Cod vs. Grouper — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Grouper fish is high in vitamins B5, B6, A, iron, and potassium. It covers your daily need for selenium 17% more than cod. Grouper fish has slightly more protein and fat content.
Unlike it, cod is richer in vitamins B3, B12, C, magnesium, and choline. Cod also provides fewer calories and saturated fats, whereas grouper fish has a lower sodium level.
Table of contents
Introduction
In this article, we will discuss the dissimilarities between grouper fish and cod and what impacts these differences have on health.
Classification
Grouper fish belongs to the order Perciformes, family Serranidae, and subfamily Epinephelinae. Cod belongs to the order Gadiformes, family Gadidae, genus Gadus.
Appearance
The hue of Atlantic codfish can range from reddish brown to gray-green. They often have patches that are reddish brown.
Grouper fish frequently have dark colors of green or brown, but certain species have brighter colors.
The length of the Atlantic cod is 51 inches, and the weight is 77 pounds. Grouper fish is 10-12 inches long and weighs around 440 pounds.
Groupers live in warm waters, whereas cod prefer cold water.
Taste and Use
Grouper fish has a gentle, delicate taste. The texture of grouper fish is thick and flaky. Cod has a subtle and delicate taste with a little bit of sweetness. The flesh is tender and crispy.
Both are suitable for various cooking methods, such as grilling, baking, or frying.
Varieties
There are numerous species of grouper fish. Black, Red, Yellowedge, Nassau, Yellowfin, and Tiger Grouper are the most common.
There are three species in the Gadus genus: Atlantic, Pacific, and Greenland.
Nutrition
Macronutrients and Calories
Overall, grouper fish and cod have similar nutritional densities, grouper fish being only a little denser. Grouper fish has 74% water, whereas cod has 76%. Both are carb-free and provide equal amounts of protein. Moreover, grouper fish has more calories, whereas cod has less fat content.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+51.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+28.2%
Calories
Compared to cod, grouper fish has more calories per hundred grams. A hundred grams of grouper fish contains 118 calories, whereas cod provides 105 calories.
Calories in one fillet or 202 grams for grouper fish is 238kcal. One fillet of cod weighs 180 grams and has 189 kcal.
Protein
Grouper fish and cod are good sources of protein. A hundred grams of grouper fish provide 24.84g of protein, whereas cod contains 22.83g.
Fats
Grouper fish is high in total fat content. A hundred grams of grouper fish contain 1.3g of fats, whereas cod provides 0.86g. Grouper fish is high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. On the other hand, cod provides less saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-43.8%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+116.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+38%
Omega-3 fatty acids
A hundred grams of grouper fish contain 0.365g of omega-3 fatty acids, whereas cod provides 0.171g. Grouper fish is high in omega-3 DHA, EPA, and DPA.
Carbohydrates
Grouper fish and cod do not contain carbohydrates.
Cholesterol
Cod is high in cholesterol levels. A hundred grams of grouper fish contain 47mg of cholesterol, whereas cod provides 55mg.
Vitamins
Grouper fish is high in vitamins B5, B6, A, and folate. On the other hand, cod is high in vitamins B2, B3, B12, and C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+1216.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+559.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+52.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+257.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+383.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+23.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25%
Minerals
Grouper fish is high in potassium, selenium, and iron. Moreover, grouper fish contain less sodium. In contrast, cod is high in magnesium, manganese, and choline.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+13.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+13.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+66.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+50%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+94.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+132.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+25%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-32.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+24.5%
Mercury content
Grouper fish have a higher mercury level than cod. The mercury concentration mean (PPM) for grouper fish is 0.448. In contrast, the PPM for cod is 0.111(1).
Glycemic Index
Grouper fish and cod are low-GI foods. The glycemic index of both foods is 0.
Acidity
The potential renal acid load (PRAL) is a way to determine the acidity of foods. The PRAL value of grouper fish is 6.3. The PRAL value of cod is 9.9. Both of them are acid-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
The study found a connection between eating lean and fatty fish and losing weight on a calorie-restricted diet(2).
Consumption of cod fish per week causes obese people to lose more weight than a diet without seafood(3).
Cod-fed mice had less adipose tissue mass and smaller white adipocytes than chicken-fed mice(4).
Compared to grouper fish, cod has fewer fats and is a good option for a low-fat diet.
Cod containing fewer calories per 100g is the better choice for a low-calorie diet.
Grouper fish and cod are excellent for the keto diet because they are carb-free.
Grouper fish and cod are not considered vegan or vegetarian.
Both are allowed in the pescetarian and the Mediterranean diets.
Grouper fish and cod are acceptable for the Paleo diet.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Fish intake may decrease the risk of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, stroke, and mortality(5).
Increased intake of cod is associated with a lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Consuming cod does not affect blood lipids or glucose levels(6).
According to the study, high consumption of cod affected the blood concentration of total neopterin, a marker of cellular immunological activation(7).
Compared to the positive control, the group given the grouper fish diet had considerably reduced liver, kidney, and heart damage. Consumption of grouper fish may lower the total cholesterol, triglycerides, and serum glucose(8).
Inflammation
Grouper fish and cod contain omega-3 fatty acids and have anti-inflammatory and inflammation-resolving properties(9).
Cod, for instance, contains proteins that may help to control the inflammatory response during recovery from skeletal muscle injury(10).
Pregnancy
Grouper fish and cod do not contain high levels of mercury and are good choices for pregnant women. Grouper has more mercury content than cod. However, you can consume grouper fish in moderate amounts(11).
References
- https://www.fda.gov/food/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17502874/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19356912
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32207773/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33576844/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8717162/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257651/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24124612/
- https://www.fda.gov/food/
Infographic
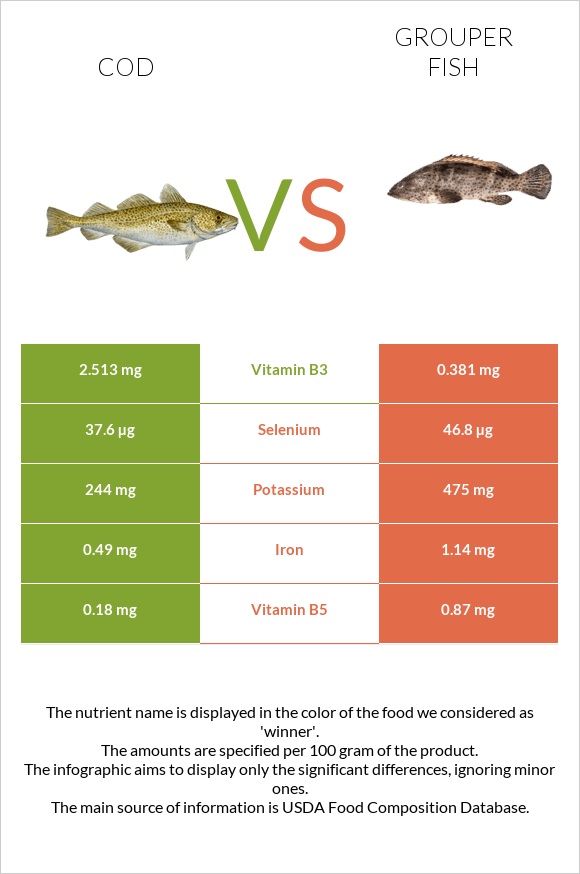
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 37.6µg | 46.8µg | 17% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.05µg | 0.69µg | 15% |
| Choline | 83.7mg | 15% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.18mg | 0.87mg | 14% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.513mg | 0.381mg | 13% |
| Iron | 0.49mg | 1.14mg | 8% |
| Potassium | 244mg | 475mg | 7% |
| Vitamin D | 46 IU | 6% | |
| Vitamin D | 1.2µg | 6% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.079mg | 0.006mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 0.81mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.283mg | 0.35mg | 5% |
| Protein | 22.83g | 24.84g | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 14µg | 50µg | 4% |
| Cholesterol | 55mg | 47mg | 3% |
| Calories | 105kcal | 118kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 0.86g | 1.3g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 1mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 42mg | 37mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 14mg | 21mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.036mg | 0.045mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.58mg | 0.51mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 138mg | 143mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 78mg | 53mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.088mg | 0.081mg | 1% |
| Folate | 8µg | 10µg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.168g | 0.299g | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.292g | 0.403g | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.02mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.124g | 0.268g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.256mg | 0.278mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.001mg | 1.089mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.052mg | 1.145mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.856mg | 2.019mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.097mg | 2.282mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.676mg | 0.735mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.891mg | 0.97mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.176mg | 1.28mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.672mg | 0.731mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.004g | 0.035g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.154g | 0.213g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.013g | 0.017g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cod - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171956/nutrients
- Grouper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171963/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






