Frozen Yogurt vs. Soft Serve — What's the Difference?


Summary
Soft serve has more choline and vitamins A, E, K, and B5. Soft serve also provides more net carbs and monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas frozen yogurt has more dietary fiber.
Frozen yogurt, on the other hand, is high in iron and provides fewer calories, net carbs, cholesterol, and saturated fats.
Table of contents
Introduction
Frozen yogurt and soft serve are frozen desserts with distinct tastes, textures, and nutrient content differences. In this article, we will discuss differences.
Taste and Appearance
Soft serve ice cream has air added to it. Ice cream with less air tastes heavy, icy, and looks more yellow. Ice cream with more air tastes creamier, smoother, and lighter and looks whiter. Usually, the best air content should be between 33 and 45 percent of the total space.
The consistency of frozen yogurt is lighter and airier than gelato, defined by its rich and velvety texture. Depending on the taste and any other ingredients, frozen yogurt can appear in a range of colors. White is a color for plain or vanilla-flavored frozen yogurt, while different colors are available for fruit-flavored choices. Light pink for strawberry, light green for key lime, and other hues for other fruit tastes are possible.
The portions of frozen yogurt and soft serve might differ based on the place and the serving. These are commonly in sizes like small, medium, and big.
Ingredients
Soft serve is a frozen dairy product. It is a heat-treated mixture of milk, cream, milk solids, sugars, stabilizers, emulsifiers, and flavorings. Soft serve usually has less fat than ice cream.
Unlike soft serve, frozen yogurt is made from milk solids, a sweetener, milk fat, yogurt culture, and sometimes added flavors and colors(natural or artificial).
Yogurt's fat content is low relative to its other ingredients. Adding fat makes the yogurt taste richer. Milk solids contribute to its sweetness and smoothness and help the yogurt resist melting. Sugar adds sweetness and helps increase the amount of solid ingredients in the yogurt. Gelatin and vegetable additives are added to yogurt to stabilize and prevent it from becoming crystal.
Probiotics
Probiotics are living bacteria that are good for your body. These organisms are already in your body and can benefit your gut health.
Frozen yogurt contains two common bacteria: Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. They may also include Bifidobacterium spp., Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Lactobacillus casei.
Taste and Use
Frozen yogurt is like ice cream - it is smooth and creamy. It usually tastes tangy and slightly sour. The taste of the food can be different depending on the brand and the extras added. Some frozen yogurts taste more like yogurt, while others taste sweeter and fruity. Frozen yogurt shops have different toppings, such as fresh fruits, chocolate chips, sprinkles, or almonds.
Soft-serve is a type of ice cream that is smoother, creamier, and lighter in texture compared to regular ice cream. The taste of the final product changes based on how much air is present. Soft-serve ice cream usually tastes sweeter and milder than regular ice cream. Usually, it starts with a taste of vanilla, but sometimes you can also find different flavors like chocolate, strawberry, or a mix of various flavors. You can eat soft-serve ice cream alone or add toppings, candies, and sauces to make it taste better.
Nutrition
In the infographics below, you will find nutritional information for 100g servings of frozen yogurt and soft serve.
Macronutrients and Calories
Soft serve is a little denser. Soft serve has 60% water, whereas frozen yogurt has 74%. Soft serve is high in fats, protein, carbs, and calories.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+19.1%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+36.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+261.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+50%
Calories
Soft serve is significantly higher in calories, providing almost twice as many calories per every 100g serving. In a 100g serving, frozen yogurt and soft serve contain 127 and 222 calories, respectively.
Protein
Soft serve has slightly more protein content compared to frozen yogurt. In a 100g serving, frozen yogurt and soft serve contain 3g and 4.1g, respectively.
Fats
Soft serve provides 4 times more total fats compared to frozen yogurt. A hundred grams of soft serve has 13g of fat content. while frozen yogurt contains only 3.6 grams of fat.
Soft serve has higher monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas frozen yogurt has over 4 times less saturated fats. In a 100g serving, frozen yogurt and soft serve contain 2.3g and 7.46g saturated fat, respectively.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-68.8%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+254%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+360%
Cholesterol
Frozen yogurt has over 7 times less cholesterol compared to soft serve. A hundred grams of frozen yogurt has 13mg of cholesterol, whereas soft serve provides 91mg.
Carbohydrates
100g of soft serve contains 22.2g of carbohydrates, of which 0.7g are dietary fiber and 21.5g are net carbs.
100g of frozen yogurt contains 21.6g of carbohydrates, all are net carbs.
A hundred grams of frozen yogurt has 12.61 grams of sugar, whereas soft serve contains 21.16 grams.
Vitamins
Soft serve is higher in most vitamins, providing 35 times more vitamin A, 7.7 times more vitamin E, three times more vitamin K, and overall more vitamins C, D, and B5.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+14.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+230.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+577.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+600%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+22.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+35.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+20%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+614.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+200%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+125%
Minerals
Soft serve provides higher potassium, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, copper, zinc, and selenium levels.
In addition, soft serve has over eight times more choline.
At the same time, frozen yogurt is higher in iron.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+119%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+20%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+31%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+13.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+233.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+85.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+30.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+57.9%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of frozen yogurt is 51. Soft serve has a glycemic index level of 79. That means frozen yogurt is low-GI food, whereas soft serve is high-GI food.
Acidity
The quantity of acid or base created by foods inside the body is known as the PRAL or potential renal acid load. Frozen yogurt has a PRAL level of -3.3. The PRAL level of soft serve is 0.6.
Based on the potential renal acid load (PRAL), frozen yogurt is alkaline-forming, whereas soft serve is acid-forming.
Weight Loss & Diets
Frozen yogurt containing fewer calories per serving might be the better choice for a low-calorie diet.
Between these two, frozen yogurt is the better choice for low-fat and low-glycemic-index diets.
Health Impact
Diabetes
People with diabetes should choose frozen yogurt over soft serve because frozen yogurt has a lower glycemic index. When you eat something with a low glycemic index, it helps to keep your insulin levels from quickly rising. Low-GI diets may help with glycemic control and weight loss (1).
Allergy
Dairy products may contain allergens. Frozen yogurt and soft serve have cow’s milk protein, so it will be good to stay away from them (2).
If you have a milk allergy, your immune system perceives the protein in milk as dangerous, similar to a bacteria or virus.
Lactose Intolerance
Different brands and recipes have different amounts of lactose in their soft serve and frozen yogurt. They contain 2-6 g lactose in ½ cup (3 ). If you are lactose-intolerant, you should avoid frozen yogurt and soft serve. Lactose-intolerant individuals lack the enzyme lactase. Lactase is an enzyme that digests lactose, a sugar in milk and dairy products. As a result, persons who are lactose intolerant cannot digest frozen yogurt and soft serve. They may feel nausea, cramping, gas, bloating, and diarrhea, but it is not fatal (4)(5).
Gut health
Probiotic (health-promoting) bacteria such as Bifidobacterium spp. and Lb. Acidophilus may added to frozen yogurt by some processors. Both can become resident in the human gastrointestinal system, may aid digestion, particularly lactose processing, and displace potentially hazardous bacteria. Additionally, as nutrition for the probiotic bacteria, 'prebiotics' such as inulin may be included in the product (6).
Cardiovascular health
Saturated fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase plasma cholesterol. Elevated plasma cholesterol levels may be a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
Because soft serve is high in saturated fats, frozen yogurt may be a good option for cardiovascular health (7).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31374573/
- https://www.allergy.org.au/
- https://med.virginia.edu/ginutrition/
- https://www.foodallergy.org/resources/milk-allergy-vs-lactose-intolerance
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532285/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30084105/
Infographic
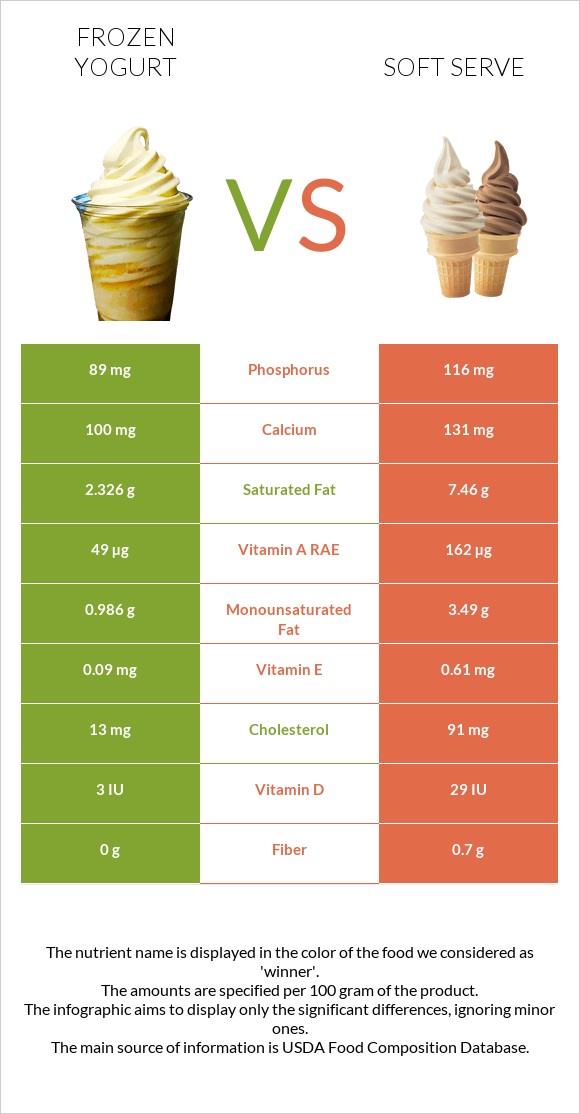
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Cholesterol | 13mg | 91mg | 26% |
| Saturated fat | 2.326g | 7.46g | 23% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.07µg | 0.5µg | 18% |
| Fats | 3.6g | 13g | 14% |
| Vitamin A | 49µg | 162µg | 13% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.506mg | 10% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.986g | 3.49g | 6% |
| Calories | 127kcal | 222kcal | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 89mg | 116mg | 4% |
| Vitamin D | 3 IU | 29 IU | 3% |
| Calcium | 100mg | 131mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.46mg | 0.21mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 0g | 0.7g | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.09mg | 0.61mg | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 0.7µg | 3% |
| Protein | 3g | 4.1g | 2% |
| Copper | 0.009mg | 0.03mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.28mg | 0.52mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 1.9µg | 3µg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.1g | 0.46g | 2% |
| Potassium | 156mg | 177mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 0.049mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.04mg | 0.048mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.3µg | 0.9µg | 1% |
| Folate | 4µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Choline | 23.1mg | 26mg | 1% |
| Caffeine | 0mg | 2mg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.7mg | 0.8mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 21.6g | 21.5g | N/A |
| Carbs | 21.6g | 22.2g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 19.92g | 21.16g | N/A |
| Sodium | 63mg | 61mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.005mg | 0% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.18mg | 0.182mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.07mg | 0.095mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.048mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.169mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.215mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.353mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.296mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.091mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.176mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.241mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.099mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Frozen yogurt - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168105/nutrients
- Soft serve - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173465/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.