Trout vs. Salmon - What's the Difference?

Summary
Salmon is a saltwater fish, and trout is a freshwater fish. Salmon is an oilier fish, being higher in calories and fats, including saturated and unsaturated fats. Salmon also provides 3 times more vitamin B9 and 2 times more vitamins B1 and B6.
However, trout is richer in protein and higher in cholesterol. Trout is also a better source of most minerals, such as calcium, zinc, and potassium.
Introduction
This article will discuss two types of fish; trout and salmon. These two types of fish are frequently thought to be similar; however, they are quite different.
This article will compare trout and salmon according to general aspects, nutritional content, and health impacts.
Habitat
The main difference between these two fish is the following;
Trout is a freshwater fish, and salmon is a saltwater fish.
The freshwater environments where trout can primarily be found are rivers, lakes, and streams. They require cool, clean water with adequate oxygen levels.
Although salmon is a saltwater fish, it swims to freshwater areas to breed during the spawning season. Later, salmon migrate to the ocean, where they stay for most of their adult life.
Taste and Appearance
Salmon is a fattier fish with a more robust flavor profile and a firmer texture, while trout has a milder, less oily taste and a flakier, more tender texture.
The appearance can help differentiate between a trout and a salmon. Both trout and salmon have streamlined bodies; however, salmon tend to have a more robust and elongated body shape. Salmon is also generally larger than trout.
The coloration of trout and salmon can vary depending on their species, environment, and life stage. However, salmon often have a silver or metallic hue on their sides, while trouts tend to have dark spots scattered along their entire body, including the fins.
Types
There are different types of salmon fish:
- Chinook (king) salmon,
- Sockeye (red) salmon,
- Chum salmon,
- Pink salmon,
- Coho (silver) salmon,
- Atlantic salmon
There are slight differences between these subtypes regarding taste and flavor.
When it comes to trout, there are also several types of trout, and most of them are spotted. The types of trouts are:
- Rainbow trout
- Cutthroat trout
- Golden trout
- Brown trout
- Lake trout,
- Brook trout
- Dolly Varden trout
- Bull trout
- Tiger trout
- Splake trout
- Palomino trout
- Gila trout
- Apache trout
- Marble trout
Considering these varieties, it is also essential to note that there are differences between farmed and wild-caught fish types. Both salmon and trout can be raised in fish farms or caught in natural bodies of water, like oceans, rivers, and lakes.
Wild-caught fish often have a more distinct flavor and firmer texture due to their natural diet and active lifestyles. Farmed fish may have a milder taste and a softer texture due to their controlled environment and diet.
Both farmed and wild-caught fish can contain contaminants, such as heavy metals, such as mercury, and persistent organic pollutants. The levels of these contaminants vary depending on the species, location, and environmental factors. In addition, farmed fish can be exposed to antibiotics.
However, studies conclude that the concentrations of mercury, polychlorinated biphenyls, and overall key contaminants were low, so the regular consumption of these fish would not cause significant health risks (1).
Further in the health section, this will be discussed in detail.
Caviars and Roe
Roe is the natural form of caviar. Roe is the unprocessed form of fish eggs that are removed from the fish and unfertilized. In comparison, caviar is prepared with salt.
Trout roe or caviar is orange, similar to that salmon. However, they are smaller and taste slightly different than that salmon caviar.
Nutritional Content Comparison
In this section, we will compare 100g servings of farmed rainbow trout and Atlantic salmon cooked with dry heat with no oil added.
The macronutrient content of these two types of fish is overall similar; however, salmon has a higher fat content, while trout is richer in protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+67.3%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+700%
Calories
Both types of fish are high-calorie foods; however, salmon contains 38 more calories per 100g serving.
A 100g serving of salmon and trout provide 206 and 168 calories, respectively.
Protein
Salmon and trout are protein-rich foods. Trout is only a little higher in protein, providing 23.8g in a 100g serving. The same serving of salmon contains 22.1g of protein.
Naturally, trout is somewhat higher in all the essential amino acids.
Fats
While these are fatty fish, they are not exceptionally high in fats.
Salmon is significantly higher in fats, including saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids. That being said, trout contains slightly more cholesterol.
To put this in numbers, salmon is 1.7 times higher in overall fats, 2 times higher in saturated fats, 1.8 times higher in monounsaturated fats, and 2.5 times richer in polyunsaturated fats. Trout contains 7mg more cholesterol per 100g serving.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+76.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+153.1%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-31.1%
Omega-3
Salmon is 2.4 times richer in DHA, 2.7 times richer in EPA, and 1.6 times richer in DPA. We will discuss the importance of omega-3 fats in the health impacts section.
Carbs
The carb content of trout and salmon is negligible.
Minerals
Trout can be considered the winner in this category, as it is 2 times richer in calcium and provides higher levels of zinc, potassium, and copper.
Salmon, on the other hand, is richer in selenium and manganese.
The diagram below shows the distribution of their minerals.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+23.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+47.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+100%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+17.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+12.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+25.6%
Vitamins
Fish are excellent sources of most vitamins.
Salmon provides 3 times more folate or vitamin B9 and 2 times more vitamins B1 and B6. It is also richer in vitamins B2, B3, and vitamin C.
That said, trout is a better source of vitamins E, D, and A, and vitamins B5 and B12.
The infographic below shows the comparison of their vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+27.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+137.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+26.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+21.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+67.6%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+183.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+44.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+144.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+45%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+34.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+46.8%
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of both is 0 due to the insignificant amount of carbs.
Health impacts
Benefits of omega-3
Omega-3 fats are very important to be included in our diets. ALA, EPA, and DHA have been shown to have several benefits.
Omega-3 fats have been studied to reduce triglyceride levels in the blood when taken in high amounts. In addition, they have cardioprotective functions, help protect the nervous system, and can reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease and depression. It can even help increase tolerance of chemotherapeutic drugs during cancer treatments (2, 3, 4, 5, 6).
Studies show farmed salmon and trout to have higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids compared to wild-caught salmon and trout. Either way, both farmed and wild salmon are considerably richer in omega-3 fats than trout (7).
Cardiovascular health
Consumption of salmon is associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease. Research shows salmon consumption decreases blood pressure, low-density lipoprotein, and triglyceride levels. In addition, an increase in high-density lipoproteins, often referred to as “good cholesterol,” has been seen (8).
The research concludes that salmon and trout fillets from farmed or wild fish can be considered lean and healthy choices due to their total lipid content. Their high omega-3 fatty acid content adds even more to the nutritional value of these fish (1).
Farmed Fish and Antibiotics
Farmed fish may be given antibiotics for various reasons, including disease prevention and treatment. Antibiotics are used in aquaculture to control bacterial infections and promote the health of fish populations.
However, the use of antibiotics in fish farming is a topic of concern due to potential environmental and human health risks. Inappropriate overuse of antibiotics in fish can cause a selective growth of bacteria resistant to certain antibiotics (9).
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6462815
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15366399/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29350557/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31422671/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30601174/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30019766/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705336/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17069820/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30204782/
Infographic
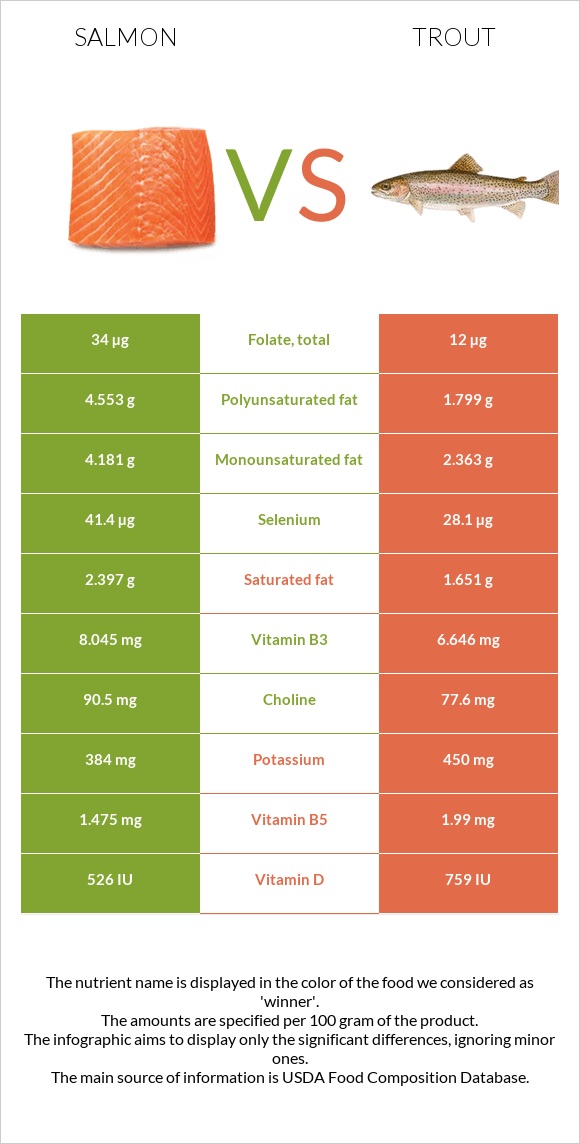
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.8µg | 4.11µg | 55% |
| Vitamin D | 13.1µg | 19µg | 30% |
| Vitamin D | 526 IU | 759 IU | 29% |
| Selenium | 41.4µg | 28.1µg | 24% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.647mg | 0.386mg | 20% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 4.553g | 1.799g | 18% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.34mg | 0.143mg | 16% |
| Vitamin E | 1.14mg | 2.79mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.475mg | 1.99mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.045mg | 6.646mg | 9% |
| Fats | 12.35g | 7.38g | 8% |
| Folate | 34µg | 12µg | 6% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.181g | 2.363g | 5% |
| Protein | 22.1g | 23.8g | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 252mg | 270mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 69µg | 100µg | 3% |
| Saturated fat | 2.397g | 1.651g | 3% |
| Calories | 206kcal | 168kcal | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 63mg | 70mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 15mg | 30mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 384mg | 450mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.135mg | 0.107mg | 2% |
| Choline | 90.5mg | 77.6mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 3.7mg | 2.9mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.049mg | 0.055mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.43mg | 0.54mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 30mg | 30mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 0.36mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 61mg | 61mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.016mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0.1µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.056g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.248mg | 0.279mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.969mg | 1.092mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.018mg | 1.148mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.796mg | 2.025mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.03mg | 2.287mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.654mg | 0.738mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.863mg | 0.973mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.139mg | 1.283mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.651mg | 0.733mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.69g | 0.259g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 1.457g | 0.616g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.17g | 0.109g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.047g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Salmon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175168/nutrients
- Trout - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173718/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





