Coconut milk vs. Condensed milk — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
In a few words, condensed milk is denser in nutrients, containing more calories, ten times more net carbs, and 3.5 times more protein. At the same time, coconut milk is three times higher in fats, especially saturated fatty acids, and richer in dietary fiber.
Condensed milk is a better source of most vitamins, providing six times more vitamin K, four times more vitamin B5, and three times more vitamin B1.
Coconut milk is 152 times richer in manganese, 18 times richer in copper, and nine times richer in iron. Condensed milk, however, contains 18 times more calcium.
Coconut milk has a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load, as opposed to condensed milk with a moderate glycemic index but a high glycemic load.
Introduction
Condensed milk and coconut milk are different types of milk with distinct flavors and uses. This article will look at how these two compare, especially regarding nutrition and their impact on health.
Production, Taste, and Use
Condensed milk is a sweetened dairy product made by removing most water from milk and adding sugar. It has a thick and syrupy consistency and a very sweet taste. It is often used as a sweetener in recipes, such as desserts and baked goods.
Coconut milk, on the other hand, is plant-based milk made by blending coconut flesh with water. It has a creamy texture and a sweet, nutty flavor. It is commonly used in Southeast Asian cuisine and in vegan and dairy-free recipes.
While condensed milk and coconut milk are used as ingredients in various recipes, they cannot be used interchangeably. Condensed milk is much sweeter and thicker than coconut milk, and its flavor would overpower a dish if used instead of coconut milk. Likewise, coconut milk would not provide the sweetness and texture needed in a recipe for condensed milk.
Nutrition
The infographics below are presented for 100g servings of canned condensed sweetened milk and raw coconut milk, expressed from grated meat and water.
However, the average serving sizes of these foods per person is one tablespoon or 15g for coconut milk and two tablespoons or 30g for condensed milk.
Macronutrients and Calories
Condensed and coconut milk significantly differ in their macronutrient contents. Condensed milk is much denser in nutrients, consisting of 27% water and 73% nutrients, while coconut milk comprises 68% water and 32% nutrients.
The primary macronutrient of condensed milk is carbohydrates, making up 54% of total mass, whereas coconut milk is fats, making up 24%.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+174%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+149%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+245.4%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+881.9%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+157.7%
Calories
While both are high-calorie foods, condensed milk is considerably higher in calories containing 91 more calories in a 100g serving.
A 100g serving of condensed milk provides 321 calories, while this number for coconut milk is 230 calories.
Carbohydrates
Condensed milk contains about ten times more carbohydrates compared to coconut milk. However, while 100% of the carbs in condensed milk are made up of net carbs, this number is only 60% for coconut milk. The other 40% of coconut milk carbohydrates are dietary fiber.
A 100g serving of condensed milk provides 54.4g of carbohydrates, while the same serving size of coconut milk has 5.54g.
While condensed milk lacks dietary fiber entirely, coconut milk provides 2.2g of fiber per 100g serving.
Protein
Condensed milk is about 3.5 times richer in protein. A 100g serving of condensed milk covers 20% of the daily needed protein value.
Both kinds of milk contain some levels of all essential amino acids; however, condensed milk is richer in all of them.
Fats
Conversely, coconut milk is 2.7 times higher in fats than condensed milk. Coconut milk falls in the top 11% of foods as a source of fats.
The fat content of coconut milk consists almost entirely of saturated fats, whereas condensed milk’s fat content comprises 66% saturated and 29% monounsaturated fats.
Thus, condensed milk is lower in saturated fats but higher in unsaturated fats,
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-74%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+139.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+29.1%
Vitamins
Condensed milk is richer in most vitamins compared to coconut milk. It is six times richer in vitamin K, four times richer in vitamin B5, three times richer in vitamin B1, and almost two times richer in vitamin B6.
Condensed milk also contains vitamins in which coconut milk is absent, such as vitamins A, D, B2, and vitamin B12.
That said, coconut milk contains nearly four times more vitamin B3 and two times more folate or vitamin B9.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+261.9%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+45.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+246.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+309.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+54.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+500%
Minerals
Coconut and condensed milk are good sources of various minerals.
Coconut milk is 152 times richer in manganese, 18 times richer in copper, nine times richer in iron, and almost two times richer in magnesium. At the same time, condensed milk provides 18 times more calcium, three times more phosphorus, and more selenium, potassium, and zinc.
Coconut milk is about two times lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+42.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+763.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+1673.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-88.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+15166.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1675%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+41.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+40.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+153%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+138.7%
Glycemic Index
Condensed and sweetened milk has a moderate glycemic index of 61 (1). Unexpectedly, coconut milk has been studied to have a much higher glycemic index value of 97 (2).
However, coconut milk has also been studied to have a low glycemic load of 5, meaning one serving of coconut milk raises glucose levels slowly.
Condensed milk has a higher glycemic load due to a larger average serving size per person. Based on our numbers, the glycemic load of condensed milk is equal to 10.
You can learn more about the glycemic impact of coconut milk on our website.
Weight Loss & Diets
Due to the significant differences between macronutrient contents, these two kinds of milk fit into different diets.
Of these two, coconut milk is preferred for low-carb and low-calorie diets, while condensed milk is the better choice for a low-fat diet. Neither is a good option for a keto diet.
Naturally, coconut milk fits in vegan and plant-based diets, unlike condensed milk.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Research shows that carbohydrate intake itself is not associated with increased cardiovascular risk or mortality; however, for people who consume carbohydrates as more than 60% of their total calorie intake, there is a higher mortality risk (3).
In experimental studies, sweetened condensed milk has been found to have proinflammatory effects (4).
Coconut milk oil has been researched to somewhat lower cardiovascular risk in lab animals (5). Another study showed that the consumption of total or saturated fat, including that from coconut, was not a predictor of coronary heart disease (6).
At the same time, frequent coconut milk intake has been associated with an increased risk of vascular disease in adults (7).
Diabetes
As mentioned above, coconut milk has a high glycemic index but a low glycemic load, while condensed milk has a moderate glycemic index but a high glycemic load.
This means that despite the lower glycemic index value, one serving size of condensed milk raises glucose levels more quickly than one serving of coconut milk.
Sweetened condensed milk has been researched to have detrimental effects on insulin sensitivity leading to insulin resistance (4).
Sources.
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5325842/
- https://www.naturalmedicinejournal.com/journal/high-fat-vs-high-carbohydrate-diet-and-cardiovascular-disease
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5479812/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339310293
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15563444/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312480029
Infographic
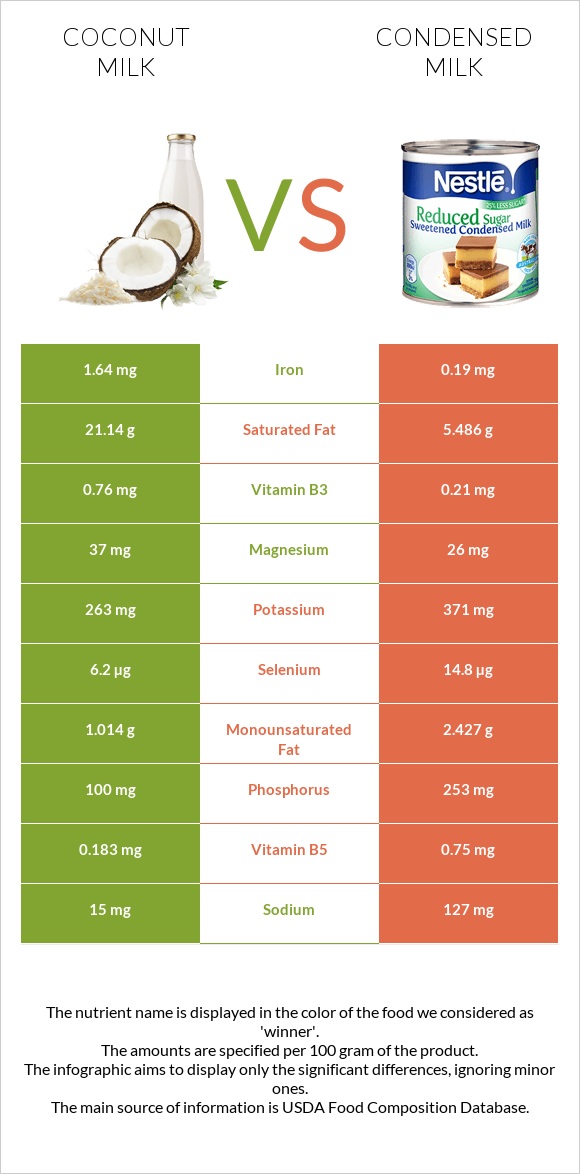
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 21.14g | 5.486g | 71% |
| Manganese | 0.916mg | 0.006mg | 40% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0mg | 0.416mg | 32% |
| Copper | 0.266mg | 0.015mg | 28% |
| Calcium | 16mg | 284mg | 27% |
| Fats | 23.84g | 8.7g | 23% |
| Phosphorus | 100mg | 253mg | 22% |
| Iron | 1.64mg | 0.19mg | 18% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0.44µg | 18% |
| Carbs | 5.54g | 54.4g | 16% |
| Selenium | 6.2µg | 14.8µg | 16% |
| Choline | 8.5mg | 89.1mg | 15% |
| Protein | 2.29g | 7.91g | 11% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 34mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.183mg | 0.75mg | 11% |
| Fiber | 2.2g | 0g | 9% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 74µg | 8% |
| Calories | 230kcal | 321kcal | 5% |
| Sodium | 15mg | 127mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.026mg | 0.09mg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1.014g | 2.427g | 4% |
| Magnesium | 37mg | 26mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 263mg | 371mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.76mg | 0.21mg | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.67mg | 0.94mg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 0 IU | 6 IU | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.033mg | 0.051mg | 1% |
| Folate | 16µg | 11µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.261g | 0.337g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 2.8mg | 2.6mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 3.34g | 54.4g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.34g | 54.4g | N/A |
| Vitamin E | 0.15mg | 0.16mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.027mg | 0.112mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.083mg | 0.357mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.09mg | 0.479mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.17mg | 0.775mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.101mg | 0.627mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.043mg | 0.198mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.116mg | 0.382mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.139mg | 0.529mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.053mg | 0.214mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Coconut milk - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170172/nutrients
- Condensed milk - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171275/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





