Jackfruit vs. Soursop — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Jackfruit contains more vitamins, minerals, protein, and calories than soursop. Soursop contains seven times more sodium than jackfruit; also, Vitamin C is 59% higher in this fruit. On the other hand, soursop has a lower glycemic index, less sugar, saturated fat than jackfruit.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Actual differences
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients and calories
- Carbohydrates
- Vitamins
- Other Vitamins
- Minerals
- Potassium
- Glycemic Index
- Acidity
- Weight Loss
- Health Benefits
- Blood pressure
- Cardiovascular Health
- Improving skin health
- Strengthening the bone
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Preventing anemia
- Anti-inflammation effect
- Downsides and Risks
- Sources
Introduction
In this article, we will explore the nutritional aspects of very exotic fruits. Jackfruit is a tropical tree fruit grown in Asia, Africa, and South America. Soursop is a fruit grown in the tropical regions of America. These fruits have some similarities; both are green, often oval and have a spiny shell. Nevertheless, nutritionally they are different. We are going to discuss their nutritional compositions and what effects they have on health.
Actual differences
Soursop, known as Graviola, Guyabano, belongs to the Annona genus (Annona muricata). This fruit has a creamy texture and robust flavor [1]. Jackfruit belongs to the Artocarpus genus (Artocarpus heterophyllus) and is known as the jack tree [2]. Soursop is a spiny fruit that may weigh up to 6 pounds. Jackfruit bears the largest fruit of all trees, reaching between 15 and 33 pounds.
Does jackfruit taste like a soursop?
Despite flavor similarities, jackfruit and soursop have different tastes. Ripe jackfruit often has a sweet taste, while soursop usually is more sour tasting.
Nutrition
Although people often compare these two fruits nutritionally, they are different. To understand that, let’s look at each of them individually. The detailed description and the nutrition infographic are presented below.
Macronutrients and calories
You can see in the chart below that soursop contains more water than jackfruit. On the other hand, jackfruit is relatively richer in carbohydrates. Please, find more detailed information in the corresponding paragraphs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+72%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+113.3%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+38.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+32.9%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+10.5%
Carbohydrates
Jackfruit is more than 7g higher in carbs than soursop. It has more amounts of starch and sugar.
Sugar
The total amount of sugars, including glucose, fructose, lactose, is higher in jackfruit than in soursop. Each jackfruit contains two times more sugars, 31g, while each soursop contains 14g sugars per 100 g [1] [8].
Calories
Overall, jackfruit contains more calories, proteins, and fat; each jackfruit has about 95 calories per 100g, while each soursop contains 66 calories per 100 g.
The amount of food energy in soursop is about 621 kJ, which is higher than in jackfruit; it has 527 kJ. Jackfruit contains 2 grams of fats, 38 grams of carbs. The fats and carbs level in soursop is two times lesser than in jackfruit [3] [4].
Vitamins
Jackfruit and soursop contain different vitamins in different amounts.
Overall, jackfruit is richer in vitamins. The amount of Vitamins A, E, B1, B6 and, Folate is higher in this fruit. Jackfruit contains five times more Vitamin A and Vitamin E than soursop.
The level of Folate in jackfruit is 71% higher than in soursop [3] [5].
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+325%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+457.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+71.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+50.4%
Other Vitamins
The amount of Vitamin B1 and Vitamin B6, again, is higher in jackfruit. On the other hand, soursop contains almost 10% more Vitamin C than jackfruit. Both fruits are equal in Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, and Vitamin B5 and lack vitamin D, Vitamins B12, and B9 [3] [5].
Minerals
The amount of minerals in these fruits is almost equal. Jackfruit contains more Potassium, Manganese, Calcium, and Zinc. Nevertheless, the level of some vitamins in Soursop is higher. It contains almost two times more iron than jackfruit. The level of Copper and Phosphorus is also higher [1] [6].
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+38.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+71.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+61.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+30%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-85.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
IronIron
+160.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+13.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+28.6%
Potassium
Potassium is an essential mineral. It supports blood pressure, cardiovascular health and may help to reduce the risk of kidney stones. Adults should be consuming at least 100 milligrams of potassium daily to support significant processes. The potassium level in jackfruit and soursop does not differ much; however, jackfruit contains more potassium than soursop. It has 303 mg of potassium, whereas soursop contains 278 mg of this mineral [6] [7].
Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index is a relative ranking of carbohydrates in foods according to how they affect blood glucose levels. Jackfruit has a much higher glycemic index than Soursop; the difference is about 75. According to studies, soursop falls under a low GI value [8] [9].
Acidity
The acidity of fruits can change depending on growing conditions. Overall, studies show that jackfruit is more acidic than soursop. The acidity of jackfruit ranges from 4.70 to 5.72. The pH of soursop is about 7.5. [8][10].
Weight Loss
Research shows that fiber may help people decrease the risk of high blood pressure and feel full longer and satisfied, reducing the total number of calories they eat. Accordingly, eating fruits that contain high levels of fiber will help you with your weight loss struggles. Soursop, in this case, is categorized as low calories fruit; it contains high levels of fiber, fewer sugars, less saturated fat, and has a lower glycemic index than jackfruit, which means this fruit is preferable in the case of diets [1] [11].
Health Benefits
The health benefits of jackfruit and soursop have been attributed to their wide range of physicochemical applications. We will discuss the functional, medicinal, and physiological properties of these fruits.
Blood pressure
One of the significant risk factors for the development of heart disease is high blood pressure. The functional components of jackfruit and soursop, such as potassium, fiber, and antioxidants, may help lower blood pressure and reverse the effects of sodium which causes a rise in blood pressure that affects the heart and blood vessels. Moreover, potassium keeps electricity flowing throughout your body, and that’s required to keep your heart beating.
The potassium level in these fruits is almost equal; therefore, these fruits are good for your heart [8] [12].
Cardiovascular Health
Did you know that consuming soursop and jackfruit could help lower high blood pressure? It's not just hearsay - research studies have suggested that these fruits contain properties that may help reduce hypertension [13.14].
Vitamin B6, found in jackfruit, may help lower the risk of thrombosis by reducing homocysteine levels in the blood. It is currently unknown whether soursop has the same effect [14].
It's a fact that jackfruit and soursop may greatly improve your lipid profile and effectively lower your LDL (bad cholesterol) levels. You may add these powerful fruits to your diet today and start reaping their numerous health benefits [15.16].
Improving skin health
These fruits provide several nutrients and antioxidants, such as vitamin C, that may improve skin health. Soursop contains high levels of Vitamin C, which may help to stop the aging clock. On the other hand, jackfruit is rich in Vitamins, especially Vitamin E and B-complex, which are wonderfully nourishing for your skin. Moreover, the potassium they contain may help keep your skin moisturized and hydrated [1] [8].
Strengthening the bone
According to studies, fruits, which contain high levels of magnesium, may help in strengthening bones. Jackfruit contains more magnesium than soursop. This mineral works with calcium to prevent bone‐related disorders such as osteoporosis [8] [11].
Diabetes
Food with a low glycemic index can help you balance your blood sugar levels. Soursop has been estimated to have a lower glycemic index than jackfruit. According to studies, diabetic rats were injected with soursop extract for two weeks. The first group, who received the extract, had blood sugar levels that were five times lower than the untreated group. More research on humans is needed; however, these results suggest that soursop may be beneficial for people with diabetes when combined with a healthy diet and active lifestyle [9] [17].
Cancer
There is a widespread misconception that soursop can make traditional cancer therapies work better. Experts warn the anticancer activity of this fruit has not been studied in humans. As a result, there is no evidence of its safety or efficacy [18]․
Jackfruit has phytonutrients, such as isoflavones and saponins contribute to its anticancer, antihypertensive, and antiulcer properties. In particular, these elements work against stomach ulcers in the human body [8].
Preventing anemia
Both soursop and jackfruit contain high levels of iron. Regularly consuming these fruits may help prevent anemia and aid proper blood circulation [19].
Anti-inflammation effect
Some studies have reported the anti-inflammation effects of jackfruit. These fruits contain high levels of flavonoids that effectively inhibit the release of inflammatory mediators from the mast cells, neutrophils. Jackfruit also has antifungal activity. The lectin, named Jackin, isolated from this fruit, can inhibit the growth of some fungi [20].
According to studies, soursop contains antibacterial properties as well. Soursop was able to inhibit the growth of multiple types of bacteria, including strains that cause gingivitis and tooth decay [21].
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Jackfruit allergy is the list of birch pollen‐related food allergies. That means some people may be allergic to jackfruit if they are also allergic to birch pollen [22].
The symptoms usually include itching in the mouth, in rare cases, rhinoconjunctivitis and mild asthmatic symptoms․
Other side effects
Animal studies show soursop has blood sugar-lowering effects, so it may have additive effects when taken with diabetic medications. Clinical relevance has yet to be determined. Besides, repeated use may cause liver and kidney toxicity, and the side effects of soursop may include movement disorders and myeloneuropathy [23].
Nevertheless, there is no report of causing any severe side effects, and it is safe for most people to eat. Rarely, jackfruit might cause sleepiness and drowsiness [22].
Sources
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123746283000396
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijfs/2019/4327183/
- https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-030-30182-8_8
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31050422/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124081178000143
- Jackfruit Taxonomy and Waste Utilization
- Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2012.00210.x
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24076471/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/11358120409487770
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6339770/#B104\
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.3109/13880209.2012.684690
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31462727/
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijfs/2019/4327183/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24826004/
- https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/85956311/10001915.pdf?1652644827=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DPlasma_Lipid_Profiles
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3156450/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6091294/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6339770/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16257591/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5198446/
- https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(04)00310-0/fulltext
- https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/integrative-medicine/herbs/graviola
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.329mg | 0.059mg | 21% |
| Fructose | 9.19g | 11% | |
| Vitamin C | 13.7mg | 20.6mg | 8% |
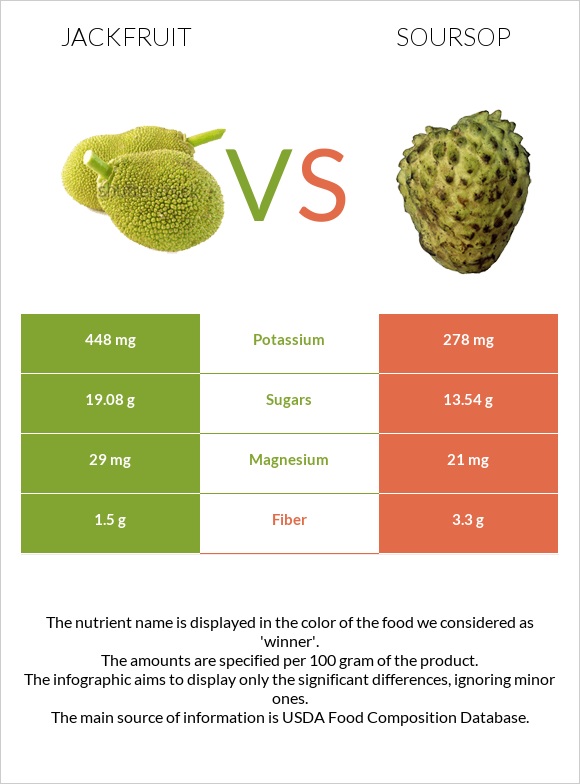
| Fiber | 1.5g | 3.3g | 7% |
| Potassium | 448mg | 278mg | 5% |
| Iron | 0.23mg | 0.6mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.105mg | 0.07mg | 3% |
| Folate | 24µg | 14µg | 3% |
| Carbs | 23.25g | 16.84g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 29mg | 21mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.34mg | 0.08mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.043mg | 2% | |
| Calories | 95kcal | 66kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 1.72g | 1g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.64g | 0.3g | 1% |
| Calcium | 24mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.076mg | 0.086mg | 1% |
| Starch | 1.47g | 1% | |
| Phosphorus | 21mg | 27mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 2mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 5µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 1% | |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 1% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.195g | 0.051g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 21.75g | 13.54g | N/A |
| Sugar | 19.08g | 13.54g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.13mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.055mg | 0.05mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.92mg | 0.9mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.235mg | 0.253mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.155g | 0.09g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.094g | 0.069g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.034mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.086mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.069mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.103mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.069mg | 0.06mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.034mg | 0.007mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.052mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.086mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.034mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.079g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.015g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +72.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +36.2% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -73.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Jackfruit - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174687/nutrients
- Soursop - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167761/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





