Gooseberry vs. Currant — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Currants contain more minerals, Vitamin B2, Vitamin C, and folate. On the other hand, gooseberry has more Vitamin B family, Vitamin A, and E, fewer sugars, and lower GI than currants.
Introduction
We will compare gooseberry and currant, focusing on the differences in nutrition profile and health impact.
What’s The Actual Difference?
Both currant and gooseberry belong to the Ribes genus in the Gooseberry family. Both are indigenous to Western Europe and are widely cultivated in many parts of the world.
The most noticeable difference between currants and gooseberries is their thorns and colors. Gooseberry bushes have thorns, whereas currents do not. Currants are bright red, black, white, and beige, whereas gooseberries are typically light green or light pink with white stripes.
Taste
Gooseberry and currant significantly differ in taste. Red gooseberries have a sweeter taste; green ones taste more sour. Usually, gooseberry tastes like a middle-ripe grape. In contrast, currants have a great balance of sweet and sour flavors.
Nutrition
Vitamins
Gooseberry contains more vitamins than currant. It has five times more Vitamin A and B5 and three times more Vitamin B5, B3, and E.
On the other hand, currant has higher Vitamin C, Vitamin B2, and folate.
Moreover, it falls in the range of the top 13% foods as a source of Vitamin C.
The amounts of Vitamin B1 are equal in these plants.
Both have no Vitamin D and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+650%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+270%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+346.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+14.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+48%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+66.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+33.3%
Minerals
Currant has a relatively higher amount of minerals than gooseberry. It has more copper, magnesium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, potassium, and iron.
Both are low in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+30%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+32%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+38.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+222.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+52.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+91.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+63%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+29.2%
Calories
Currant has more calories than gooseberry. It contains 56 calories per 100g, while gooseberry contains only 44 calories per 100g.
Glycemic Index
The GI of currant is 25, and the glycemic index of gooseberry is 15; both are considered low GI.
Macronutrients
As the chart below shows, gooseberry is slightly richer in water than currant. In contrast, currant is higher in carbs. Please, read more in the corresponding sections.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+190%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+59.1%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+35.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+32.7%
Carbs
Currant contains 14g per 100g, whereas gooseberry has 10g per 100g. They both have high net carbs: 9.5 g of net carbs in currant and 6g in gooseberry.
Fiber
Both are excellent sources of fiber: 4.3g fiber per 100g. These berries are rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Fats
Both gooseberry and currant have fats of less than 1g.
Cholesterol
Both have no cholesterol.
Health Impact
Cancer
Gooseberries contain cancer-fighting compounds, such as quercetin, kaempferol, caffeic and ellagic acids. Studies show that quercetin may inhibit the growth of various cancers, including prostate, cervical, lung, breast, and colon (1).
Currants are high in plant compounds such as flavonoids, phytosterols, and essential oils. According to research, these compounds may help to fight against free radicals, which play a role in developing cancer and other health conditions (2).
Cardiovascular Health
Gooseberries are good for your heart because they are high in potassium and phytonutrients. Potassium regulates blood pressure and heart rate, lowering the risk of stroke and heart disease. Blood vessel function is improved by anthocyanins and flavanols (3).
Red currants contain lycopene, an antioxidant carotenoid that may reduce the risk of heart disease. Furthermore, the magnesium content in currants is responsible for low blood pressure, making them heart-healthy (4).
Side Effects
Allergy
People allergic to latex may also be allergic to gooseberry and red/black currant. Intense tingling and itching of the lips, tongue, and throat are common symptoms (5).
Infographic
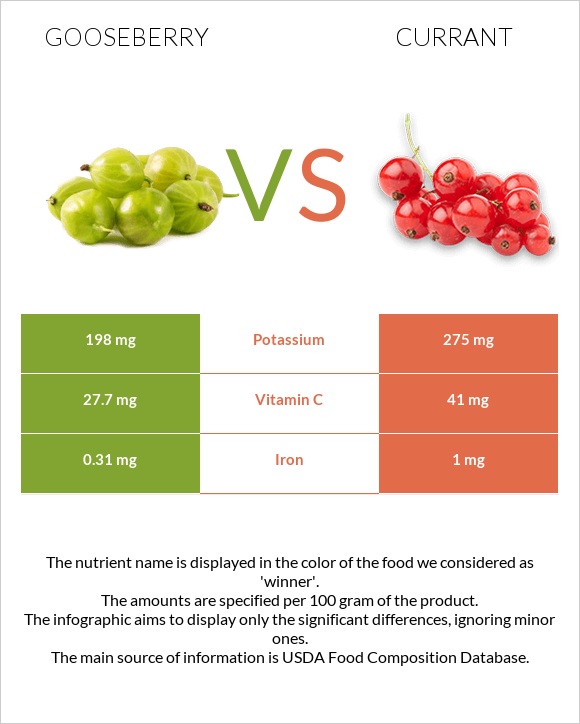
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 27.7mg | 41mg | 15% |
| Iron | 0.31mg | 1mg | 9% |
| Vitamin K | 11µg | 9% | |
| Copper | 0.07mg | 0.107mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.286mg | 0.064mg | 4% |
| Fructose | 3.53g | 4% | |
| Potassium | 198mg | 275mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 27mg | 44mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.37mg | 0.1mg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.144mg | 0.186mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg | 0.05mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.317g | 0.088g | 2% |
| Calories | 44kcal | 56kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 0.88g | 1.4g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.58g | 0.2g | 1% |
| Carbs | 10.18g | 13.8g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 13mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 25mg | 33mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.12mg | 0.23mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 15µg | 2µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.3mg | 0.1mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08mg | 0.07mg | 1% |
| Folate | 6µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 5.88g | 9.5g | N/A |
| Sugar | 7.37g | N/A | |
| Fiber | 4.3g | 4.3g | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 0.04mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.038g | 0.017g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.051g | 0.028g | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +82.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +260.2% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -55.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Gooseberry - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173030/nutrients
- Currant - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173964/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.