
Chicken thigh is higher in total fats; to be more specific, chicken thigh contains higher amounts of saturated fats. The American Heart Association recommends in its guidelines a diet lower in saturated fats to reduce risks of cardiovascular diseases (3).
Thus, in this case, chicken breast is a better option to approach cardiovascular patients and, in addition, to reduce overall risks of cardiovascular diseases.
However, other data show otherwise. Some meta-analysis papers cannot conclude a specific relationship between the consumption of saturated fats and cardiovascular diseases (4)(5).
Further research and analysis are needed to conclude a definite answer.
Infographic
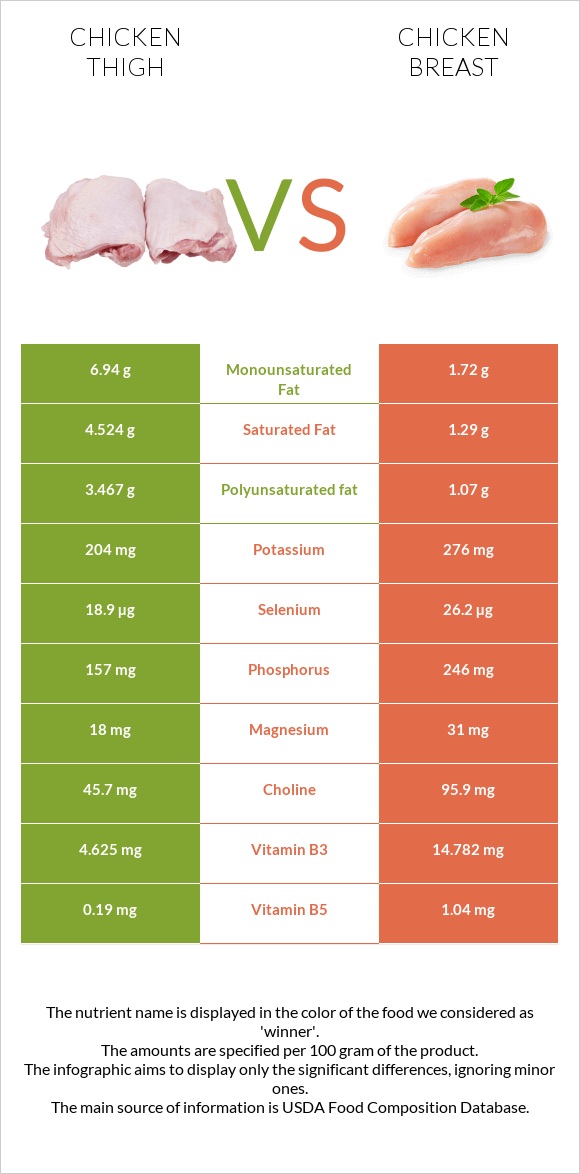
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B3 | 7.12mg | 14.782mg | 48% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.38mg | 0.64mg | 20% |
| Choline | 95.9mg | 17% | |
| Zinc | 2.79mg | 1.08mg | 16% |
| Protein | 28.18g | 33.44g | 11% |
| Selenium | 20.5µg | 26.2µg | 10% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.255mg | 0.125mg | 10% |
| Fats | 10.3g | 4.71g | 9% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.43g | 1.07g | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 199mg | 246mg | 7% |
| Saturated fat | 2.78g | 1.29g | 7% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.285mg | 1.04mg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 3.82g | 1.72g | 5% |
| Cholesterol | 102mg | 91mg | 4% |
| Iron | 1.46mg | 1.14mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.09mg | 0.054mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.42mg | 3% | |
| Calories | 218kcal | 187kcal | 2% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.33µg | 0.37µg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.4µg | 2% | |
| Magnesium | 26mg | 31mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 259mg | 276mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 95mg | 79mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 7µg | 1% | |
| Vitamin D | 0.2µg | 0.1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.088mg | 0.079mg | 1% |
| Folate | 9µg | 4µg | 1% |
| Protein per 100 calories | 12.926605504587156g | 17.88235294117647g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 77.35982966643009kcal | 55.92105263157895kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 1.18g | 0.51g | N/A |
| Carbs | 1.18g | 0.51g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 8 IU | 5 IU | 0% |
| Calcium | 13mg | 16mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.027mg | 0.021mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.329mg | 0.39mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.188mg | 1.412mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.486mg | 1.765mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.115mg | 2.509mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.384mg | 2.836mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.778mg | 0.925mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.121mg | 1.328mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.397mg | 1.659mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.874mg | 1.037mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.01g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.05g | 0.03g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.03g | 0.02g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Chicken thigh - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172387/nutrients
- Chicken breast - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171078/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.