Durian vs. Jackfruit: Difference in Nutrition and Health Impacts


Summary
Durian is richer in fiber, copper, zinc, and vitamins B1 and B2. Durian has a lower glycemic index. In comparison, jackfruit is lower in calories, carbs, and fats. Durian has a pungent smell and intense taste.
Introduction
Jackfruit and durian are king-sized exotic fruits widely spread in South-East Asia. They are not the same and are entirely different fruits.
Durian and jackfruit have their specific smells. Durian has an intense smell, and jackfruit has a musky and fruity smell.
Often durian fruit is considered the smelliest fruit in the world. This smell is due to different sulfur-containing compounds.
General Differences
Both jackfruit and durian are tropical fruits, whereas jackfruit is related to the mulberry and the fig and belongs to the Moraceae family. In contrast, durian belongs to the Malvaceae family.
Jackfruit is the largest fruit growing on a tree; it can reach about 50kg or 110lb, while the largest durian can weigh 14kg or 30lb.
Jackfruit pods are covered by latex, and durian pods are not; they can be easily accessed and eaten.
Taste and Smell
Fully ripened jackfruit has a gummy and fibrous texture. It is often used as a meat substitute. The edible parts are grown in a custard-like pod inside the shell.
Its flesh is crunchy and sweet. The flavor resembles a combination of bananas, pineapple, mango, or bubble gum. Unripe durian has a chicken-like flavor, which is useful in vegan diets. On the other hand, durian has a creamy and soft texture; the flavor is a mix of sweet and savory, or sweet cheese.
Nutritional Content
Macronutrients
Before passing on to the next part, I would like to mention that there isn’t a drastic difference in the nutritional content of jackfruits and durians.
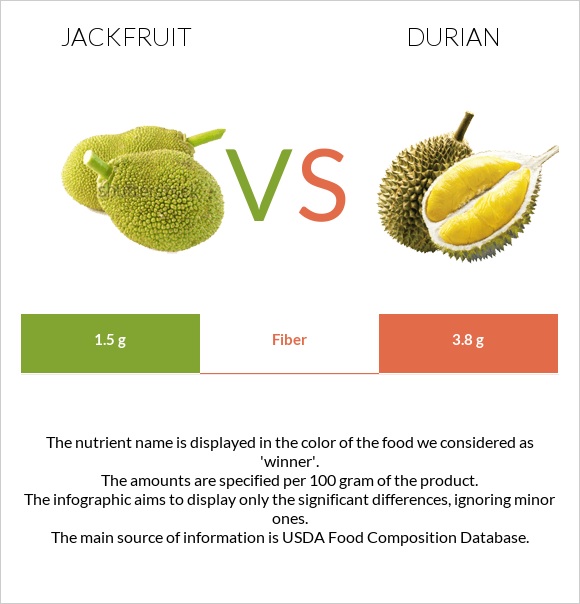
Durian is higher in calories, fats, and dietary fiber.
Both have very low amounts of protein.
Minerals
From the viewpoint of minerals, durian wins hands down.
Durian is significantly higher in copper and moderately higher in zinc, iron, and phosphorus. However, jackfruit is 4 times higher in calcium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+300%
Contains
more
IronIron
+87%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+172.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+115.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+85.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+655.8%
Vitamins
In the vitamin comparison, durian is the medal-holder again. Durian is richer in vitamin B9, vitamin B3, and vitamin C.
Jackfruit is two times higher in vitamin A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+43.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+256.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+263.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+16.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Health Benefits
Jackfruit and durian have apparent antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, anti-lipidemic, and anticancer properties. That is why all parts (stem, seeds, roots, pulp) are being researched for health-beneficial properties.
Antibacterial and Anti-inflammatory
Jackfruit has antibacterial properties against foodborne pathogens and urinary tract infections. (1)(2)(3)
It also has anti-inflammatory effects (4). This benefit was also found in durian pulp extracts (5).
Jackfruit contains potent antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, flavonoids, carotenoids, and vitamin C. Research shows jackfruit and durian pulps are natural sources of these compounds (4).
Cardiovascular Health
According to different studies, the extract of jackfruit leaves noticeably reduces blood glucose and cholesterol levels and improves glucose tolerance (6,7). Research shows that durian rind extract can lower blood glucose levels in diabetic rats (8).
Cancer
It seems essential to emphasize that jackfruit has powerful anticancer qualities. It is effective against colorectal, hepatic cancers, and leukemia (9.10).
Digestion
Durian contains twice as much fiber as jackfruit, which benefits gastrointestinal health. It may help with constipation and reduces the risks of colorectal cancer. In addition to that, fiber-rich foods are associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and obesity. (11,12,13).
Downsides and Risks
As jackfruit and durian lower blood glucose levels, their combination with diabetes medications can cause hypoglycemia.
Jackfruit also has a soothing effect, so it should be avoided when doing activities that require high concentration and attention. It is also not recommended to consume jackfruit with sedative medications.
What about the side effects and interactions of durian? Since durian has a hyperthermic effect, it should not be used with paracetamol and alcohol. According to one study, the hyperthermic effect of durian consumption with paracetamol is insignificant, but it can notably decrease blood pressure (14).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25856717
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20629886
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24524024
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6339770/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8830296/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20931077
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5476885/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30871187
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27815471
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22132163
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0963996920303410
- https://www.jms.mabjournal.com/index.php/mab/article/view/2391
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Siew_Gan/publication/24186411
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19335713/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.105mg | 0.374mg | 22% |
| Copper | 0.076mg | 0.207mg | 15% |
| Manganese | 0.043mg | 0.325mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.055mg | 0.2mg | 11% |
| Fructose | 9.19g | 11% | |
| Fiber | 1.5g | 3.8g | 9% |
| Fats | 0.64g | 5.33g | 7% |
| Vitamin C | 13.7mg | 19.7mg | 7% |
| Calories | 95kcal | 147kcal | 3% |
| Iron | 0.23mg | 0.43mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 21mg | 39mg | 3% |
| Folate | 24µg | 36µg | 3% |
| Calcium | 24mg | 6mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.34mg | 2% | |
| Protein | 1.72g | 1.47g | 1% |
| Carbs | 23.25g | 27.09g | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.13mg | 0.28mg | 1% |
| Starch | 1.47g | 1% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.92mg | 1.074mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.329mg | 0.316mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.195g | 1% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.094g | 1% | |
| Protein per 100 calories | 1.8105263157894738g | 1g | N/A |
| Calories per 10 g protein | 552.3255813953489kcal | 1000kcal | N/A |
| Net carbs | 21.75g | 23.29g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 29mg | 30mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 448mg | 436mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 19.08g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 2mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 5µg | 2µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.235mg | 0.23mg | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.155g | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.034mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.086mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.069mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.103mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.069mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.034mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.052mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.086mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.034mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.079g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.015g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +17% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +13% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +732.8% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +16.5% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +20.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Jackfruit - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174687/nutrients
- Durian - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168192/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




