Coriander vs Cumin - In-Depth Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cumin contains more iron, manganese, calcium, magnesium, copper, phosphorus, Vitamin B family, Vitamin E, zinc, and potassium than coriander. However, coriander has more Vitamin A, Vitamin K, and folate, low in sugars, sodium, saturated fats, and price.
Introduction
This article will discuss the main differences in the nutrition of turmeric and cumin, focusing on their health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Both turmeric and cumin are the main ingredients in the Indian kitchen. However, they differ in taste and appearance. Turmeric has a golden yellow color and a bitter taste with a peppery flavor, whereas cumin is earthy, spicy, and slightly bitter and has a brown color. Cumin is used in some cheeses, it can be an ingredient in chili powder, or you can add it to dry rubs for roasted or grilled meats, soups, and the breading for fried foods. In contrast, turmeric is one of the main ingredients in curry and vegetable curry.
Nutrition
You can find nutritional infographics at the bottom of this page that visually show the differences between coriander (leaves, raw) and cumin seeds.
Calories
Cumin seeds are considered high calorie-foods; they contain ten times higher calories.
Cumin seeds have 375 calories per 100g, whereas coriander contains 23 calories per 100g.
Fats
Cumin seeds contain 40 times more fats than coriander. It has 22.27g of fats per 100g, whereas coriander provides only 0.52g of fat.
Carbs
Cumin seeds have 44.24g of carbs per 100g, of which 10.5g is fiber and 33.74g are net carbs.
Coriander contains only 3.67g of net carbs, of which 2.8g is fiber and 0.87g are net carbs.
However, people usually consume them in tiny amounts so that the number of carbs doesn't matter much.
Cholesterol
Both coriander and cumin have no cholesterol.
Minerals
Cumin seeds have 12 times more calcium, 36 times more iron, 13 times more magnesium, nine times more phosphorus, six times more zinc, and two times more copper and potassium.
Cumin seeds fall in the range of the top 2% of foods as a source of iron and can fully convert your daily iron need.
However, coriander provides less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -72.6% |
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +1307.7% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +1289.6% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +243.2% |
| Contains more IronIron | +3649.2% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +285.3% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +860% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +939.6% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +682.4% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +477.8% |
Vitamins
Cumin seeds contain a significantly higher amount of Vitamin E, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B3, folate, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B6.
Cumin seeds fall in the top 14% of foods as a source of Vitamin B1 and are in the top 18% of foods as a source of Vitamin A.
Coriander is higher in Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Vitamin C, and folate. The amount of Vitamin K is 56 times higher in coriander.
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +250.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +426.6% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +5640.7% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +520% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +33.2% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +837.3% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +101.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin B3Vitamin B3 | +311% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +191.9% |
Glycemic Index
The estimated glycemic index of cumin is 0, while coriander has a GI of 32. Both are considered low GI foods.
Health Benefits
Diabetes
Several studies have found that cumin can help to lower blood glucose levels. Cumin supplementation resulted in a significant reduction in blood glucose and increased total hemoglobin and glycosylated hemoglobin in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. It also reduced total cholesterol levels and prevented weight loss [1]. However, more research on humans is needed.
Coriander seeds, extract, and oils may aid in blood sugar control. According to animal studies, coriander seeds lower blood sugar by promoting enzyme activity that aids in the removal of sugar from the blood [2].
Cancer
Based on test-tube and animal studies, terpinene, quercetin, and tocopherols found in coriander may have anticancer, immune-boosting, and neuroprotective properties [3].
Research indicates that the chemopreventive effects of cumin are associated with its ability to modulate the metabolism of carcinogens. Several mice studies demonstrate [4] significant suppression of the growth of stomach tumors and cervical tumors with cumin.
Cardiovascular Health
According to research, estrogens in the body may aid in lipid metabolism, protecting the heart from coronary heart disease. Estrogen levels drop significantly during menopause, making a woman vulnerable to heart disease. Cumin extract has hypolipidemic properties, making it a potential treatment for certain menopausal disorders [5].
Based on research, coriander extract may be a diuretic, assisting your body in flushing out excess sodium and water, which may help to lower your blood pressure. According to some studies, coriander may also help lower cholesterol [6].
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Cumin contains bioactive compounds known as curcumin. Curcumin is a powerful antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin has been shown in studies to inhibit the action of free radicals and stimulate the activity of other antioxidants [7].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Coriander can cause allergic reactions. Asthma, nasal swelling, hives, and swelling inside the mouth are all symptoms of such reactions.
A compound known as profilin is responsible for cumin allergies. Individuals who are allergic to profilin may also be allergic to coriander. Cumin allergy can also aggravate pollen allergies. Common symptoms include itching, swelling, and tingling in the mouth [8].
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12220968/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814699001132
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5618098/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1207/s15327914nc4702_10
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2841243/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18831331/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17044766/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30883393/
Infographic
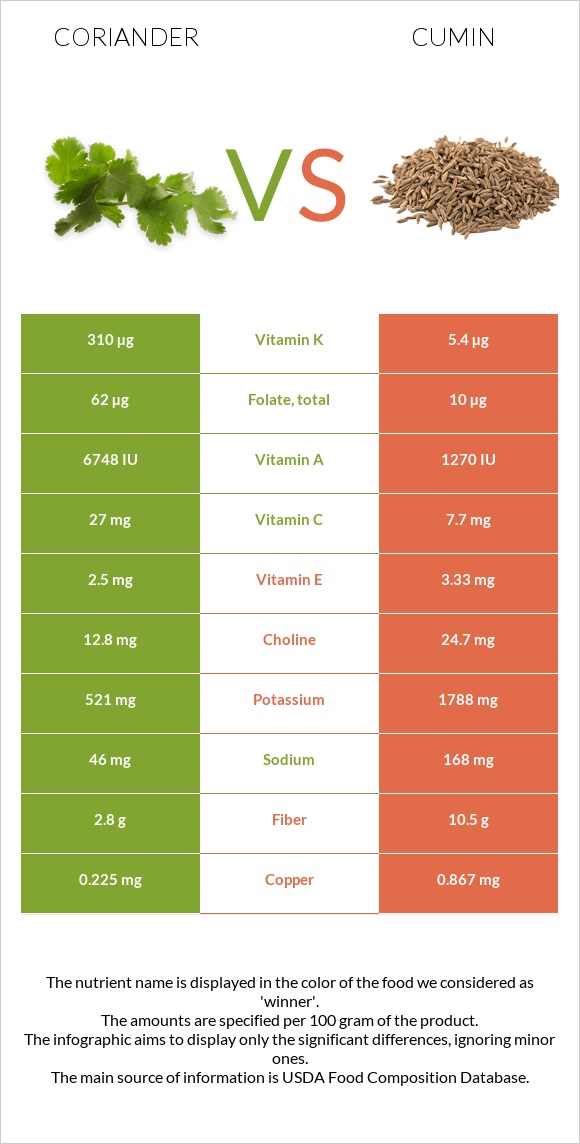
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 1.77mg | 66.36mg | 807% |
| Vitamin K | 310µg | 5.4µg | 254% |
| Manganese | 0.426mg | 3.333mg | 126% |
| Calcium | 67mg | 931mg | 86% |
| Magnesium | 26mg | 366mg | 81% |
| Copper | 0.225mg | 0.867mg | 71% |
| Phosphorus | 48mg | 499mg | 64% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.067mg | 0.628mg | 47% |
| Zinc | 0.5mg | 4.8mg | 39% |
| Potassium | 521mg | 1788mg | 37% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.275g | 14.04g | 34% |
| Fats | 0.52g | 22.27g | 33% |
| Protein | 2.13g | 17.81g | 31% |
| Fiber | 2.8g | 10.5g | 31% |
| Vitamin A | 337µg | 64µg | 30% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.114mg | 4.579mg | 22% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.149mg | 0.435mg | 22% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.04g | 3.279g | 22% |
| Vitamin C | 27mg | 7.7mg | 21% |
| Calories | 23kcal | 375kcal | 18% |
| Carbs | 3.67g | 44.24g | 14% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.162mg | 0.327mg | 13% |
| Folate | 62µg | 10µg | 13% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.57mg | 11% | |
| Selenium | 0.9µg | 5.2µg | 8% |
| Saturated fat | 0.014g | 1.535g | 7% |
| Vitamin E | 2.5mg | 3.33mg | 6% |
| Sodium | 46mg | 168mg | 5% |
| Choline | 12.8mg | 24.7mg | 2% |
| Net carbs | 0.87g | 33.74g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.87g | 2.25g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +1044% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +736.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +4182.7% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +1105.4% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +418.4% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -99.1% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +5005.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +8097.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Coriander - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169997/nutrients
- Cumin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170923/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






